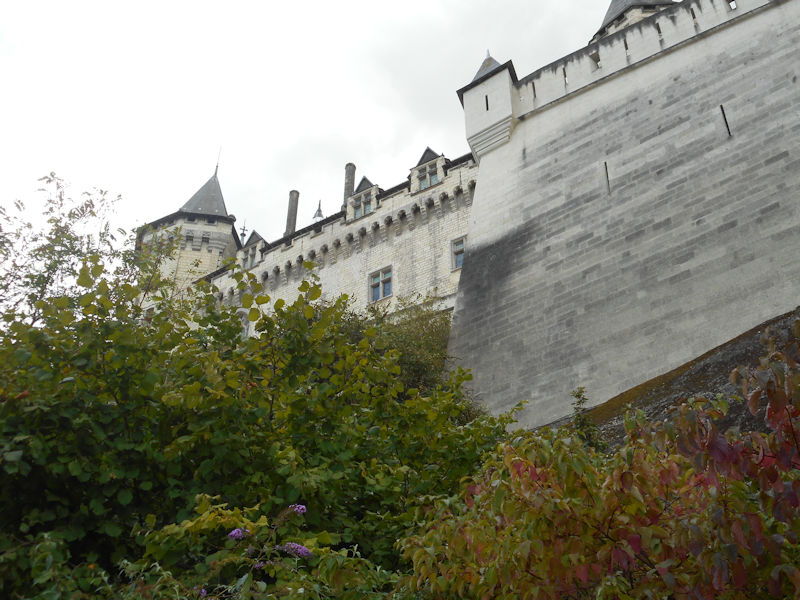
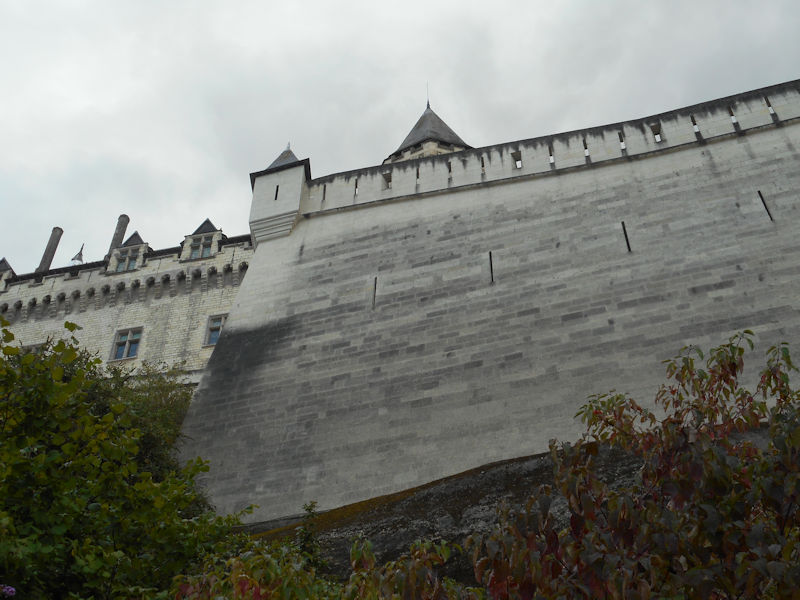
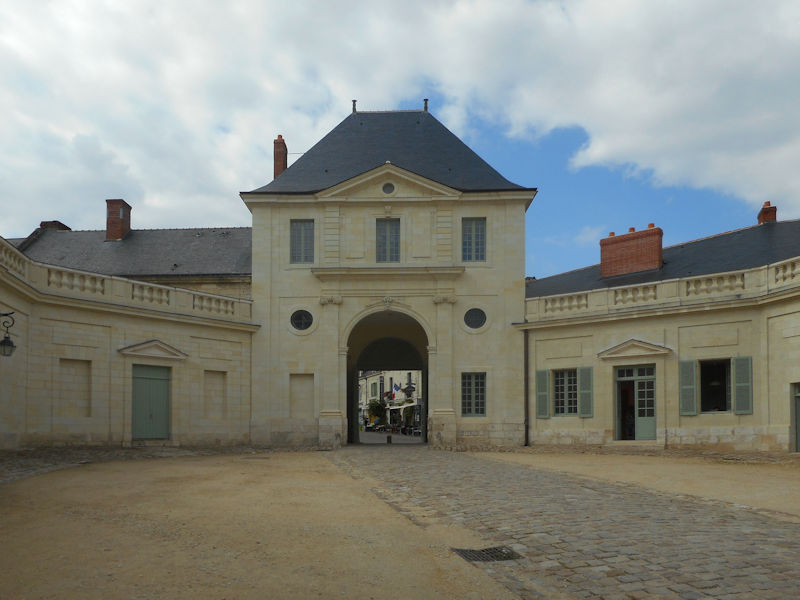
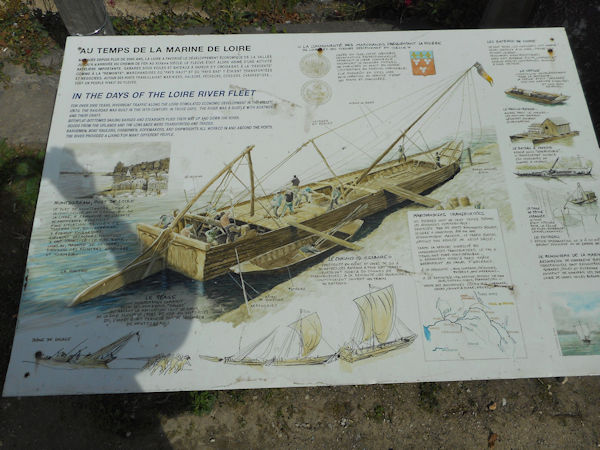
HISTORY
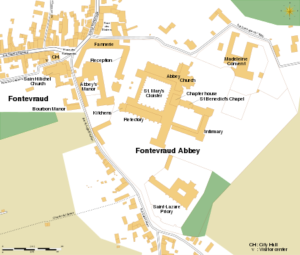

The following is from Wikipedia
Founder
Robert of Arbrissel had served as the Archpriest of the Diocese of Rennes, carrying out the reformist agenda of its bishop. When the bishop died in 1095, Robert was driven out of the diocese due to the hostility of the local clergy. He then became a hermit in the forest of Craon, where he practiced a life of severe penance, together with a number of other men who went on to found major monastic institutions. His eloquence and asceticism attracted many followers, for whom in 1096 he founded a monastery of canons regular at La Roë, of which he was the first abbot. In that same year Pope Urban II summoned him to Angers and appointed him an apostolic missionary, authorizing him to preach anywhere. His preaching drew large crowds of devoted followers, both men and