Moss still thrives from the moisture on stones and trees from the night cold.
CLICK Refresh FOR SLIDES
Moss still thrives from the moisture on stones and trees from the night cold.
CLICK Refresh FOR SLIDES

The Bois de Boulogne is a large public park located along the western edge of the 16th arrondissement of Paris, near the suburb of Boulogne-Billancourt and Neuilly-sur-Seine. It was created between 1852 and 1858 during the reign of the Emperor Napoleon III.
It is the second-largest park in Paris, slightly smaller than the Bois de Vincennes on the eastern side of the city. It covers an area of 845 hectares (2088 acres), which is about two and a half times the area of Central Park in New York and slightly less (88%) than that of Richmond Park in London.
Within the boundaries of the Bois de Boulogne are an English landscape garden with several lakes and a cascade; two smaller botanical and landscape gardens, the Château de Bagatelle and the Pré-Catelan; a zoo and amusement park in the Jardin d’Acclimatation; GoodPlanet Foundation‘s Domaine de Longchamp dedicated to ecology and humanism, The Jardin des Serres d’Auteuil, a complex of greenhouses holding a hundred thousand plants; two tracks for horse racing, the Hippodrome de Longchamp and the Auteuil Hippodrome; a tennis stadium where the French Open tennis tournament is held each year; and other attractions.
For the two 1896 short films, see Bois de Boulogne (film).
The Bois de Boulogne is a remnant of the ancient oak forest of Rouvray, which included the present-day forests of Montmorency, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Chaville, and Meudon. Dagobert, the King of the Franks (629-639), hunted bears, deer, and other game in the forest. His grandson, Childeric II, gave the forest to the monks of the Abbey of Saint-Denis, who founded several monastic communities there. Philip Augustus (1180–1223) bought back the main part of the forest from the monks to create a royal hunting reserve. In 1256, Isabelle de France, sister of Saint-Louis, founded the Abbey of Longchamp at the site of the present hippodrome.
The Bois received its present name from a chapel, Notre Dame de Boulogne la Petite, which was built in the forest at the command of Philip IV of France (1268–1314). In 1308, Philip made a pilgrimage to Boulogne-sur-Mer, on the French coast, to see a statue of the Virgin Mary which was reputed to inspire miracles. He decided to build a church with a copy of the statue in a village in the forest not far from Paris, in order to attract pilgrims. The chapel was built after Philip’s death between 1319 and 1330, in what is now Boulogne-Billancourt.
During the Hundred Years’ War, the forest became a sanctuary for robbers and sometimes a battleground. In 1416-17, the soldiers of John the Fearless, the Duke of Burgundy, burned part of the forest in their successful campaign to capture Paris. Under Louis XI, the trees were replanted, and two roads were opened through the forest.
In 1526, King Francis I of France began a royal residence, the Château de Madrid, in the forest in what is now Neuilly and used it for hunting and festivities. It took its name from a similar palace in Madrid, where Francis had been held prisoner for several months. The Chateau was rarely used by later monarchs, fell into ruins in the 18th century, and was demolished after the French Revolution.

The Chateau de Madrid in the Bois de Boulogne, built in 1526 by Francis I of France.
The Chateau de la Muette was the home of Queen Marguerite de Valois after her marriage was annulled by King Henry IV of France. It was demolished after the French Revolution.
Despite its royal status, the forest remained dangerous for travelers; the scientist and traveler Pierre Belon was murdered by thieves in the Bois de Boulogne in 1564.[6]
During the reigns of Henry II and Henry III, the forest was enclosed within a wall with eight gates. Henry IV planted 15,000 mulberry trees, with the hope of beginning a local silk industry. When Henry annulled his marriage to Marguerite de Valois, she went to live in the Château de la Muette, on the edge of the forest.
In the early 18th century, wealthy and important women often retired to the convent of the Abbey of Longchamp, located where the hippodrome now stands. A famous opera singer of the period, Madmoiselle Le Maure, retired there in 1727 but continued to give recitals inside the Abbey, even during Holy Week. These concerts drew large crowds and irritated the Archibishop of Paris, who closed the Abbey to the public.[7]
Louis XVI and his family used the forest as a hunting ground and pleasure garden. In 1777, the Comte d’Artois, Louis XVI‘s brother, built a charming miniature palace, the Château de Bagatelle, in the Bois in just 64 days, on a wager from his sister-in-law, Marie Antoinette. Louis XVI also opened the walled park to the public for the first time.
On 21 November 1783, Pilâtre de Rozier and the Marquis d’Arlandes took off from the Chateau de la Muette in a hot air balloon made by the Montgolfier brothers. Previous flights had carried animals or had been tethered to the ground; this was the first manned free flight in history. The balloon rose to a height of 910 meters (3000 feet), was in the air for 25 minutes, and covered nine kilometers.[8]

The first free manned flight was launched by the Montgolfier Brothers from the Chateau de la Muette, on the edge of the Bois de Boulogne, on November 21, 1783.
Following the defeat of Napoleon Bonaparte in 1814, 40,000 soldiers of the British and Russian armies camped in the forest. Thousands of trees were cut down to build shelters and for firewood.
From 1815 until the French Second Republic, the Bois was largely empty, an assortment of bleak ruined meadows and tree stumps where the British and Russians had camped and dismal stagnant ponds.[9]
The Bois de Boulogne was the idea of Napoleon III, shortly after he staged a coup d’état and elevated himself from the President of the French Republic to Emperor of the French in 1852. When Napoleon III became Emperor, Paris had only four public parks – the Tuileries Gardens, the Luxembourg Garden, the Palais Royale, and the Jardin des Plantes – all in the center of the city. There were no public parks in the rapidly growing east and west of the city. During his exile in London, he had been particularly impressed by Hyde Park, by its lakes and streams and its popularity with Londoners of all social classes. Therefore, he decided to build two large public parks on the eastern and western edges of the city where both the rich and ordinary people could enjoy themselves.[10]
These parks became an important part of the plan for the reconstruction of Paris drawn up by Napoleon III and his new Prefect of the Seine, Baron Georges-Eugène Haussmann. The Haussmann plan called for improving the city’s traffic circulation by building new boulevards; improving the city’s health by building a new water distribution system and sewers; and creating green spaces and recreation for Paris’ rapidly growing population. In 1852, Napoleon donated the land for the Bois de Boulogne and for the Bois de Vincennes, which both belonged officially to him. Additional land in the plain of Longchamp, the site of the Chateau de Madrid, the Chateau de Bagatelle, and its gardens were purchased and attached to the proposed park, so it could extend all the way to the Seine. Construction was funded out of the state budget, supplemented by selling building lots along the north end of the Bois, in Neuilly,[11]
Napoleon III was personally involved in planning the new parks. He insisted that the Bois de Boulogne should have a stream and lakes, like Hyde Park in London. “We must have a stream here, as in Hyde Park,” he observed while driving through the Bois, “to give life to this arid promenade”.[12]
The first plan for the Bois de Boulogne was drawn up by the architect Jacques Hittorff, who, under King Louis Philippe, had designed the Place de la Concorde, and the landscape architect Louis-Sulpice Varé, who had designed French landscape gardens at several famous châteaux. Their plan called for long straight alleys in patterns crisscrossing the park, and, as the Emperor had asked, lakes and a long stream similar to the Serpentine in Hyde Park.
Unfortunately, Varé failed to take into account the difference in elevation between the beginning of the stream and the end; if his plan had been followed, the upper part of the stream would have been empty, and the lower portion flooded. When Haussmann saw the partially finished stream, he saw the problem immediately and had the elevations measured. He dismissed the unfortunate Varé and Hittorff, and designed the solution himself; an upper lake and a lower lake, divided by an elevated road, which serves as a dam, and a cascade which allows the water to flow between the lakes. This is the design still seen today.[13]
In 1853, Haussmann hired an experienced engineer from the corps of Bridges and Highways, Jean-Charles Alphand, whom he had worked with in his previous assignment in Bordeaux, and made him the head of a new Service of Promenades and Plantations, in charge of all the parks in Paris. Alphand was charged to make a new plan for the Bois de Boulogne. Alphand’s plan was radically different from the Hittorff-Varé plan. While it still had two long straight boulevards, the Allée Reine Marguerite and the Avenue Longchamp, all the other paths and alleys curved and meandered. The flat Bois de Boulogne was to be turned into an undulating landscape of lakes, hills, islands, groves, lawns, and grassy slopes, not a reproduction of but an idealization of nature. It became the prototype for the other city parks of Paris and then for city parks around the world.[14]
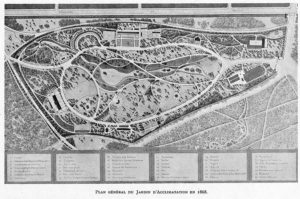
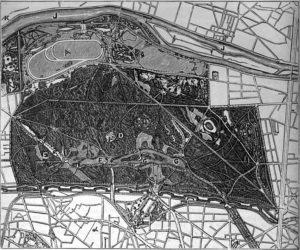
The plan of the park from 1879 shows the two straight alleys of the old Bois, and the lakes, winding lanes and paths built by Alphand.

