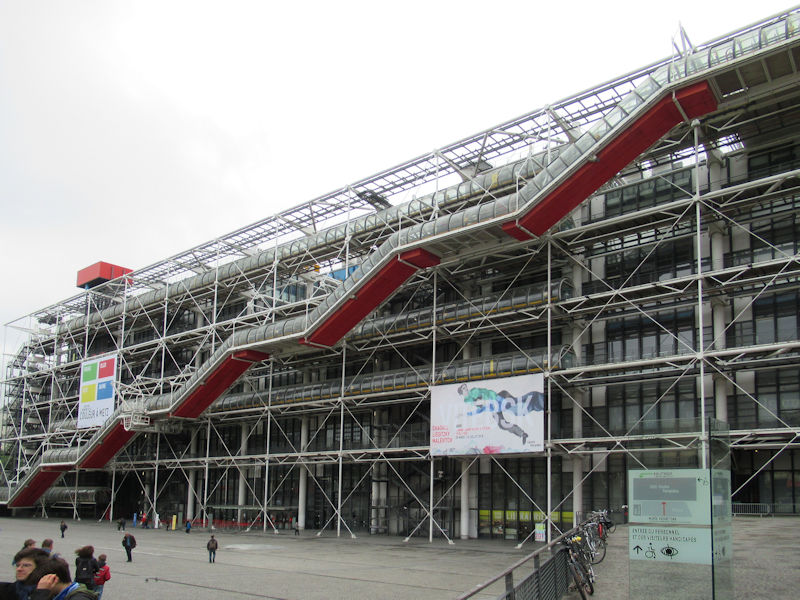
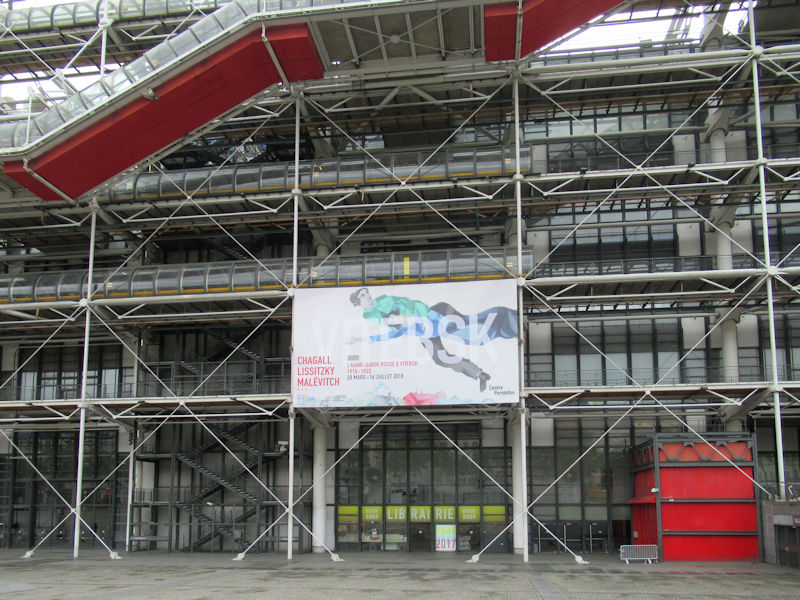
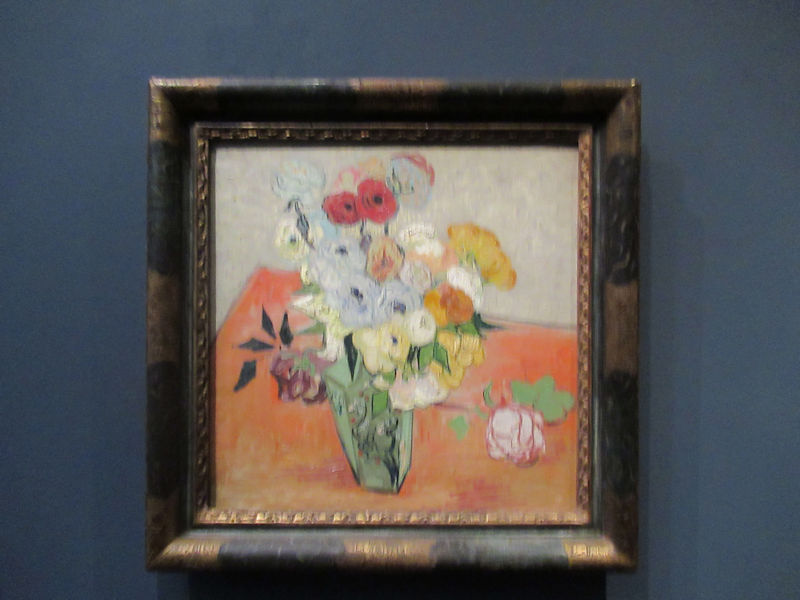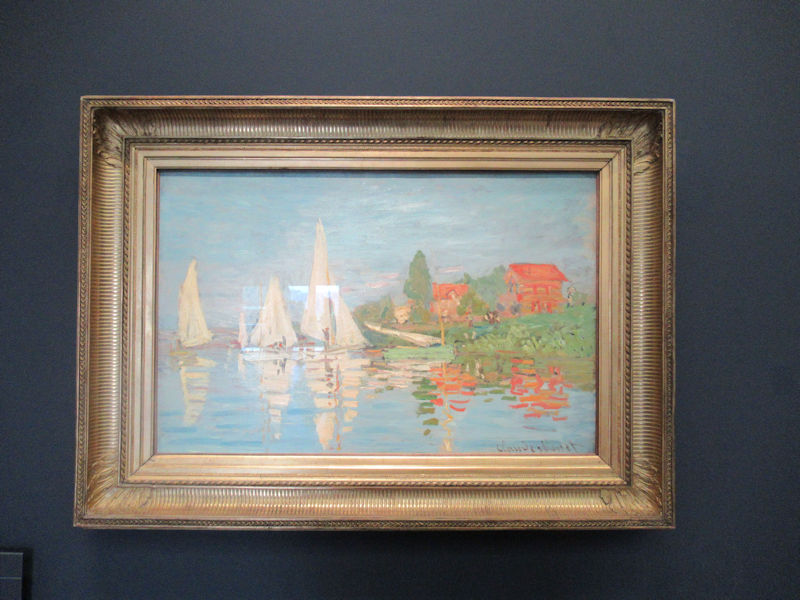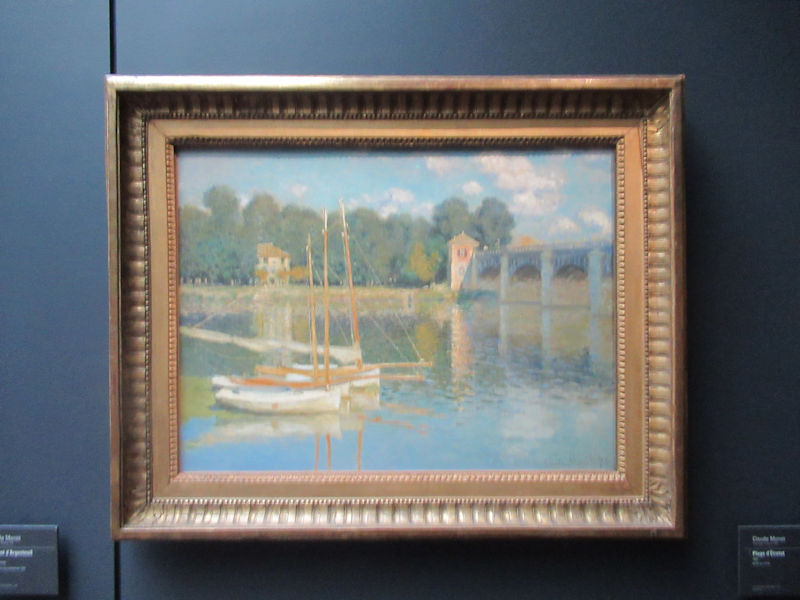Centre Georges-Pompidou from Notre-Dame de Paris, 2011
The Musée National d’Art Moderne National Museum of Modern Art) is the national museum for modern art of France. It is located in Paris and is housed in the Centre Pompidou in the 4th arrondissement of the city. It is among the most visited art museums in the world and one of the largest for modern and contemporary art.