women, even lepers. As a result, many men wished to embrace the religious life, whom he sent to his abbey. When the canons of that house objected to the influx of candidates of lower social states, he resigned his office and left the community.
Fontevraud
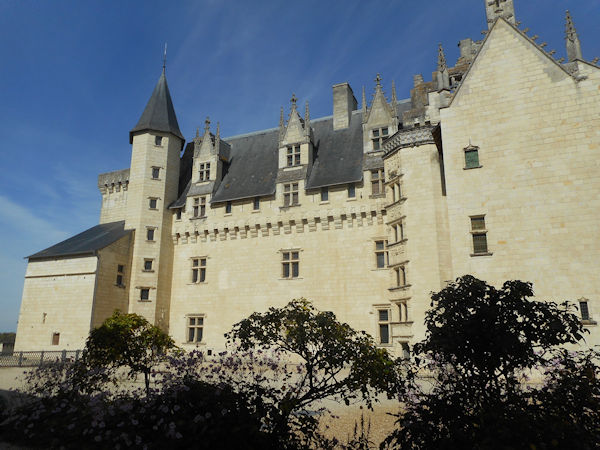
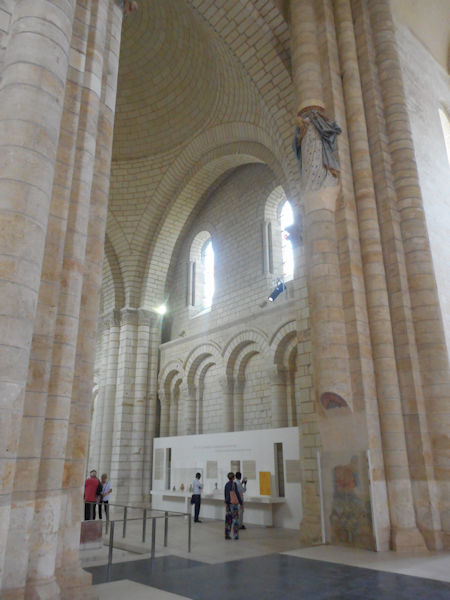
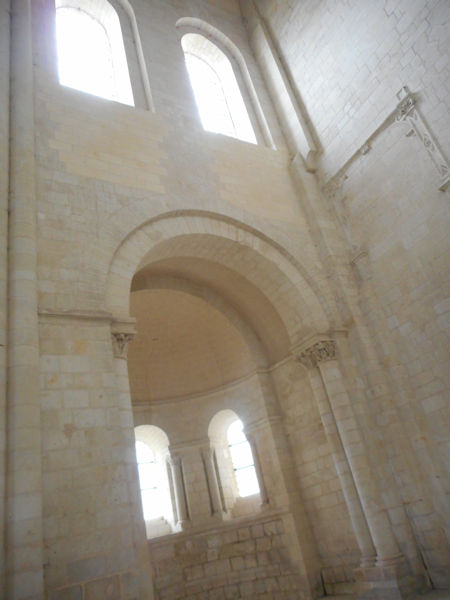
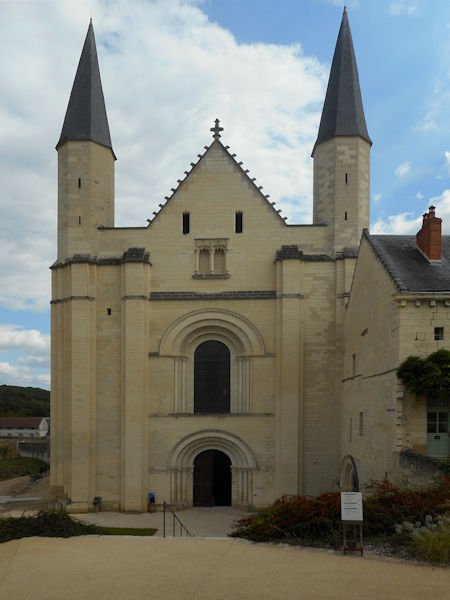
Around 1100 Robert and his followers settled in a valley called Fons Ebraldi where he established a monastic community. Initially the men and women lived together in the same house, in an ancient ascetic practice called Syneisaktism. This practice had been widely condemned by Church authorities, however, and under pressure the community soon segregated according to gender, with the monks living in small priories where they lived in community in service to the nuns and under their rule. They were recognized as a religious community in 1106, both by the Bishop of Angers and by Pope Paschal II. Robert, who