L’aquarium; vue intérieure, 1860.
The Jardin zoologique at the Bois de Boulogne included an aquarium that housed both fresh and salt water sea animals. The interior is depicted here.
The building of the park was an enormous engineering project which lasted for five years. The upper and lower lakes were dug, and the earth piled into islands and hills. Rocks were brought from Fontainbleau and combined with cement to make the cascade and an artificial grotto.
The pumps from the Seine could not provide enough water to fill the lakes and irrigate the park, so a new channel was created to bring the water of the Ourcq River, from Monceau to the upper lake in the Blois, but this was not enough. An artesian well 586 meters deep was eventually dug in the plain of Passy which could produce 20,000 cubic meters of water a day. This well went into service in 1861.[15]
The water then had to be distributed around the park to water the lawns and gardens; the traditional system of horse-drawn wagons with large barrels of water would not be enough. A system of 66 kilometers of pipes was laid, with a faucet every 30 or 40 meters, a total of 1600 faucets.
Alphand also had to build a network of roads, paths, and trails to connect the sights of the park. The two long straight alleys from the old park were retained, and his workers built an additional 58 kilometers of roads paved with stones for carriages, 12 kilometers of sandy paths for horses, and 25 kilometers of dirt trails for walkers. As a result of Louis Napoléon’s exile in London and his memories of Hyde Park, all the new roads and paths were curved and meandering.[16]
The planting of the park was the task of the new chief gardener and landscape architect of the Service of Promenades and Plantations, Jean-Pierre Barillet-Deschamps, who had also worked with Haussmann and Alphand in Bordeaux. His gardeners planted 420,000 trees, including hornbeam, beech, linden, cedar, chestnut, and elm, and hardy exotic species, like redwoods. They planted 270 hectares of lawns, with 150 kilograms of seed per hectare, and thousands of flowers. To make the forest more natural, they brought 50 deer to live in and around the Pré-Catelan.
The park was designed to be more than a collection of pictureque landscapes; it was meant as a place for amusement and recreation, with sports fields, bandstands, cafes, shooting galleries, riding stables, boating on the lakes, and other attractions. In 1855, Gabriel Davioud, a graduate of Ecole des Beaux-Arts, was named the chief architect of the new Service of Promenades and Plantations. He was commissioned to design 24 pavilions and chalets, plus cafes, gatehouses, boating docks, and kiosks. He designed the gatehouses where the guardians of the park lived to look like rustic cottages. He had a real Swiss chalet built out of wood in Switzerland and transported to Paris, where it was reassembled on an island in the lake and became a restaurant. He built another restaurant next to the park’s most picturesque feature, the Grand Cascade. He designed artificial grottoes made of rocks and cement, and bridges and balustrades made of cement painted to look like wood. He also designed all the architectural details of the park, from cone-shaped shelters designed to protect horseback riders from the rain to the park benches and direction signs.[17]
At the south end of the park, in the Plain of Longchamp, Davioud restored the ruined windmill which was the surviving vestige of the Abbey of Longchamp, and, working with the Jockey Club of Paris, constructed the grandstands of the Hippodrome of Longchamp, which opened in 1857.
At the northern end of the park, between the Sablons gate and Neuilly, a 20-hectare section of the park was given to the Societé Imperiale zoologique d’Acclimatation, to create a small zoo and botanical garden, with an aviary of rare birds and exotic plants and animals from around the world.
In March 1855, an area in the center of the park, called the Pré-Catelan, was leased to a concessionaire for a garden and amusement park. It was built on the site of a quarry where the gravel and sand for the park’s roads and paths had been dug out. It included a large circular lawn surrounded by trees, grottos, rocks, paths, and flower beds. Davioud designed a buffet, a marionette theater, a photography pavilion, stables, a dairy, and other structures. The most original feature was the Théâtre des fleurs, an open-air theater in a setting of trees and flowers. Later, an ice skating rink and shooting gallery were added. The Pré-Catelan was popular for concerts and dances, but it had continual financial difficulties and eventually went bankrupt. The floral theater remained in business until the beginning of the First World War, in 1914.[18]
The garden-building team brought together by Haussmann were Alphand, Barrillet-Deschamps and Davioud and went on to build The Bois de Vincennes, Parc Monceau Parc Montsouris, and the Parc des Buttes-Chaumont, using the experience and aesthetics they had developed in the Bois de Boulogne. They also rebuilt the Luxembourg gardens and the gardens of the Champs- Elysees, created smaller squares and parks throughout the center of Paris, and planted thousands of trees along the new boulevards that Haussmann had created. In the 17 years of Napoleon III’s reign, they planted no less than 600,000 trees and created a total 1,835 hectares of green space in Paris, more than any other ruler of France before or since.[19]
During the Franco-Prussian War (1870–71), which led to the downfall of Napoleon III and the long siege of Paris, the park suffered some damage from German artillery bombardment, the restaurant of the Grand Cascade was turned into a field hospital, and many of the park’s animals and wild fowl were eaten by the hungry population. In the years following, however, the park quickly recovered.
The Bois de Boulogne became a popular meeting place and promenade route for Parisians of all classes. The alleys were filled with carriages, coaches, and horseback riders, and later with men and women on bicycles, and then with automobiles. Families having picnics filled the woods and lawns, and Parisians rowed boats on the lake, while the upper classes were entertained in the cafes. The restaurant of the Pavillon de la Grand Cascade became a popular spot for Parisian weddings. During the winter, when the lakes were frozen, they were crowded with ice skaters.[20]
The activities of Parisians in the Bois, particularly the long promenades in carriages around the lakes, were often portrayed in French literature and art in the second half of the 19th and the beginning of the 20th centuries. Scenes set in the park appeared in Nana by Émile Zola and in Education Sentimentale by Gustave Flaubert.[21] In the last pages of Du côté de chez Swann in À la recherche du temps perdu (1914), Marcel Proust minutely described a walk around the lakes taken as a child.[22] The life in the park was also the subject of the paintings of many artists, including Eduard Manet, Pierre-Auguste Renoir, and Vincent van Gogh.
In 1860, Napoleon opened the Jardin d’Acclimatation, a separate concession of 20 hectares at the north end of the park; it included a zoo and a botanical garden, as well as an amusement park. Between 1877 and 1912, it also served as the home of what was called an ethnological garden, a place where groups of the inhabitants of faraway countries were put on display for weeks at a time in reconstructed villages from their homelands. They were mostly Sub-Saharan Africans, North Africans, or South American Indians, and came mostly from the French colonies in Africa and South America, but also included natives of Lapland and Cossacks from Russia. These exhibitions were extremely popular and took place not only in Paris, but also in Germany, England, and at the Chicago Exposition in the United States; but they were also criticized at the time and later as being a kind of “human zoo“. Twenty-two of these exhibits were held in the park in the last quarter of the 19th century. About ten more were held in the 20th century, with the last one taking place in 1931.

Le jardin d’acclimatation en 1860, gravure d’A. Provost.
In 1905, a grand new restaurant in the classical style was built in the Pré-Catelan by architect Guillaume Tronchet. Like the cafe at the Grand Cascade, it became a popular promenade destination for the French upper classes.[23]
At the 1900 Summer Olympics, the land hosted the croquet and tug of war events.[24][25] During the 1924 Summer Olympics, the equestrian events took place in the Auteuil Hippodrome.
The Bois de Boulogne was officially annexed by the city of Paris in 1929 and incorporated into the 16th arrondissement.
Soon after World War II, the park began to come back to life. In 1945, it held its first motor race after the war: the Paris Cup. In 1953, a British group, Les Amis de la France, created the Shakespeare Garden on the site of the old floral theater in the Pré-Catelan.[26]
From 1952 until 1986, the Duke of Windsor, the title granted to King Edward VIII after his abdication, and his wife, Wallis Simpson, the Duchess of Windsor, lived in the Villa Windsor, a house in the Bois de Boulogne behind the garden of the Bagatelle. The house was (and still is) owned by the City of Paris and was leased to the couple. The Duke died in this house in 1972, and the Duchess died there in 1986. The lease was purchased by Mohamed al-Fayed, the owner of the Ritz Hotel in Paris. The house was visited briefly by Diana, Princess of Wales and her companion, Dodi Fayed, on 31 August 1997, the day they died in a traffic accident in the Alma tunnel.