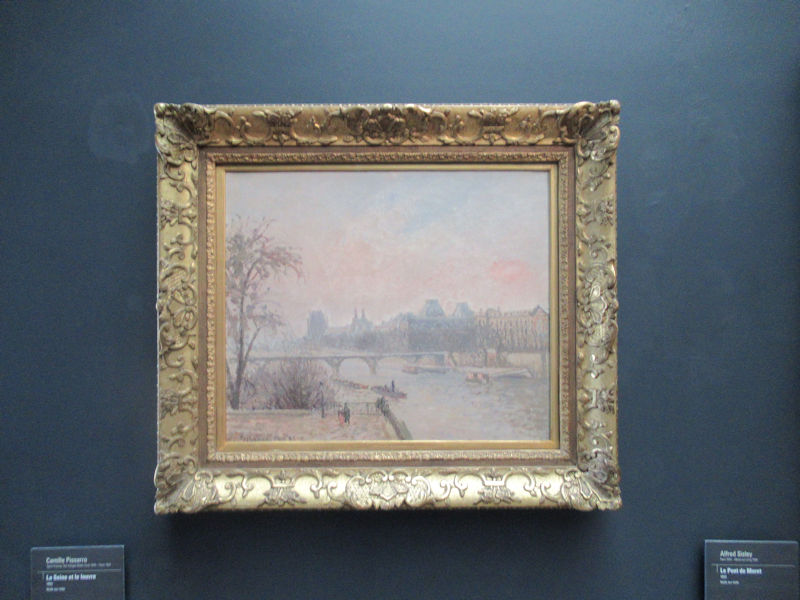
In 1937, the Musée National d’Art Moderne succeeded the Musée du Luxembourg, established in 1818 by King Louis XVIII as the first museum of contemporary art created in Europe, devoted to living artists whose work was due to join the Louvre 10 years after their death. Imagined as early as 1929 by Auguste Perret to replace the old Palais du Trocadero, the construction of a museum of modern art was officially decided in 1934 in the western wing of the Palais de Tokyo. Completed in 1937 for that year’s International Exhibition of Arts and Technology, it was temporarily used for another purpose, since the exhibition of national and foreign art indépendant was then preferably held in the Petit Palais and the Musée du Jeu de Paume. Although due to open in 1939, construction was eventually interrupted by the war; following the nomination of its first Chief Conservator in September 1940, the museum partially opened in 1942 with only a third of the collection brought back from some national collection caches hidden in the province. But its real inauguration didn’t take place until 1947, after World War II and the addition of the foreign schools collection of the Musée du Luxembourg, which had been held at the Musée du Jeu de Paume since 1922.
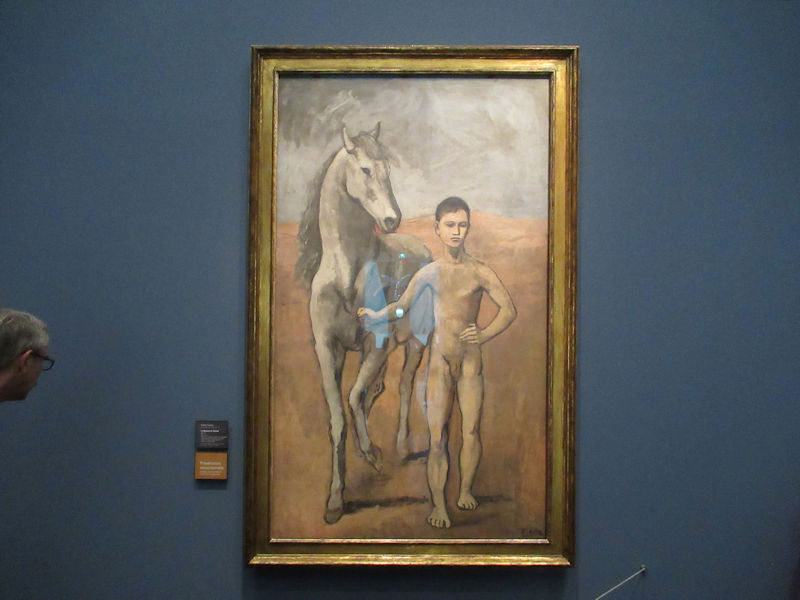
In 1947, then housed in the Palais de Tokyo, its collection was dramatically increased by its first director, Jean Cassou, thanks to his special relationship with many prominent artists or their families, such as Picasso and Braque. With the creation of the Centre Pompidou, the museum moved to its current location in 1977.