soon resumed his life of itinerant preaching, appointed Hersende of Champagné to lead the community. Later her assistant, Petronilla of Chemillé, was elected as the first abbess in 1115.
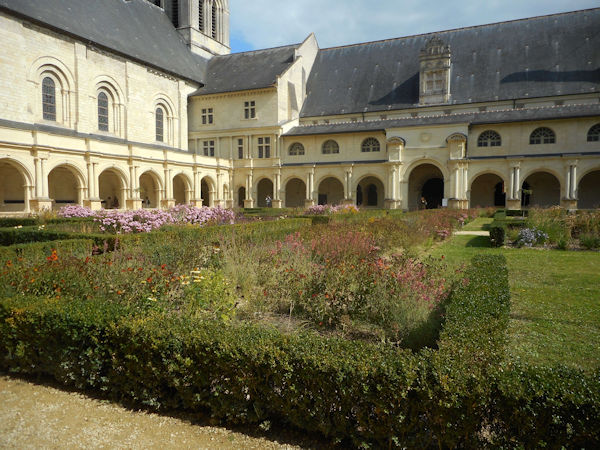
Robert wrote a brief Rule of Life for the community, based upon the Rule of St. Benedict. Unlike the other monastic orders characterized by double monasteries, the monks and nuns of the Order of Fontevrault followed the same Rule. In his Rule, Robert dealt with four principal points: silence, good works, food and clothing, encouraging the utmost in simplicity of life and dress. He directed that the abbess should never be chosen from among those who had been brought up at Fontevrault, but that she should be someone who had had experience of the world (de conversis sororibus). This latter injunction was observed only in the case of the first two abbesses and was canceled by Pope Innocent III in 1201. At the time of Robert’s death in 1117, there were about 3,000 nuns in the community.