The Villa Windsor (originally named Chateau Le Bois) is a graceful 19th-century building of 14 rooms surrounded by a large tree-filled garden. It was built around 1860 and once owned by the Renault family but the French government sequestered the property after World War II and Charles de Gaulle occupied the house in the late 1940’s.
Link for summary of all stations showing line numbers and photos
Plan-des-Bus
By 1845, Paris and the railway companies were already thinking about an urban railway system to link inner districts of the city. The railway companies and the French government wanted to extend main-line railroads into a new underground network, whereas the Parisians favoured a new and independent network and feared national takeover of any system it built.[9] The disagreement lasted from 1856 to 1890. Meanwhile, the population became more dense and traffic congestion grew massively. The deadlock put pressure on the authorities and gave the city the chance to enforce its vision.
Prior to 1845, the urban transport network consisted primarily of a large number of omnibus lines, consolidated by the French government into a regulated system with fixed and unconflicting routes and schedules.[10] The first concrete proposal for an urban rail system in Paris was put forward by civil engineer Florence de Kérizouet. This plan called for a surface cable car system.[11] In 1855, civil engineers Edouard Brame and Eugène Flachat proposed an underground freight urban railroad, due to the high rate of accidents on surface rail lines.[11] On 19 November 1871 the General Council of the Seine commissioned a team of 40 engineers to plan an urban rail network.[12] This team proposed a network with a pattern of routes “resembling a cross enclosed in a circle” with axial routes following large boulevards. On 11 May 1872 the Council endorsed the plan, but the French government turned down the plan.[12] After this point, a serious debate occurred over whether the new system should consist of elevated lines or of mostly underground lines; this debate involved numerous parties in France, including Victor Hugo, Guy de Maupassant, and the Eiffel Society of Gustave Eiffel, and continued until 1892.[13] Eventually the underground option emerged as the preferred solution because of the high cost of buying land for rights-of-way in central Paris required for elevated lines, estimated at 70,000 francs per metre of line for a 20-metre-wide railroad.[14]
The last remaining hurdle was the city’s concern about national interference in its urban rail system. The city commissioned renowned engineer Jean-Baptiste Berlier, who designed Paris’ postal network of pneumatic tubes, to design and plan its rail system in the early 1890s.[14] Berlier recommended a special track gauge of 1,300 mm (4 ft 3 3⁄16 in) (versus the standard gauge of 1,435 mm or 4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) to protect the system from national takeover, which inflamed the issue substantially.[15] The issue was finally settled when the Minister of Public Works begrudgingly recognized the city’s right to build a local system on 22 November 1895, and by the city’s secret designing of the trains and tunnels to be too narrow for main-line trains, while adopting standard gauge as a compromise with the state.[15]
On 20 April 1896, Paris adopted the Fulgence Bienvenüe project, which was to serve only the city proper of Paris. Many Parisians worried that extending lines to industrial suburbs would reduce the safety of the city. Paris forbade lines to the inner suburbs and, as a guarantee, Métro trains were to run on the right, as opposed to existing suburban lines, which ran on the left.
Unlike many other subway systems (such as that of London), this system was designed from the outset as a system of (initially) nine lines.[16] Such a large project required a private-public arrangement right from the outset – the city would build most of the permanent way, while a private concessionaire company would supply the trains and power stations, and lease the system (each line separately, for initially 39-year leases).[further explanation needed][16] In July 1897, six bidders competed, and The Compagnie Generale de Traction, owned by the Belgian Baron Édouard Empain, won the contract; this company was then immediately reorganized as the Compagnie de Chemin de Fer Metropolitan.[16]
Construction began on November 1898.[17] The first line, Porte Maillot–Porte de Vincennes, was inaugurated on 19 July 1900 during the Paris World’s Fair. Entrances to stations were designed in Art Nouveau style by Hector Guimard. Eighty-six of his entrances are still in existence.
Bienvenüe’s project consisted of 10 lines, which correspond to today’s Lines 1 to 9. Construction was so intense that by 1920, despite a few changes from schedule, most lines had been completed. The shield method of construction was rejected in favor of the cut-and-cover method in order to speed up work.[18] Bienvenüe, a highly regarded engineer, designed a special procedure of building the tunnels to allow the swift repaving of roads, and is credited with a largely swift and relatively uneventful construction through the difficult and heterogeneous soils and rocks.[19]
Lines 1 and 4 were conceived as central east-west and north-south lines. Two lines, ligne 2 Nord (line 2 North) and ligne 2 Sud (line 2 South), were also planned but line 2 South was merged with line 5 in 1906. Line 3 was an additional east-west line to the north of line 1 and line 5 an additional north-south line to the east of line 4. Line 6 would run from Nation to Place d’Italie. Lines 7, 8 and 9 would connect commercial and office districts around the Opéra to residential areas in the north-east and the south-west. Bienvenüe also planned a circular line, the ligne circulaire intérieure, to connect the six main-line stations. A section opened in 1923 between Invalides and the Boulevard Saint-Germain before the plan was abandoned.
On 31 January 1904, a second concession was granted to the Société du chemin de fer électrique souterrain Nord-Sud de Paris (Paris North-South underground electrical railway company), abbreviated to the Nord-Sud (North-South) company. It was responsible for building three proposed lines:
Line A was inaugurated on 4 November 1910, after being postponed because of floods in January that year. Line B was inaugurated on 26 February 1911. Because of the high construction costs, the construction of line C was postponed. Nord-Sud and CMP used compatible trains that could be used on both networks, but CMP trains used 600 volts third rail, and NS −600 volts overhead wire and +600 volts third rail. This was necessary because of steep gradients on NS lines. NS distinguished itself from its competitor with the high-quality decoration of its stations, the trains’ extreme comfort and pretty lighting.
Nord-Sud did not become profitable and bankruptcy became unavoidable. By the end of 1930, the CMP bought Nord-Sud. Line A became Line 12 and line B Line 13. Line C was built and renamed line 14, that Line was reorganized in 1937 with Lines 8 and 10. This partial line is now the south part of line 13.
The last Nord-Sud train set was decommissioned on 15 May 1972.[20]
Bienvenüe’s project was nearly completed during the 1920s. Paris planned three new lines and extensions of most lines to the inner suburbs, despite the reluctance of Parisians. Bienvenüe’s inner circular line having been abandoned, the already-built portion between Duroc and Odéon for the creation of a new east-west line that became line 10, extended west to Porte de Saint-Cloud and the inner suburbs of Boulogne.
The line C planned by Nord-Sud between Montparnasse station and Porte de Vanves was built as line 14 (different from present line 14). It extended north in encompassing the already-built portion between Invalides and Duroc, initially planned as part of the inner circular. The over-busy Belleville funicular tramway would be replaced by a new line, line 11, extended to Châtelet. Lines 10, 11 and 14 were thus the three new lines envisaged under this plan.
Most lines would be extended to the inner suburbs. The first to leave the city proper was line 9, extended in 1934 to Boulogne-Billancourt; more followed in the 1930s. World War II forced authorities to abandon projects such as the extension of Lines 4 or 12 to the northern suburbs. By 1949, eight lines had been extended: Line 1 to Neuilly-sur-Seine and Vincennes, Line 3 to Levallois-Perret, Line 5 to Pantin, Line 7 to Ivry-sur-Seine, Line 8 to Charenton, Line 9 to Boulogne-Billancourt, Line 11 to Les Lilas and Line 12 to Issy-les-Moulineaux.
World War II had a massive impact on the Métro. Services were limited and many stations closed. The risk of bombing meant the service between Place d’Italie and Étoile was transferred from Line 5 to line 6, so that most of the elevated portions of the Métro would be on Line 6. As a result, Lines 2 and 6 now form a circle. Most stations were too shallow to be used as bomb shelters. The French Resistance used the tunnels to conduct swift assaults throughout Paris.[21]
It took a long time to recover after liberation in 1944. Many stations had not reopened by the 1960s and some closed for good. On 23 March 1948, the CMP (the underground) and the STCRP (bus and tramways) merged to form the RATP, which still operates the Métro.
The network grew saturated during the 1950s. Outdated technology limited the number of trains, which led the RATP to stop extending lines and concentrate on modernisation. The MP 51 prototype was built, testing both rubber-tyred metro and basic automatic driving on the voie navette. The first replacements of the older Sprague trains began with experimental articulated trains and then with mainstream rubber-tyred metro MP 55 and MP 59, some of the latter still in service (line 11). Thanks to newer trains and better signalling, trains ran more frequently.
The population boomed from 1950 to 1980. Cars became more popular and suburbs grew further from the city. The main railway stations, termini of the suburban rail lines, were overcrowded during rush hour. The short distance between metro stations slowed the network and made it unprofitable to build extensions. The solution in the 1960s was to revive a project abandoned at the end of the 19th century: joining suburban lines to new underground portions in the city centre as the Réseau express régional (regional express network; RER).
The RER plan initially included one east-west line and two north-south lines. RATP bought two unprofitable SNCF lines—the Ligne de Saint-Germain (westbound) and the Ligne de Vincennes (eastbound) with the intention of joining them and to serve multiple districts of central Paris with new underground stations. The new line created by this merger became line A. The Ligne de Sceaux, which served the southern suburbs and was bought by the CMP in the 1930s, would be extended north to merge with a line of the SNCF and reach the new Charles de Gaulle Airport in Roissy. This became line B. These new lines were inaugurated in 1977 and their wild success outperformed all the most optimistic forecasts to the extent that line A is the most used urban rail line in the world with nearly 300 million journeys a year.
Because of the enormous cost of these two lines, the third planned line was abandoned and the authorities decided that later developments of the RER network would be more cheaply developed by SNCF, alongside its continued management of other suburban lines. However, the RER developed by SNCF would never match the success of the RATP’s two RER lines. In 1979, SNCF developed line C by joining the suburban lines of Gare d’Austerlitz and Gare d’Orsay, the latter being converted into a museum dedicated to impressionist paintings. During the 1980s, it developed line D, which was the second line planned by the initial RER schedule, but serving Châtelet instead of République to reduce costs. A huge Métro-RER hub was created at Châtelet-Les Halles, the world’s largest underground station.[22]
The same project of the 1960s also decided to merge lines 13 and 14 to create a quick connection between Saint-Lazare and Montparnasse as a new north-south line. Distances between stations on the lengthened line 13 differ from that on other lines in order to make it more “express” and hence to extend it farther in the suburbs. The new Line 13 was inaugurated on 9 November 1976.
In October 1998, Line 14 was inaugurated. It was the first fully new Métro line in 63 years. Known during its conception as Météor (Métro Est-Ouest Rapide), it is one of the two fully automatic lines within the network along with Line 1. It was the first with platform screen doors to prevent suicides and accidents. It was conceived with extensions to the suburbs in mind, similar to the extensions of the line 13 built during the 1970s. As a result, most of the stations are at least a kilometre apart. Like the RER lines designed by the RATP, nearly all stations offer connections with multiple Métro lines. The line runs between Saint-Lazare and Olympiades.
Lines 7 and 13 are the only two on the network to be split in branches. The RATP would like to get rid of those saturated branches in order to improve the network’s efficiency. A project existed to attribute to line 14 one branch of each line, and to extend them further into the suburbs. This project was abandoned. In 1999, the RER line E was inaugurated. Known during its conception as Eole (Est-Ouest Liaison Express), it is the fifth RER line. It terminates at Haussmann – Saint-Lazare, but a new project, financed by EPAD, the public authority managing the La Défense business district, should extend it west to La Défense – Grande Arche and the suburbs beyond.
In work started in 2007 and completed in November 2011, Line 1 was converted to driverless operation. The line was operated with a combination of driver-operated trains and driver-less trains until the delivery of the last of its driver-less MP 05 trains in February 2013. The same conversion is on-going for Line 4, with an expected completion date in 2022.
Several extensions to the suburbs opened in the last years. Line 8 was extended to Pointe du Lac in 2011, line 12 was extended to Aubervilliers in 2012 and line 4 was extended to Mairie de Montrouge in 2013.
| Line name | Opened | Last extension |
Stations served |
Length | Average interstation |
Journeys made (per annum) |
Termini | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Line 1 | 1900 | 1992 | 25 | 16.6 km / 10.3 miles | 692 m | 213,921,408 | La Défense Château de Vincennes |
|
| Line 2 | 1900 | 1903 | 25 | 12.3 km / 7.7 miles | 513 m | 95,945,503 | Porte Dauphine Nation |
|
| Line 3 | 1904 | 1971 | 25 | 11.7 km / 7.3 miles | 488 m | 91,655,659 | Pont de Levallois Gallieni |
|
| Line 3bis | 1971 | 1971 | 4 | 1.3 km / 0.8 miles | 433 m | Porte des Lilas Gambetta |
||
| Line 4 | 1908 | 2013 | 27 | 12.1 km / 6.6 miles | 424 m | 155,348,608 | Porte de Clignancourt Mairie de Montrouge |
|
| Line 5 | 1906 | 1985 | 22 | 14.6 km / 9.1 miles | 695 m | 92,778,870 | Bobigny Place d’Italie |
|
| Line 6 | 1909 | 1942 | 28 | 13.6 km / 8.5 miles | 504 m | 104,102,370 | Charles de Gaulle–Étoile Nation |
|
| Line 7 | 1910 | 1987 | 38 | 22.4 km / 13.9 miles | 605 m | 121,341,833 | La Courneuve Villejuif Mairie d’Ivry |
|
| Line 7bis | 1967 | 1967 | 8 | 3.1 km / 1.9 miles | 443 m | Louis Blanc Pré Saint-Gervais |
||
| Line 8 | 1913 | 2011 | 38 | 23.4 km / 13.8 miles | 614 m | 92,041,135 | Balard Pointe du Lac |
|
| Line 9 | 1922 | 1937 | 37 | 19.6 km / 12.2 miles | 544 m | 119,885,878 | Pont de Sèvres Mairie de Montreuil |
|
| Line 10 | 1923 | 1981 | 23 | 11.7 km / 7.3 miles | 532 m | 40,411,341 | Boulogne Gare d’Austerlitz |
|
| Line 11 | 1935 | 1937 | 13 | 6.3 km / 3.9 miles | 525 m | 46,854,797 | Châtelet Mairie des Lilas |
|
| Line 12 | 1910[33] | 2012 | 29 | 13.9 km / 8.6 miles | 515 m | 81,409,421 | Front Populaire Mairie d’Issy |
|
| Line 13 | 1911[33] | 2008 | 32 | 24.3 km / 15.0 miles | 776 m | 114,821,166 | Châtillon – Montrouge Saint-Denis Les Courtilles |
|
| Line 14 | 1998 | 2007 | 9 | 9 km / 5.6 miles | 1,129 m | 62,469,502 | Saint-Lazare Olympiades |
|
See also: Paris ticket “t+” and Public transport fares in the Île-de-France
Fares are sold at kiosks and at automated machines in the station foyer. Entrance to platforms is by automated gate, opened by smart cards and simple tickets. Gates return tickets for passengers to retain for the duration of the journey. There is normally no system to collect or check tickets at the end of the journey, and tickets can be inspected at any point. The exit from all stations is clearly marked as to the point beyond which possession of a ticket is no longer required. The standard ticket is ticket “t+”. It is valid for a multi-transfer journey within one and a half hours from the first validation. It can be used on the Métro, buses and trams, and in zone 1 of the RER. It allows unlimited transfers between the same mode of transport (i.e. Métro to Métro, bus to bus and tram to tram), between bus and tram, and between metro and RER zone 1. When transferring between the Metro and the RER, it is necessary to retain the ticket. The RER requires a valid ticket for entry and exit, even for a transfer. It costs €1.90 or ten (a carnet) for €14.50 as of June 2017.[28]
Other fares use the Navigo pass, an RFID-based contactless smart card. Fares include:

Le Palais des Tournelles
The Marais area is situated between the 3rd and 4th arrondissements of Paris. Spared by the great Haussmannian works in the 19th century, it is above all an area of exceptional architecture and there remain many magnificent manors built during the 17th century, now mainly housing museums. Originally settled on a vast marshy area, (the name Marais means “Marsh”), the district had its heyday in the early 17th century when King Henry IV decided to build a sublime place dedicated to stroll: la Place des Vosges (inaugurated in 1612).
The hôtel des Tournelles is a now-demolished collection of buildings from the 14th century onwards north of place des Vosges. It was named after its many ‘tournelles’ or little towers.[1][2]
It was owned by the kings of France for a long period of time, though they did not often live there. Henry II of France died there in 1559 of wounds he received in a joust. After his death, his widow Catherine de Médici, abandoned the building, by then quite derelict and old-fashioned. It was turned into a gunpowder magazine, then sold to finance the construction of the Tuileries, designed and developed to suit the queen’s Italian style.
At the beginning of the 15th century, the district around the hôtel formed a huge rectangle, marked out by the rue Saint-Antoine, rue des Tournelles, rue de Turenne and rue Saint-Gilles, a rectangle broken from within by the park of the royal estate. During the English occupation of Paris (1420-1436), John of Lancaster, Duke of Bedford, extended the district by purchasing eight and a half acres from the nuns of Sainte-Catherine for 200 livres 16 sous, thus extending the property to the fortified wall of Paris, which was then situated on what is now known as the boulevard Richard Lenoir.
This extension was annulled in 1437 after the English left. The main entrance to the hôtel was at the bottom of a cul-de-sac currently known as Impasse Guéménée. The hôtel was said to be able to accommodate 6,000 people.
Like the Hôtel Saint-Pol, the hôtel des Tournelles was a collection of buildings spread over an estate of more than 20 acres (8.1 ha), including twenty chapels, several pleasure grounds, ovens and twelve galleries including the Duke of Bedford’s famous galerie des courges (so-called due to the painted green squash or courges on its walls. Under its tiled roof the Duke’s arms, devices and heraldry were displayed). It also included a maze called ‘Dedalus’, two parks planted with trees, six kitchen gardens and a ploughed field. The council chamber was notable for the magnificence of its decoration. Three other rooms bore the names salle des Écossais (room of the Scots), salle de brique (brick room) and salle pavée (paved room).
One part of the hôtel des Tournelles, named Logis du Roi, had an entrance decorated with the French coat of arms, painted by Jean de Boulogne, known as Jean de Paris. In 1464, Louis XI built a gallery there which connected this house to the Hôtel-Neuf of Madame d’Étampes, across the rue Saint-Antoine. He also built an observatory for his doctor, Jacques Coitier. Menageries based on those at the hôtel Saint-Paul were later added to house some of the animals previously held at the hôtel Saint-Paul. New specimens were imported from Africa, such as lions, giving the enclosures the name of hôtel des lions du Roi.
No traces remain of the hôtel besides a copy of one of its gates, which forms the south gate of the église Saint-Nicolas-des-Champs, and some cellars buried below buildings in the district.
At the beginning of the 14th century, the building that became the Hôtel des Tournelles was merely a house facing the hôtel Saint-Pol. Pierre d’Orgemont, seigneur de Chantilly and chancellor of France and the Dauphiné under Charles VI, or perhaps his eldest son Pierre, rebuilt it in 1388. It was bequeathed to the younger Pierre in 1387. This house may have formerly been the property of Jean d’Orgemont, the presumed father of the elder Pierre.[3][4] On 19 March 1387 Pierre d’Orgemont divided his lands among his ten children, leaving the maison des Tournelles to his eldest son Pierre, bishop of Paris, who was already living there.[5] After his father’s death in 1389, the bishop sold the house on 16 May 1402 for 140,000 gold écus, to the duc de Berry, brother of Charles V. In 1404 the duc de Berry gave it to his nephew Louis, the duc d’Orléans and the younger brother of Charles VI, in exchange for the hôtel de Gixé on rue de Jouy. The duc d’Orléans was assassinated on 23 November 1407 and the hôtel passed to his heirs, becoming the property of Charles VI, who lived there from 1417 onwards. The house took the name Maison royale des Tournelles.
Thanks to the Treaty of Troyes, the English entered Paris on 18 November 1420. After Charles VI‘s death on 22 October 1422 in Paris, the hôtel was seized and became the primary residence of John of Lancaster, the Duke of Bedford, younger brother of Henry V of England and regent for the kingdom of France until his nephew Henry VI came of age. In 1436, after the English left Paris, Charles VII gave the hôtel to his Orléans cousins. When John died in 1467, the property passed to his widow, Marguerite, Duchess of Rohan. In 1486 Marguerite left the buildings to her son Charles of Orléans, father of Francis I of France. It thus became a royal residence once again. In 1563 it was still called the “hôtel des Tournelles et d’Angoulème”. It thus passed to John of Orléans, count of Angoulême, and was for a time called the hôtel d’Angoulême (not to be confused with the later Hôtel d’Angoulême Lamoignon).
Different kings of this era stayed for short or long periods at the hôtel – Louis XI made a few brief stays there:
| “ | Item, the following Thursday [1 June 1440], the Delphin [the future Louis XI] came to Paris and was lodged at the ostel [sic] des Tournelles, hard by the porte Sainct-Anthoine, and stayed only one night, not showing himself in Paris, nor his father the king coming either…[6] | ” |
Fleeing his coronation festivities,[clarification needed] the new king took refuge there on Tuesday 1 September 1461 after dinner[7] but left for Tours by 25 September.
Nor did Louis’ successors Charles VIII of France and Louis XII of France stay there much, though the latter did die there on 1 January 1515. Francis I of France did not live there, preferring the château de Fontainebleau, the Louvre and the castles on the River Loire. The Hôtel des Tournelles was used as a residence by his mother Louise of Savoy then by his mistress Anne de Pisseleu, a tradition repeated by Henry II of France when he made it the residence of Diane de Poitiers. In 1524 the magician Cornélius Agrippa lived there under the name Agrippa de Nettesheim, as doctor and astrologer to Louise de Savoie, to whom he made dead and living people appear.[citation needed]
The hôtel saw several lavish and unusual festivals, such as the “danse macabre” on 23 August 1451 before Charles, Duke of Orléans. Henry II celebrated his coronation there in 1547 and then the signing of the Treaties of Cateau-Cambrésis in 1559. The last festival held there was also in 1559, to mark the double marriage of Élisabeth de France to Philip II of Spain and of the king’s sister Marguerite de France to the duke of Savoy. On this occasion, a tournament was organised on 29 June on rue Saint-Antoine, the widest street in Paris at the time and thus known as the La Grant rue St Anthoine, with the same dimensions as in the present day. During a joust in front of the hôtel de Sully (level with what is now number 62), Henry II was seriously wounded by an accidental lance thrust by Gabriel de Lorges, count of Montgomery, captain of the king’s Scottish guard. Moved to the hôtel des Tournelles, the king died there on 10 July 1559 in terrible agony, despite attempts to save him by both the famous surgeon Ambroise Paré and the surgeon to the king of Spain, Andreas Vesalius.
Catherine de Médici, an Italian princess who had grown up in Roman palaces, disliked the Hôtel des Tournelles’s medieval appearance and took Henry’s death as a pretext to sell it off. Gaining total power as regent to her young sons, the heirs of Henry, she turned the property into an arsenal, then had it closed and demolished. On 28 January 1563, in the name of her son Charles IX of France, she issued letters patent ordering the demolition.[8] This took place in stages and financed her major works on the more modern royal residences in Paris, particularly on the Madrid and the Tuileries. Some of the materials from the old hôtel were reused in the construction of the palace. The stables were reused to create the important Marché aux chevaux, horse market, where two thousand horses were sold every Saturday.
Certain parcels of land from the Hôtel’s estate were sold off, though a large estate remained and was used in military training. In January 1589 the estate was used to exercise the mercenaries charged with defending Paris against Henry IV of France. It also became a traditional site for bloody duels – on 27 April 1578, at 5 am, three favourites of Henry III of France beat three favourites of the duke of Guise in a duel there, with all six men ending up killed or seriously wounded.
In August 1603, Henry IV tried to re-use part of the Hôtel’s buildings to create a silk, gold and silver factory, bringing in 200 Italian artisans for this purpose, but the attempt failed. Finally, on 4 March 1604, he issued an edict instructing his minister Sully to measure out the site. He donated a parcel of 6,000 toises (yards) to his main noblemen, who built pavilions there, on the condition that they stuck to the layout, materials and main dimensions laid down by the architects Androuet du Cerceau and Claude Chastillon. On 29 March 1605 Henry wrote to Sully:
| “ | My friend, I pray you to remember what we talked of together lately, of this place where I wish that I wish to be built before the lodge which serves as a horse market for manufactures, to the end that if you have not marked out there – for renting the rest of the other places to and rent for the rest, it is doubtless that they will be unfaithful and I pray you to give me the news.[9] | ” |
Thus the place Royale, later known as the place des Vosges, was born.
Click Refresh to view slides