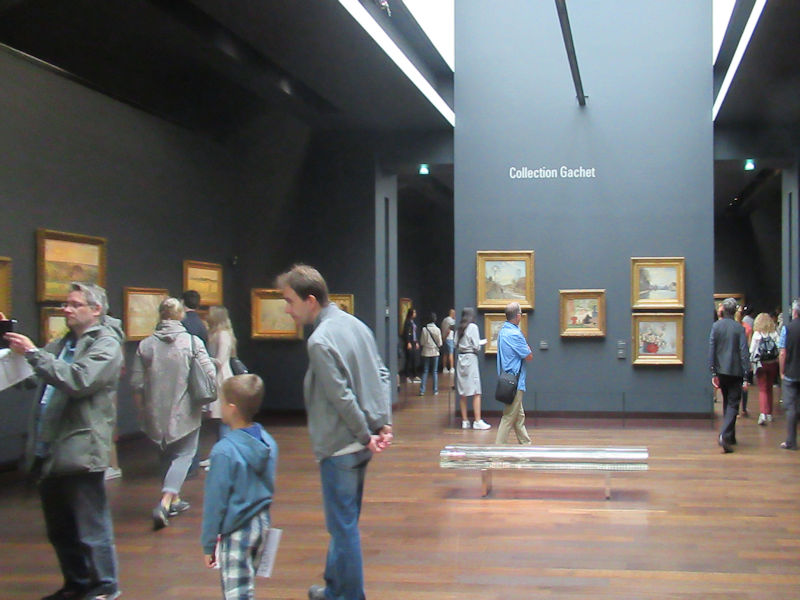
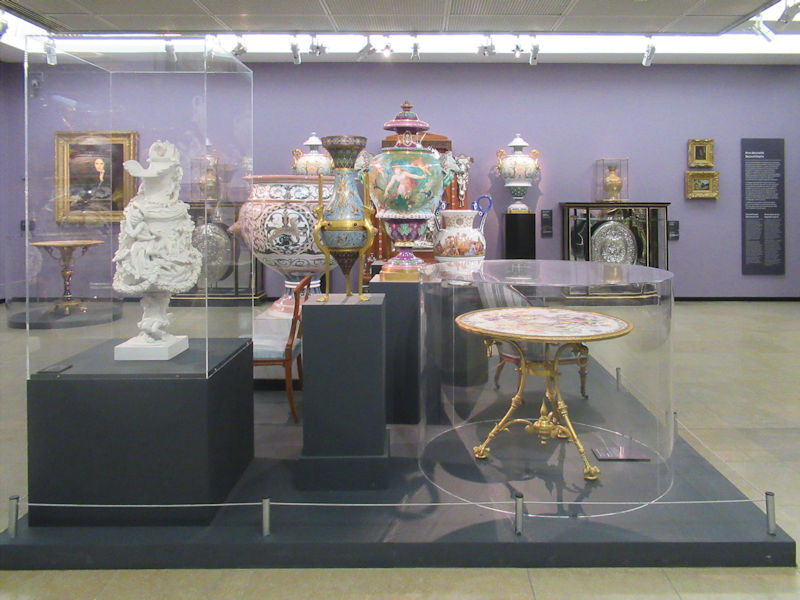
The museum has the second largest collection of modern and contemporary art in the world, after the Museum of Modern Art in New York, with more than 100,000 works of art by 6,400 artists from 90 countries since Fauvism in 1905. These works include painting, sculpture, drawing, print, photography, cinema, new media, architecture, and design. A part of the collection is exhibited every two years alternately in an 18,500-square-metre (199,000 sq ft) space divided between two floors, one for modern art (from 1905 to 1960, on the 5th floor), the other for contemporary art (from 1960, on the 4th floor), and 5 exhibition halls, on a total of 28,000 m2 (300,000 sq ft) within the museum. The Atelier Brancusi is located in its own building adjacent to the Centre Pompidou.[2]
The works displayed in the museum often change in order to show to the public the variety and depth of the collection. Many major temporary exhibitions of modern and contemporary art have taken place on a separate floor (the 6th) over the years, among them many one-person exhibitions. Since 2010, the museum has also displayed unique, temporary exhibitions in its provincial branch, the Centre Pompidou-Metz, in a 10,000-square-metre (110,000 sq ft) space divided between 3 galleries and since 2011, in a small mobile museum touring the province.