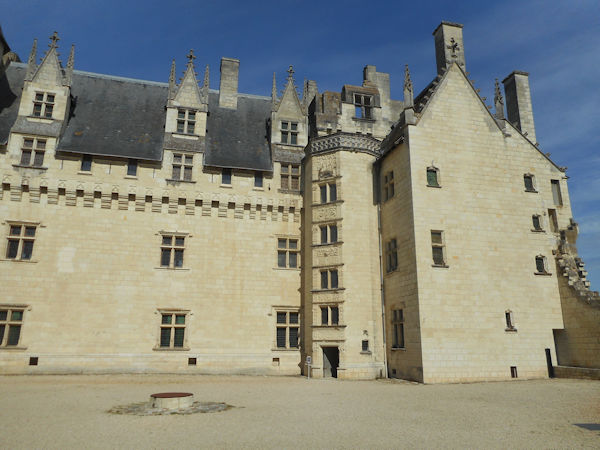
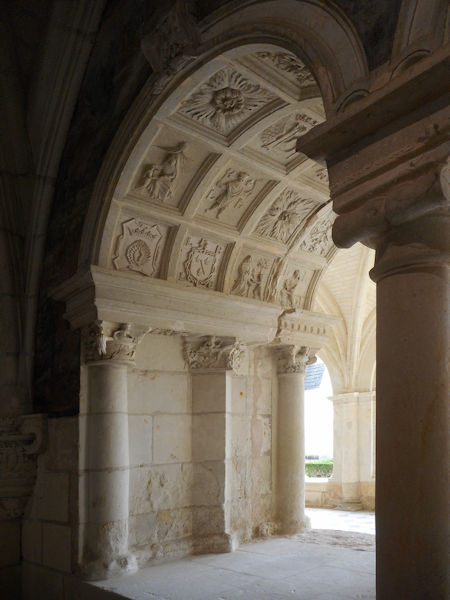
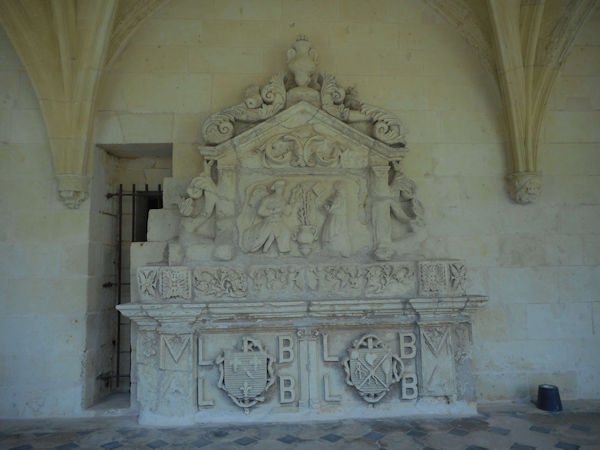
In the early years the Plantagenets were great benefactors of the abbey and while Isabella d’Anjou was the abbess, King Henry II’s widow, Eleanor of Aquitaine, made the abbey her place of residence. Abbess Louise de Bourbon left her crest on many of the alterations to the abbey building which she made during her term of office.