Jardin des Tuileries, Place de la Concorde, Saint-Germain-l’Auxerrois
The 1st arrondissement of Paris is one of the 20 arrondissements (administrative districts) of the capital city of France. Situated principally on the right bank of the River Seine, it also includes the west end of the Île de la Cité. The arrondissement is one of the oldest in Paris, the Île de la Cité having been the heart of the city of Lutetia, conquered by the Romans in 52 BC, while some parts on the right bank (including Les Halles) date back to the early Middle Ages. It is the least populated of the city’s arrondissements and one of the smallest by area, a significant part of which is occupied by the Louvre Museum and the Tuileries Gardens. Much of the remainder of the arrondissement is dedicated to business and administration.
Each of the 20 Paris arrondissements is divided into four quarters (quartiers). The 1st Arrondissement is comprised of four quartiers as follows:
From Planet Bpm : The Saint-Germain-l’Auxerrois district is the heart of the French capital. It spreads from the western tip of Île de la Cité to the Jardin des Tuileries, the biggest, oldest garden in Paris. Fluctuat nec mergitur. (“She is battered by the waves, but does not sink”) was the motto of the boatmen’s guild which had its headquarters here during the reign of Hugh Capet, and the phrase subsequently became the city’s own motto.
Saint-Germain-l’Auxerrois surrounds the Louvre, whose buildings house a significant portion of French history. Originally built around 1190 by Philip II, ‘Augustus’, as a fortress to contain royal treasure before the monarch left to join the Crusades, the Louvre is now devoted entirely to culture, displaying Western art from the Middle Ages to 1848, treasures of Antiquity and, since 2005, Islamic art. The Church of Saint-Germain-l’Auxerrois, after which the district is named, adjoins the Louvre and can be visited outside service times.  The grounds of the Jardin des Tuileries host three major Paris museums: the Musée de l’Orangerie, devoted to Monet’s Nymphéas and the Jean Walter and Paul Guillaume collections, the Musée du Jeu de Paume, which exhibits contemporary art and photography, and the Musée des Arts Décoratifs with its significant fashion and textiles collection as well as a more recent section devoted to advertising.
The grounds of the Jardin des Tuileries host three major Paris museums: the Musée de l’Orangerie, devoted to Monet’s Nymphéas and the Jean Walter and Paul Guillaume collections, the Musée du Jeu de Paume, which exhibits contemporary art and photography, and the Musée des Arts Décoratifs with its significant fashion and textiles collection as well as a more recent section devoted to advertising.
Île de la Cité in the eastern part of the district also has some emblematic historical buildings such as the Conciergerie, the first royal residence in the city and later a forbidding prison under the Terror. It is a stone’s throw from Sainte-Chapelle, a masterpiece of the Gothic style with richly hued stained glass windows built by St Louis within the Palais de la Cité, now the Palais de Justice law courts.
Les Halles was the traditional central market of Paris. In 1183, King Philippe II Auguste enlarged the marketplace in Paris and built a shelter for the merchants, who came from all over to sell their wares. The church of Saint-Eustache was constructed in the 16th century. The circular Halle aux Blés (Corn Exchange), designed by Nicolas Le Camus de Mézières, was built between 1763 and 1769 at the west end of Les Halles. Its circular central court was later covered with a dome, and it was converted into the Bourse de Commerce in 1889.[6] In the 1850s, Victor Baltard designed the famous glass and iron buildings, Les Halles, which would last until the 1970s. Les Halles was known as the “Belly of Paris”, as it was called by Émile Zola in his novel Le Ventre de Paris, which is set in the busy marketplace of the 19th century.
Unable to compete in the new market economy and in need of massive repairs, the colourful ambience once associated with the bustling area of merchant stalls disappeared in 1971, when Les Halles was dismantled; the wholesale market was relocated to the suburb of Rungis. Two of the glass and cast iron market pavilions were dismantled and re-erected elsewhere; one in the Paris suburb of Nogent-sur-Marne, the other in Yokohama, Japan.[6]
The site was to become the point of convergence of the RER, a network of new express underground lines which was completed in the 1960s. Three lines leading out of the city to the south, east and west were to be extended and connected in a new underground station. For several years, the site of the markets was an enormous open pit, nicknamed “le trou des Halles” (trou = hole), regarded as an eyesore at the foot of the historic church of Saint-Eustache. Construction was completed in 1977 on Châtelet-Les-Halles, Paris’s new urban railway hub. The Forum des Halles, a partially underground multiple story commercial and shopping center, opened at the east end of the site in 1979 and remains there today. A public garden covering four hectares opened in 1986.[6] Many of the surrounding streets were pedestrianized.
Gare de Châtelet – Les Halles is Paris’s most used rail station, serving 750,000 travelers on an average weekday. The buildings and their surroundings have been criticized for their design. In 2002 Mayor Bertrand Delanoë announced that the City of Paris would begin public consultations regarding the remodeling of the area, calling Les Halles “a soulless, architecturally bombastic concrete jungle”.[7][8]
A design competition for the Forum and gardens was held, with entries from Jean Nouvel, Winy Maas, David Mangin, and Rem Koolhaas. Mangin’s design for the gardens, which proposed replacing the landscaped mounds and paths of the 1980s design with a simplified pattern of east-west pedestrian promenades and a large central lawn, was selected. The plan also includes extending the pedestrianized area further east to include all the streets bordering the gardens. Another competition was held for the redesign of the Forum. Ten teams submitted plans, and the proposal by Patrick Berger and Jacques Anziutti was selected in 2007. Their design includes a large undulating glass canopy which will cover the redesigned Forum.[8] STIF and RATP began plans for the remodeling of the Châtelet-Les-Halles station in 2007, and the following year Berger and Anziutti were awarded a contract for redesign of the station.
The station redesign includes new entrances on Rue Berger, Rue Rambuteau, and Place Marguerite de Navarre, an expanded RER concourse, and improved pedestrian circulation. Construction began in 2010 on a project which includes the gardens, Forum, and station, and is scheduled to continue through 2016. The clients are the City of Paris, RATP, which operates the Paris Metro, and La Société Civile du Forum des Halles de Paris, which operates the Forum.[6]
Part of the actual demolition of the site is featured in the 1974 film Touche pas à la femme blanche (Don’t Touch the White Woman!), which iconoclastically restages General Custer‘s ‘last stand’ in a distinctly French context in and around the area.
In 1977, Roberto Rossellini made a 54-minute documentary film that testified to the public’s response to the demolition of Les Halles and the construction of Centre Georges Pompidou. “The result was a sceptical vision rather than a pure celebration.”[9]
The open-air market and Baltard’s pavilions were digitally reconstructed for the 2004 film Un long dimanche de fiançailles (A Very Long Engagement), which was set after the First World War.
Formed for the first time at the time of the French Revolution , the district of Palais-Royal was formed of four districts :
In 1790 this district takes the revolutionary name of section of the Mountain .
By prefectural decree of , the section of the Mountain, now section of the Butte-des-Moulins , which was located in the former 2nd arrondissement of Paris takes the name of district of the Palais Royal .
Its limits are then:
The law of June 16, 1859 assigns this administrative district to the 1st arrondissement , with the following limits:
The district of the Palais-Royal is formed of a rectangle, limited to the West by the street Saint-Roch, to the East by the streets of Marengo and Croix-des-Petits-Champs, to the North by the street of Little Champs, and to the South by the Rue de Rivoli.
In the heart of the 1st district, the district is between the neighborhoods of Place-Vendôme in the West, Les Halles in the East, Saint-Germain-l’Auxerrois in the South, Vivienne, in the 2nd district, in the North.
The two main North-South axes are Rue de Richelieu in the west of the Jardin du Palais Royal and Rue Croix-des-Petits-Champs in the East. The garden being crossed by no way, besides the lanes that limit it, only rue Saint-Honoré crosses the neighborhood from side to side in the east-west direction. The Haussmannian breakthrough that is the Avenue de l’Opera cuts the grid drawn in the seventeenth century oblique. The rue Coquillière, which connects the district Les Halles was pierced in the twelfth century at the time of the construction of the enclosure of Philippe Auguste; it is the oldest way of the district.
The district is organized around the eponymous Royal Palace and its garden , open to the public.
Clockwise:
Clockwise:
Clockwise:
In the subway :
The section of the Place Vendôme was created in 1790, administrative district which became in 1792 the section of the Spades then in 1795 the area of the Place-Vendôme, located then in the 1st district of Paris whose limits started from the place Vendôme and following on the left, the streets of Neuve-des-Petits-Champs, Louis-le-Grand, Chaussée-d’Antin, Saint-Lazare, Arcade, Madeleine, Faubourg-Saint-Honoré and Saint-Honoré. ‘in the Place Vendôme 1 .
A new administrative district is created by the imperial decree of November 1 , 1859, whose annexed map defines the district as: “[Quartier] Place Vendome [sic] . A line starting from the rue de Rivoli and following the axis of the streets of [sic] Saint-Florentin, Richepance and Duphot. New-Capucines streets, Neuve-des-Petits-Champs. Neuve-Saint-Roch, of the Dauphin. And from Rivoli to the point of departure 2 .“