Collections
Modern art (1905–1960)
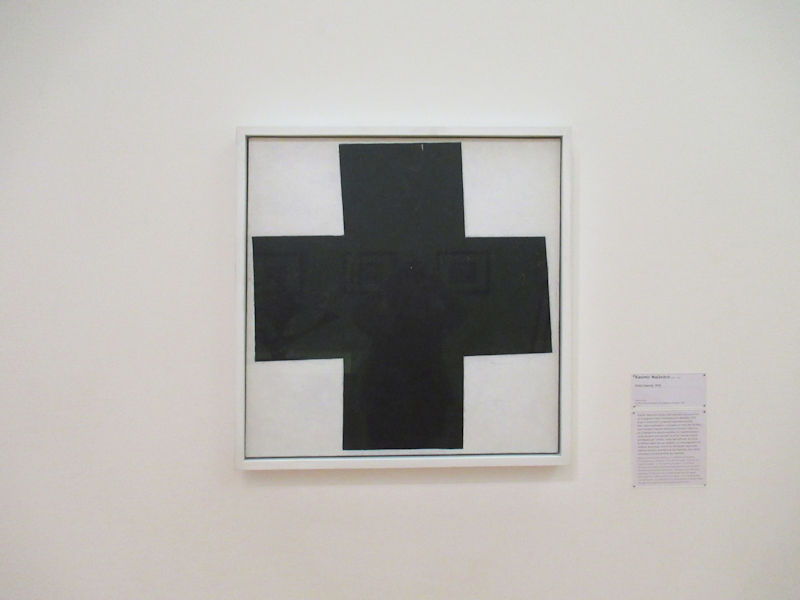
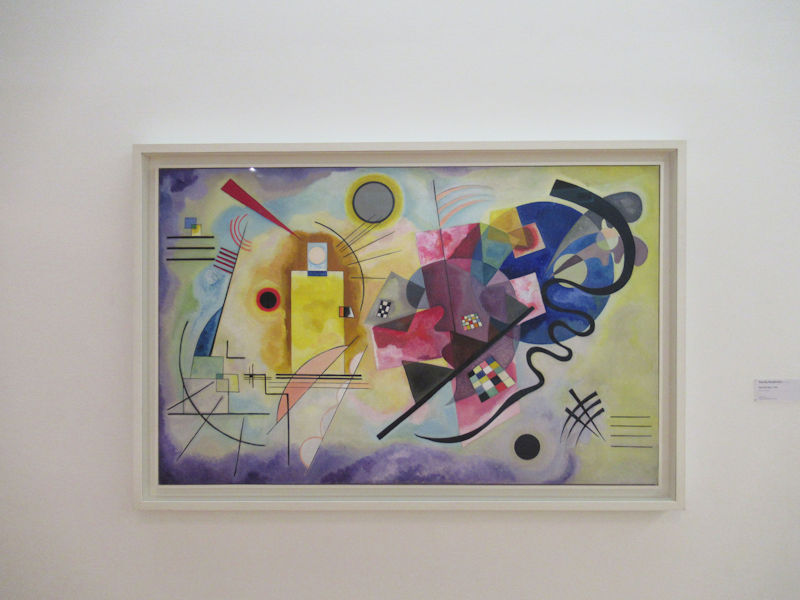