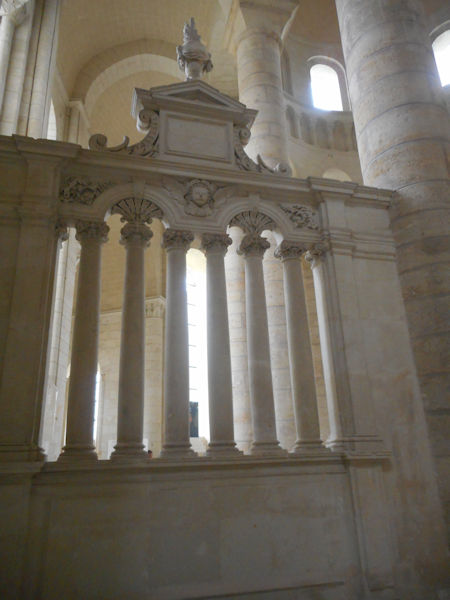
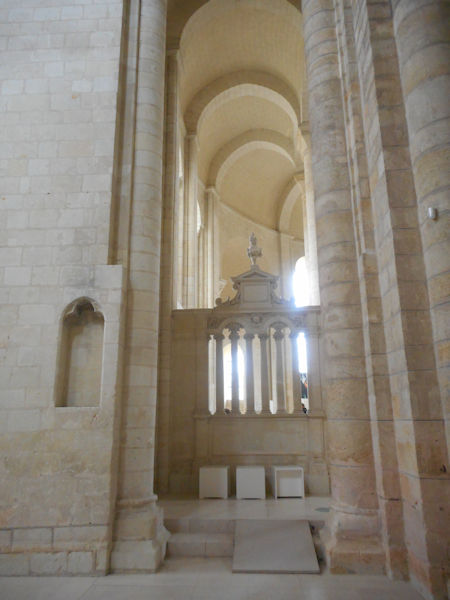
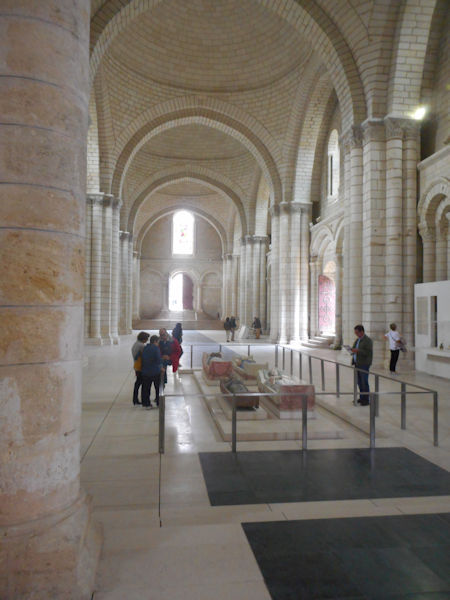
Tomb of Richard I of England (front) and Isabella of Angoulême (back)
Decline
With the passing of the Plantagenet dynasty, however, Fontevrault and her dependencies began to fall upon hard times. At the end of the 12th century, the Abbess of Fontevrault, Matilda of Flanders (1189-1194), complained about the extreme poverty which the abbey was suffering. As a result, in 1247 the nuns were permitted to receive inheritances to provide income for their needs, contrary to monastic custom. The fragile economic basis of the Order was exacerbated by the devastation of the Hundred Years War, which lasted throughout the 14th century. A canonical visitation of fifty of the priories of the Order in 1460 showed most of them to be barely occupied, if not abandoned.

Abbess Louise Françoise de Rochechouart (1664-1742)

Abbess Gabrielle de Rochechouart (1645-1704)
Suppression
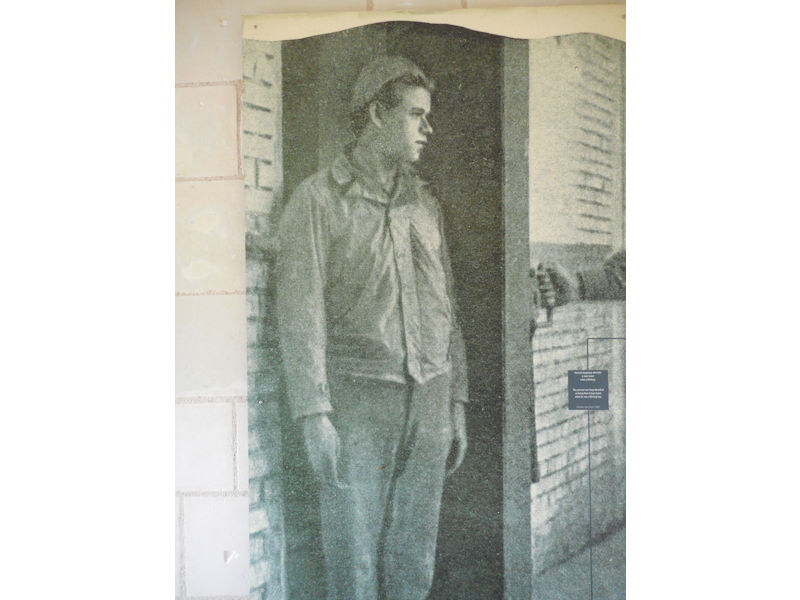
The Order was dispersed during the French Revolution. In November 1789, all property of the Catholic Church was declared to be the property of the nation. On 17 August 1792, a Revolutionary decree ordered evacuation of all monasteries, to be completed by 1 October 1792. At that time, there were still some 200 nuns and a small community of monks in residence at Fontevraud. The last abbess, Julie Sophie Charlotte de Pardaillan d’Antin, is said to have died in poverty in Paris in 1797. The abbey later became a prison from 1804 to 1963, when it was given to the French Ministry of Culture.