François Mansart (23 January 1598 – 23 September 1666) was a French architect credited with introducing classicism into Baroque architecture of France. The Encyclopædia Britannica cites him as the most accomplished of 17th-century French architects whose works “are renowned for their high degree of refinement, subtlety, and elegance”.
François Mansart was born to a master carpenter in Paris. He was not trained as an architect; his relatives helped train him in as a stonemason and a sculptor. He is thought to have learned the skills of architect in the studio of Salomon de Brosse, the most popular architect of Henry IV‘s reign.
Mansart was highly recognized from the 1620s onward for his style and skill as an architect, but he was viewed as a stubborn and difficult perfectionist, tearing down his structures in order to start building them over again. Only the richest could afford to have him work for them, as Mansart’s constructions cost “more money than the Great Turk himself possesses”.
The only surviving example of his early work is the Château de Balleroy, commissioned by a chancellor to Gaston, Duke of Orléans, and started in 1626. The duke himself was so pleased with the result that he invited Mansart to renovate his Château de Blois (1635). The architect intended to rebuild this former royal residence completely, but his design was stymied and only the north wing was reconstructed to Mansart’s design, cleverly using classical orders. In 1632, Mansart designed the Church of St. Mary of the Angels using the Pantheon as an inspiration.
Most of Mansart’s buildings were subsequently reconstructed or demolished. The best preserved example of his mature style is the Château de Maisons, which uniquely retains the original interior decoration, including a magnificent staircase. The structure is strictly symmetrical, with much attention given to relief. It is thought to have heralded and inspired the 18th-century Neoclassicism.
In the 1640s, Mansart worked on the convent and church of the Val-de-Grâce in Paris, a much coveted commission from Anne of Austria. His alleged profligacy led to his being replaced with a more tractable architect, who basically followed Mansart’s design.
In the 1650s, Mansart was targeted by political enemies of the prime minister Cardinal Mazarin, for whom Mansart frequently worked. In 1651, they published “La Mansarade”, a pamphlet accusing the architect of wild extravagance and machinations.
After Louis XIV‘s accession to the throne, Mansart lost many of his commissions to other architects. His designs for the remodeling of Louvre and for the royal mausoleum at Saint-Denis were never executed, in the case of the Louvre because he would not submit detailed plans. Some of his plans were subsequently reused by his grandnephew, Jules Hardouin Mansart. Mansart died in Paris in 1666.

The Temple du Marais, sometimes known as the Temple Sainte-Marie, or historically, as the Church of Sainte Marie de la Visitation, is a Protestant church located in the 4th arrondissement of Paris, in the district of Le Marais at 17 Rue Saint-Antoine. It was originally built as a Roman Catholic convent by the Order of the Visitation of Holy Mary, whose sisters were commonly called the Visitandines. The church was closed in the French Revolution and later given to a Protestant congregation which continues its ministry to the present. The closest métro station is Bastille
From Wikipedia:
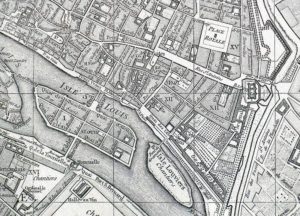
Vaugondy’s map of Paris (4e arrondissement) – 1760
The 4th arrondissement of Paris is located on the right bank of the Seine . It is bordered on the west by the 1st arrondissement , on the north by the 3rd arrondissement , on the east by the 11th and 12th arrondissements and on the south by the Seine and the 5th arrondissement . The eastern part of Île de la Cité and Île Saint – Louis are also part of the 4th arrondissement. Île Saint-Louis is the result of the union in the Middle Ages of Île Notre-Dame and Île aux Vaches. According to the General code of local authorities, it also bears the name of “arrondissement of the Hôtel-de-Ville” but this name is rarely used in the daily life.
The first dwellings on the Ile de la Cité may date from the Gallic period. In Roman times, Île de la Cité is connected to both banks by bridges located on the site of the current Little Bridge and Notre Dame Bridge . The route of Rue Saint-Martin corresponds to that of the main Roman road.
The extension of the houses on the right bank dates back to the fifth century with the construction of the sanctuary of St. Gervais. In the 9th century, Saint-Gervais is protected by a wall that was probably located at the rue de Rivoli and extend to the Seine , rue des Barres to the rue de la Tacherie . The town develops around the market of Greve (current place of the Hotel-de-Ville ) from the 11th century.
In 1111 , the city was plundered by Robert I , Count of Meulan, who destroyed the two bridges of the island. Louis VI decided to rebuild further west the bridge on the right bank and protect it with a chatelet. The construction of Pont au Change at the site brought about the appearance of a new district around the Châtelet where butchers settled.
Until the beginning of the 17th century, Île Saint-Louis was uninhabited and was a pasture area for livestock. It was fully sold under the reign of Louis XIII (1610-1643). It was at this time that it took its current name in honor of the king.
The current boundaries of the 4th arrondissement were set in 1860 , during the Second Empire , following the law of the giving rise to a new division of Paris into 20 districts .
For more of this article read Arrondissement 4e – translated from Wikipedia
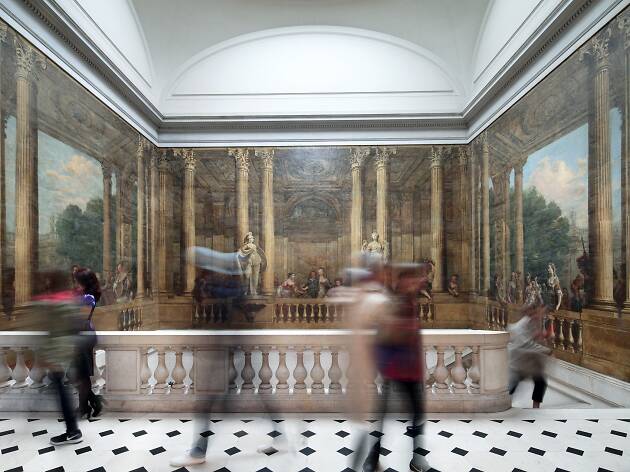


The ‘arts and trades’ museum is, in fact, Europe’s oldest science museum, founded in 1794 by the constitutional bishop Henri Grégoire, initially as a way to educate France’s manufacturing industry in useful scientific techniques. Housed in the former Benedictine priory of St-Martin-des-Champs, it became a museum proper in 1819; it’s a fascinating, attractively laid out…
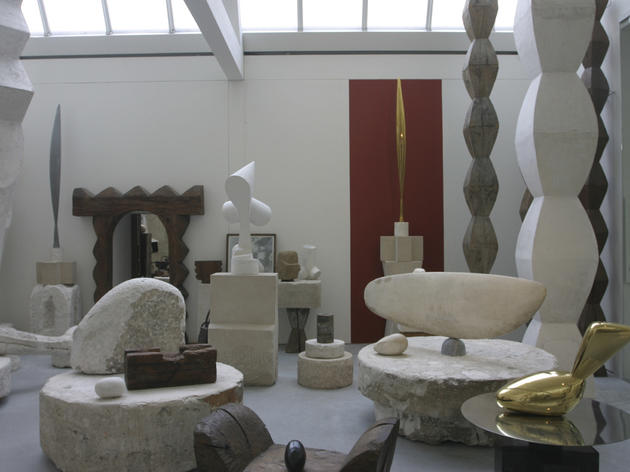