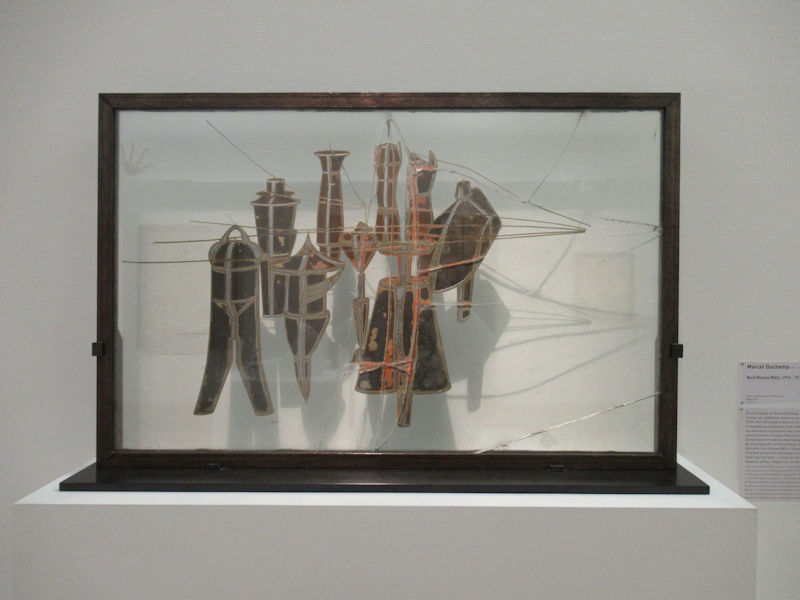
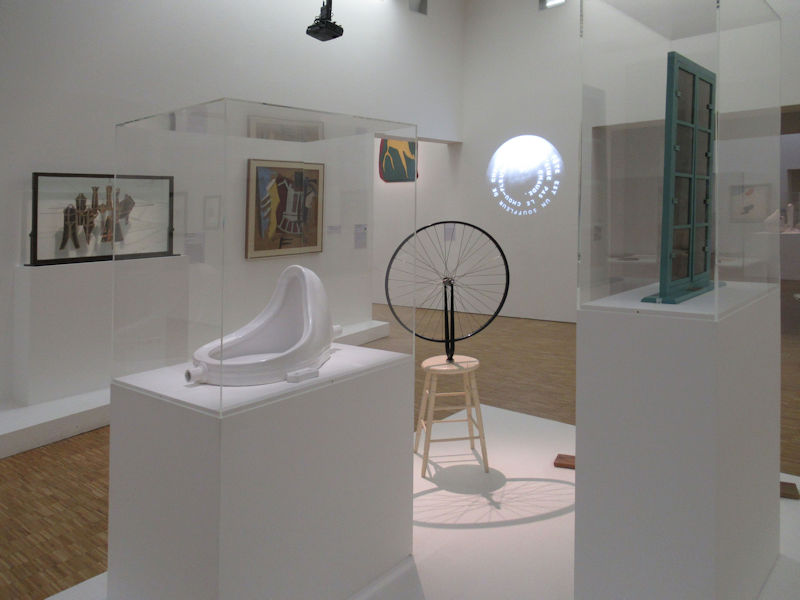
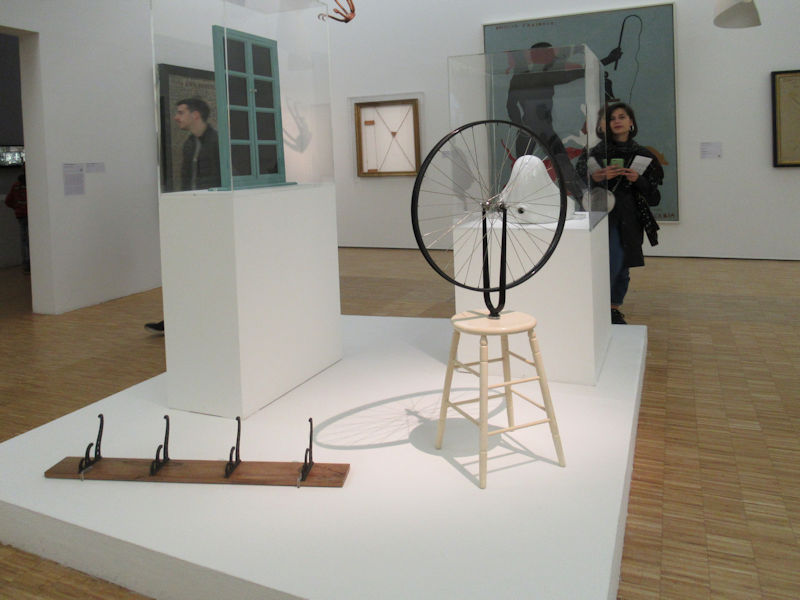
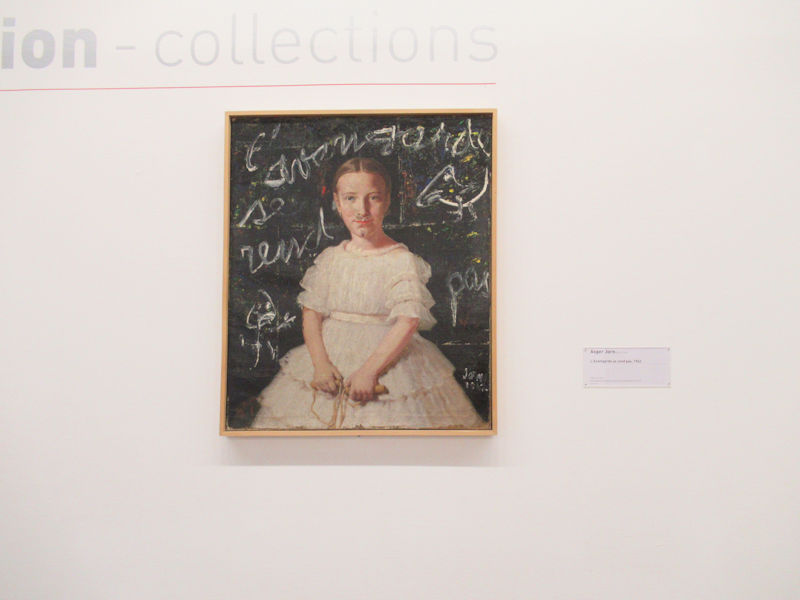