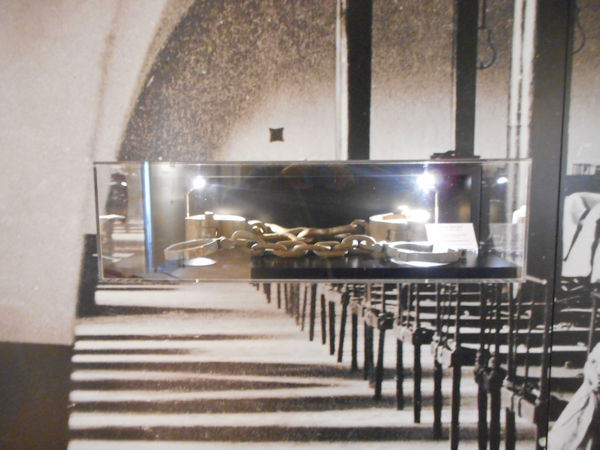
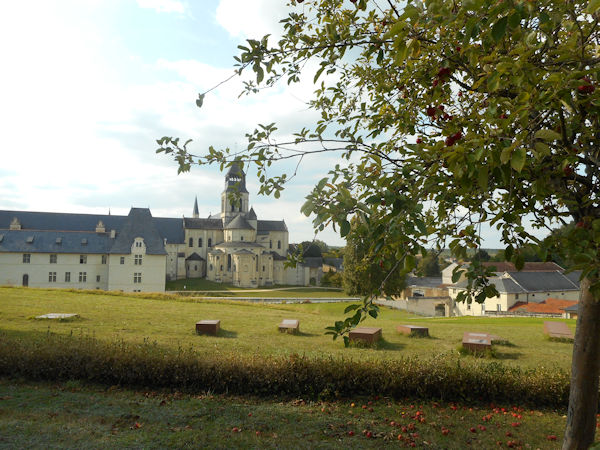
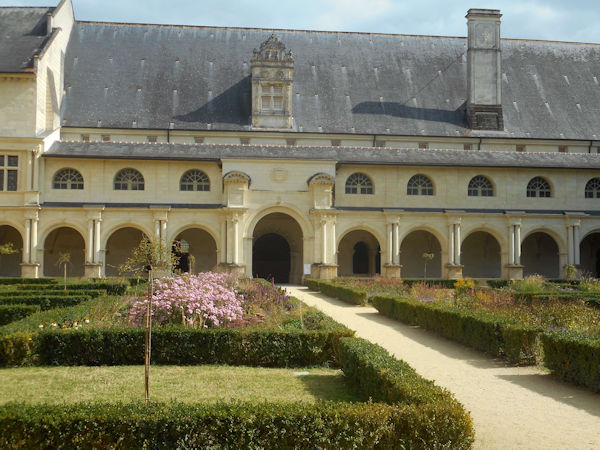
The projected prison in the former abbey was planned to hold 1,000 prisoners, and required major changes, including new barracks in addition to the transformation of monastic buildings into dormitories, workshops, and common areas. Prisoners–-men, women and children-–began arriving in 1814. Eventually, it held some 2,000 prisoners, earning the prison the reputation of being the “toughest in France after Clairvaux”. Political prisoners experienced the harshest conditions: some French Resistance prisoners were shot there under the Vichy Government. Following the closing of the prison came a major restoration, and opening to the public in 1985, with completion of the abbey church’s restoration in 2006 under architect Lucien Magne.
CLICK Refresh FOR SLIDES