When Constantin Brancusi died in 1957, he left his studio and its contents to the state, and it was later moved and rebuilt by the Centre Pompidou. His fragile works in wood and plaster, the endless columns and streamlined bird forms show how Brancusi revolutionised sculpture.
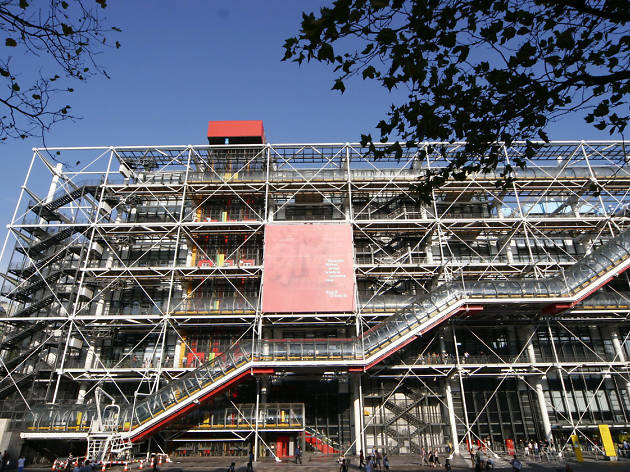

The primary colours, exposed pipes and air ducts make the Centre Pompidou one of the best-known sights in Paris. The then-unknown Italo-British architectural duo of Renzo Piano and Richard Rogers won the competition with their ‘inside-out’ boilerhouse approach, which put air-conditioning, pipes, lifts and the escalators on the outside…
Probably the capital’s best photography exhibition space, hosting retrospectives by Larry Clark and Martine Barrat, along with work by emerging photographers. The building, an airy mansion with a modern extension, contains a huge permanent collection. The venue organises the biennial Mois de la Photo and the Art Outsiders festival of new media web art in September.
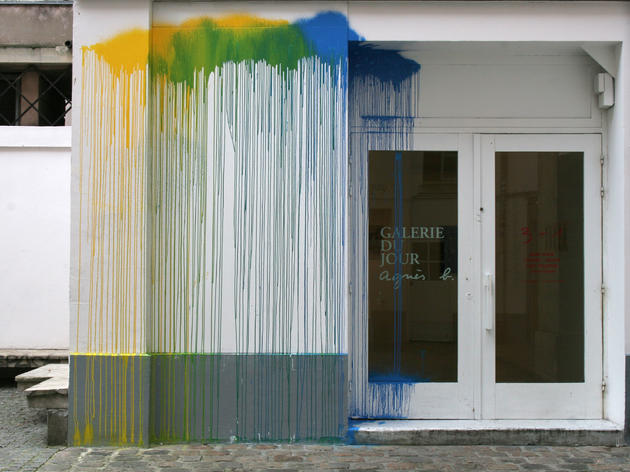

‘We say gallery, but we could also say a place for showing the other faces and the side issues of things’ explained Agnès B. in November 1984, when she launched La Galerie du Jour a few steps from the Centre Pompidou. The designer and founder of the wildly successful eponymous label shows here anything that pleases her – painting, sculpture, contemporary art and…

Centre Georges-Pompidou from Notre-Dame de Paris, 2011
The Musée National d’Art Moderne National Museum of Modern Art) is the national museum for modern art of France. It is located in Paris and is housed in the Centre Pompidou in the 4th arrondissement of the city. It is among the most visited art museums in the world and one of the largest for modern and contemporary art.
In 1937, the Musée National d’Art Moderne succeeded the Musée du Luxembourg, established in 1818 by King Louis XVIII as the first museum of contemporary art created in Europe, devoted to living artists whose work was due to join the Louvre 10 years after their death. Imagined as early as 1929 by Auguste Perret to replace the old Palais du Trocadero, the construction of a museum of modern art was officially decided in 1934 in the western wing of the Palais de Tokyo. Completed in 1937 for that year’s International Exhibition of Arts and Technology, it was temporarily used for another purpose, since the exhibition of national and foreign art indépendant was then preferably held in the Petit Palais and the Musée du Jeu de Paume. Although due to open in 1939, construction was eventually interrupted by the war; following the nomination of its first Chief Conservator in September 1940, the museum partially opened in 1942 with only a third of the collection brought back from some national collection caches hidden in the province. But its real inauguration didn’t take place until 1947, after World War II and the addition of the foreign schools collection of the Musée du Luxembourg, which had been held at the Musée du Jeu de Paume since 1922.
In 1947, then housed in the Palais de Tokyo, its collection was dramatically increased by its first director, Jean Cassou, thanks to his special relationship with many prominent artists or their families, such as Picasso and Braque. With the creation of the Centre Pompidou, the museum moved to its current location in 1977.
The museum has the second largest collection of modern and contemporary art in the world, after the Museum of Modern Art in New York, with more than 100,000 works of art by 6,400 artists from 90 countries since Fauvism in 1905. These works include painting, sculpture, drawing, print, photography, cinema, new media, architecture, and design. A part of the collection is exhibited every two years alternately in an 18,500-square-metre (199,000 sq ft) space divided between two floors, one for modern art (from 1905 to 1960, on the 5th floor), the other for contemporary art (from 1960, on the 4th floor), and 5 exhibition halls, on a total of 28,000 m2 (300,000 sq ft) within the museum. The Atelier Brancusi is located in its own building adjacent to the Centre Pompidou.[2]
The works displayed in the museum often change in order to show to the public the variety and depth of the collection. Many major temporary exhibitions of modern and contemporary art have taken place on a separate floor (the 6th) over the years, among them many one-person exhibitions. Since 2010, the museum has also displayed unique, temporary exhibitions in its provincial branch, the Centre Pompidou-Metz, in a 10,000-square-metre (110,000 sq ft) space divided between 3 galleries and since 2011, in a small mobile museum touring the province.
Many styles of modern art, including Fauvism, Expressionism, Cubism, Dada, Abstract art, Surrealism are represented with works by Matisse, André Derain, Maurice de Vlaminck, Raoul Dufy, Albert Marquet, Le Douanier Rousseau, Paul Signac, Georges Braque, Pablo Picasso, Jean Metzinger, Albert Gleizes, Fernand Léger, Juan Gris, Frida Kahlo, Ernst Ludwig Kirchner, August Macke, Alexej von Jawlensky, Emil Nolde, Oskar Kokoschka, Otto Dix, George Grosz, Kurt Schwitters, Marcel Duchamp, Francis Picabia, Carlo Carrà, Umberto Boccioni, Giacomo Balla, Gino Severini, Marc Chagall, Natalia Goncharova, Mikhail Larionov, Alexander Rodchenko, František Kupka, Piet Mondrian, Theo van Doesburg, Paul Klee, Wassily Kandinsky, Kasimir Malevich, Jacques Villon, Robert Delaunay, Sonia Delaunay, Georges Rouault, Balthus, Max Beckmann, Constantin Brâncuși, Alexander Calder, Chaïm Soutine, Amedeo Modigliani, Kees van Dongen, Jean Arp, Giorgio de Chirico, André Breton, Magritte, Max Ernst, Joan Miró, Man Ray, Alberto Giacometti, René Iché, Nicolas de Staël, André Masson, Yves Tanguy, Jean Tinguely, Simon Hantaï, Yves Klein, Jackson Pollock, Mark Rothko, Barnett Newman, Willem de Kooning, and Francis Bacon.
Pop Art, Nouveau Réalisme, Conceptual art and other tendencies or groups are represented with works by Andy Warhol, Richard Hamilton, Rauschenberg, Dan Flavin, Eduardo Arroyo, Dan Graham, Daniel Buren, George Brecht, Arman, César, Bill Viola, Anish Kapoor, Wim Delvoye, Yves Klein, Niki de Saint-Phalle, Yaacov Agam, Vasarely, John Cage, Cindy Sherman, Dieter Roth, Beuys, Roy Lichtenstein, Burhan Dogancay, Dubuffet, Nam June Paik, Wolf Vostell, Gilbert & George, David Hockney and Louise Bourgeois.
Works of architecture and design include Philippe Starck, Jean Nouvel, and Dominique Perrault.
![]()
Designed as an “evolving spatial diagram” by architects Renzo Piano and Richard Rogers, the architecture of the Centre Pompidou boasts a series of technical characteristics that make it unique in the world – the inspiration, even the prototype, of a new generation of museums and cultural centres. It is distinctive firstly in the way it frees up the space inside, with each floor extending through the building entirely uninterrupted by load-bearing structures. The whole of each 7 500 m2 floor is thus available for the display of works or other activities, and can be divided up and reorganised at will, ensuring maximum flexibility. With its use of steel (15 000 tons) and glass (11 000 m²) and the externalisation of its load-bearing structure together with circulation and services, it was a truly pioneering building for its time, an heir to the great iron buildings of the Industrial Age. In many ways futuristic, the Centre Pompidou is heir to the architectural utopias of the 1960s, exemplified in the work of Archigram and Superstudio. Its innovative, even revolutionary character has made the Centre Pompidou one of the most emblematic buildings of the 20th century.
Click Refresh to view slider
View of the Musée d’Orsay.
Collections : French and European art from 1848 to 1914
Number of objects : 79,470 of which 5,765 on deposit – 4,000 works permanently presented
Architect : Gae Aulenti
Location : 62, rue de Lille, 75007 Paris
The Musée d’Orsay is a national museum inaugurated in 1986, located in the 7th arrondissement of Paris along the left bank of the Seine. It is installed in the former Orsay train station, built by Victor Laloux from 1898 to 1900 and refitted as a museum by decision of the President of the Republic Valéry Giscard d’Estaing. The collections present Western art from 1848 to 1914, in all its diversity: painting, sculpture, decorative arts, graphic art, photography, architecture, etc. It is one of the largest museums in Europe.
The museum has the largest collection of Impressionist and Post-Impressionist paintings in the world, with nearly 1,100 paintings 2 in total of more than 3,450, and can be seen as masterpieces of painting and sculpture such as Edouard Manet’s Breakfast on the Grass and Olympia, a proof of Degas’s Fourteen-year-old Little Dancer, The Origin of the World, A Burial in Ornans, The Painter’s Studio in Courbet, Card players Cezanne or five paintings of the series of Cathedrals Rouen Monet and Mill Ball Galette Renoir.
Temporary monographic or thematic exhibitions periodically cover the work of an artist, a current or a question in the history of art. An auditorium hosts diverse events, concerts, cinema, shadow theater, conferences and seminars and shows specifically for a young audience.
Click Refresh to view slides
The history of the Musée d’Orsay, of its building is quite unusual. In the centre of Paris on the banks of the Seine, opposite the Tuileries Gardens, the museum was installed in the former Orsay railway station, built for the Universal Exhibition of 1900. So the building itself could be seen as the first “work of art” in the Musee d’Orsay, which displays collections of art from the period 1848 to 1914.