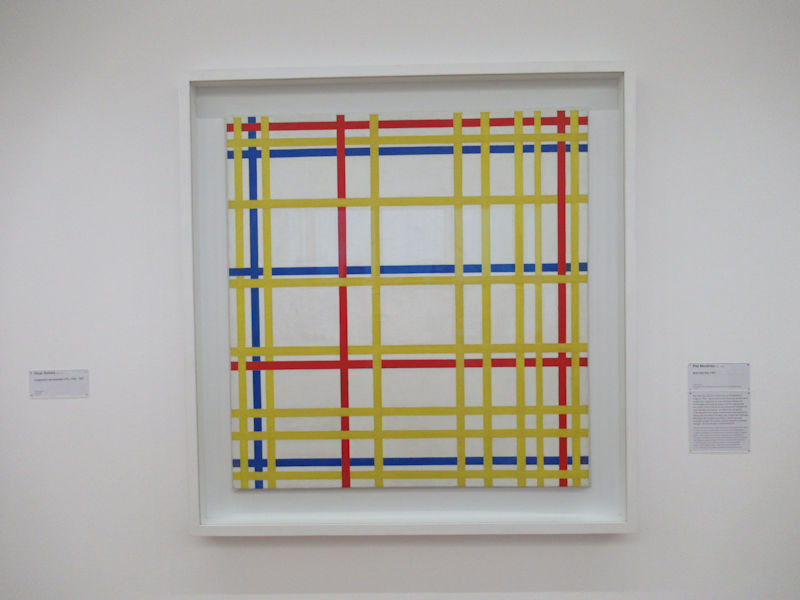
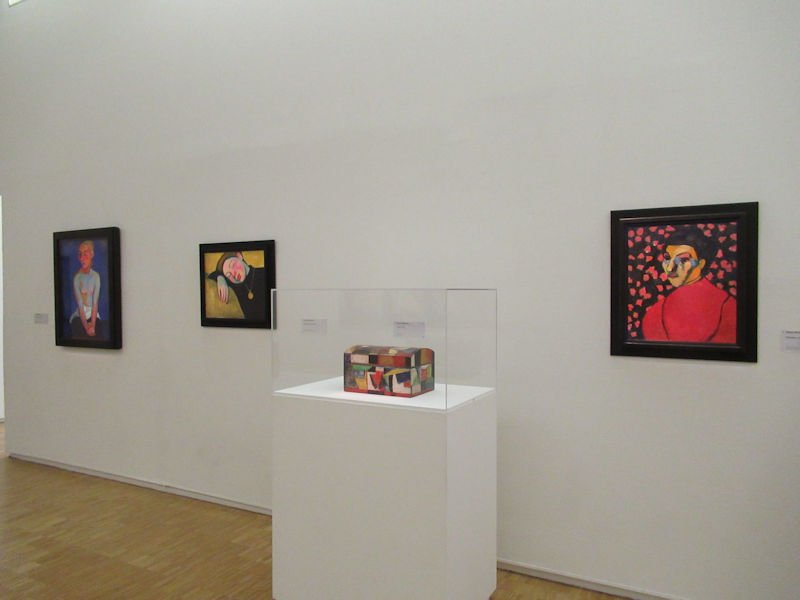
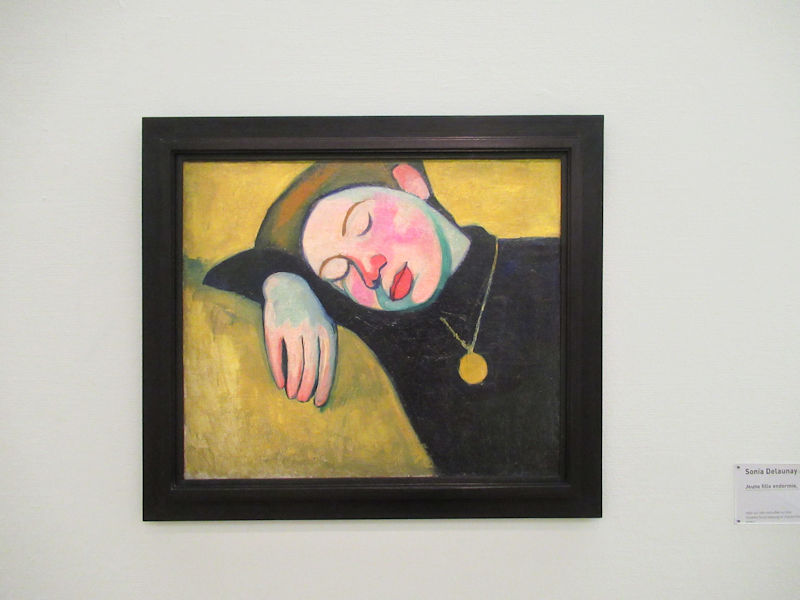