On the eve of the 1900 World Fair, the French government ceded the land to the Orleans railroad company, who, disadvantaged by the remote location of the Gare d’Austerlitz, planned to build a more central terminus station on the site of the ruined Palais d’Orsay. In 1897, the company consulted three architects: Lucien Magne, Emile Bénard and Victor Laloux. The project was a challenging one due to the vicinity of the Louvre and the Palais de la Légion d’honneur: the new station needed to be perfectly integrated into its elegant surroundings. Victor Laloux, who had just completed the Hôtel de Ville in Tours, was chosen as winner of the competition in 1898.![]()
The Gare d’Orsay then successively served different purposes : it was used as a mailing centre for sending packages to prisoners of war during the Second World War, then those same prisoners were welcomed there on their returning home after the Liberation. It was then used as a set for several films, such as Kafka’s The Trial adapted by Orson Welles, and as a haven for the Renaud-Barrault Theatre Company and for auctioneers, while the Hôtel Drouot was being rebuilt.
The hotel closed its doors on January 1st, 1973, not without having played a historic role: the General de Gaulle held the press conference announcing his return to power in its ballroom (the Salle des Fêtes).
![]()
In 1975, the Direction des Musées de France already considered installing a new museum in the train station, in which all of the arts from the second half of the 19th century would be represented. The station, threatened with destruction and replacement by a large modern hotel complex, benefitted instead from the revival of interest in nineteenth-century architecture and was listed on the Supplementary Inventory of Historical Monuments on March 8, 1973. The official decision to build the Musée d’Orsay was taken during the interministerial council of October 20, 1977, on President Valéry Giscard d’Estaing’s initiative. The building was classified a Historical Monument in 1978 and a civil commission was created to oversee the construction and organisation of the museum. The President of the Republic, François Mitterrand, inaugurated the new museum on December 1st, 1986, and it opened to the public on December 9th.
Click Refresh to view slides
The museum is located on the site of the Palais d’Orsay, built in 1810 and decorated with frescoes by Théodore Chassériau 3, which in 1840 hosts the State Council on the ground floor and two years later late the Court of Accounts on the first floor. It was burned down in 1871 during the Paris Commune and left in the state of ruins until the construction by Victor Laloux of the station of Orsay, former terminus of the Company of the Railway of Paris in Orleans, to welcome the visitors and foreign delegations from the 1900 World Exhibition.
Its esplanade, to the west, was arranged in 1985 and endowed with numerous statues including the group called Statues of the 6 continents, initially installed on the terrace of the palace of Trocadéro during the world exhibition of 1878 4.
The Musée d’Orsay opened in the converted train station, the. To allow its transformation into a museum of arts of the nineteenth century, according to the will of the President of the Republic Valery Giscard d’Estaing, the building was reconfigured from 1983 to 1986 by architects Renaud Bardon, Pierre Colboc and Jean-Paul Philippon, laureates of an architectural competition organized in 1979, then joined by the Italian interior designer Gae Aulenti.
In the night of during the Nuit Blanche, individuals broke into the museum and seriously damaging a painting by Claude Monet, The Bridge of Argenteuil, dating from 1874, making a tear of 10 cm 5. The painting has been restored since.
Click Refresh to view slides
Inaugurated at the Marsan Pavilion of the Louvre in 1905, the Museum of Decorative Arts was considered in 1879 on the site attributed to the station of Orsay in 1897, which will finally find this museum vocation in 1986. The Gate of Hell of Rodin, whose plaster is visible at the median level – terrace Rodin, was to constitute the monumental entrance.
In 1977, a collection of decorative arts objects from the 1848-1914 period was created at the Musée d’Orsay. Apart from the Charpentier dining room of 1900, reconstituted in a clean space ( period room ), furniture and objects are shown out of context. Consisting of representative works of the production of ceramics, glassware, jewelery and furniture, this collection testifies to the mutation of the production of objets d’art related to the industrial revolution, that of the fine arts applied to the industry. It has some masterpieces long unknown or poorly considered and also exhibits evidence of the exceptional quality of luxury industries of that time. The museum division of the collections of objects of art distinguishes by their location those produced under the Second Empire (1852-1870) and in the first two decades of the Third Republic (1870-1940) of those corresponding to the Art Nouveau style (to from 1890).
The Musée d’Orsay exhibits and preserves the largest collection of Impressionist paintings (more than 480 paintings) 6 and post-Impressionists (more than 600 paintings 2 cloisonnists, neo-Impressionists, Symbolists, Nabis …) at world, as well as outstanding paintings of the Barbizon School, realistic, naturalistic, orientalist and academic, including foreign schools. Nearly 5,200 paintings make up the collection, but a large number of works, including some 1,720 paintings , including about 100 non-localized or destroyed, are deposited in public buildings or provincial museums, such as 20 of the 95 paintings 7 of Vuillard, 21 of Bonnard’s 87 paintings , 19 of 83 paintings by Renoir or 33 of Maurice Denis’s 79 paintings.
This non-exhaustive list lists the main painters represented at the Musée d’Orsay with the number of their works painted in the collections as well as the title of their main achievements, whether or not they are exhibited, given the regular renewal of the clashes. This list also mentions pastels, for the artists concerned: indeed, although not belonging to the painting department, a certain number of pastels are exhibited in the permanent collections of the museum.
Other artists
William Bouguereau,
Dante and Virgil (1850).
Gustave Courbet,
The Painter’s Workshop (1855).
Jean-François Millet,
Gleaners (1857).
Edouard Manet,
Olympia, (1863).
Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec,
The bed (around 1892).
Paul Gauguin,
Arearea or Joyeusetés (1892).
Paul Cézanne,
Still life with apples and oranges (1895 – 1900).
Paul Signac,
Entrance to the port of La Rochelle (1921).
The photography collection of the Musée d’Orsay was entirely made from scratch from the late 1970s when the project of transforming the former Orsay railway station into a museum of the XIX th century has been taken, no museum fine arts in France does not yet have a section dedicated to photography. It became apparent that this major invention of the XIX th century was to take place in the future museum 9. The works of many photographers are preserved in the collections of the Musée d’Orsay, including those of Hippolyte Bayard, Édouard Baldus, Christian Bérard, Louis-Jacques-Mande Daguerre, Felix Nadar, Nicephore Niepce, Constant Alexander Fam …

Wikipedia
The Louvre or the Louvre Museum (French: Musée du Louvre), is the world’s largest art museum and a historic monument in Paris, France. A central landmark of the city, it is located on the Right Bank of the Seine in the city’s 1st arrondissement (district or ward). Approximately 38,000 objects from prehistory to the 21st century are exhibited over an area of 72,735 square metres (782,910 square feet). In 2017, the Louvre was the world’s most visited art museum, receiving 8.1 million visitors.
The museum is housed in the Louvre Palace, originally built as a fortress in the late 12th to 13th century under Philip II. Remnants of the fortress are visible in the basement of the museum. Due to the urban expansion of the city, the fortress eventually lost its defensive function and, in 1546, was converted by Francis I into the main residence of the French Kings. The building was extended many times to form the present Louvre Palace. In 1682, Louis XIV chose the Palace of Versailles for his household, leaving the Louvre primarily as a place to display the royal collection, including, from 1692, a collection of ancient Greek and Roman sculpture. In 1692, the building was occupied by the Académie des Inscriptions et Belles Lettres and the Académie Royale de Peinture et de Sculpture, which in 1699 held the first of a series of salons. The Académie remained at the Louvre for 100 years. During the French Revolution, the National Assembly decreed that the Louvre should be used as a museum to display the nation’s masterpieces.
The museum opened on 10 August 1793 with an exhibition of 537 paintings, the majority of the works being royal and confiscated church property. Because of structural problems with the building, the museum was closed in 1796 until 1801. The collection was increased under Napoleon and the museum was renamed Musée Napoléon, but after Napoleon’s abdication many works seized by his armies were returned to their original owners. The collection was further increased during the reigns of Louis XVIII and Charles X, and during the Second French Empire the museum gained 20,000 pieces. Holdings have grown steadily through donations and bequests since the Third Republic. The collection is divided among eight curatorial departments: Egyptian Antiquities; Near Eastern Antiquities; Greek, Etruscan and Roman Antiquities; Islamic Art; Sculpture; Decorative Arts; Paintings; Prints and Drawings.
Click Refresh to view slides