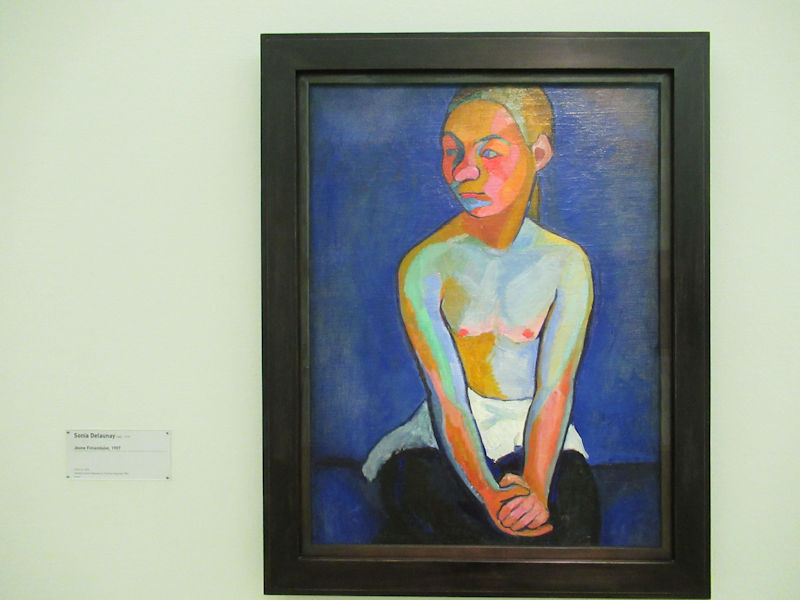
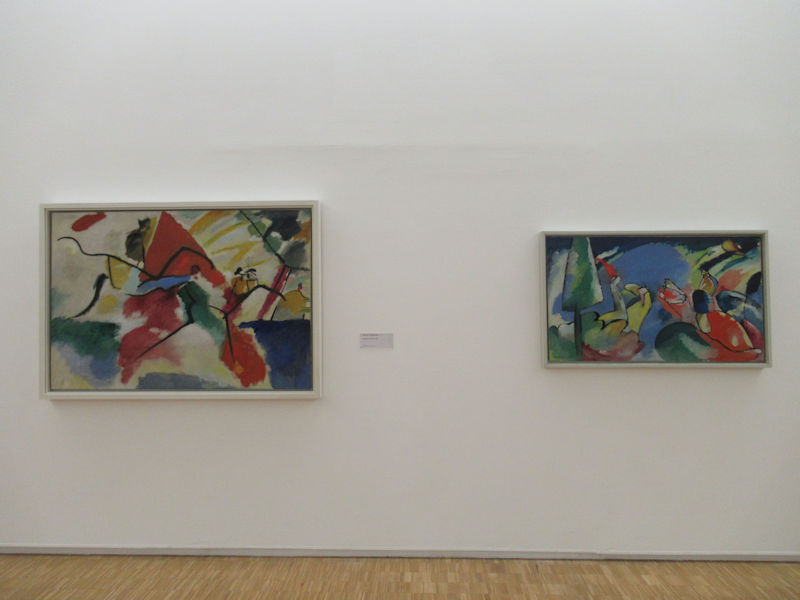
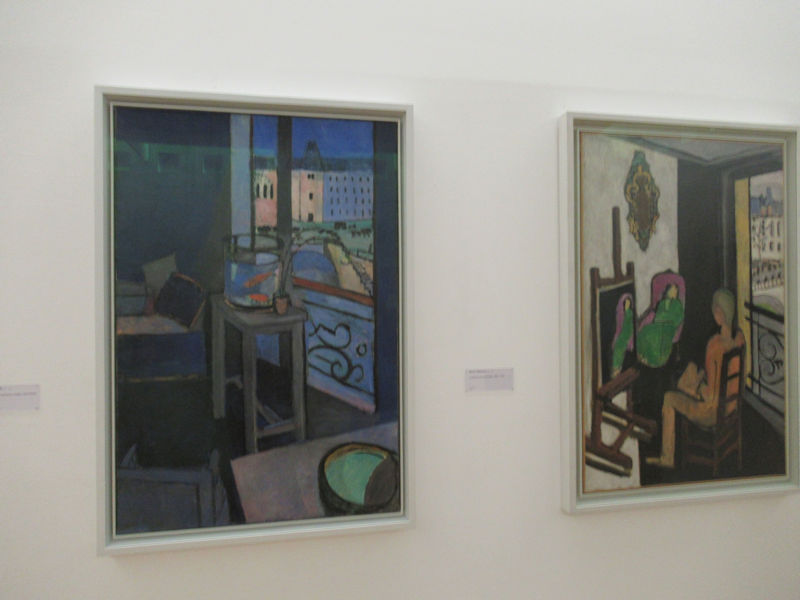
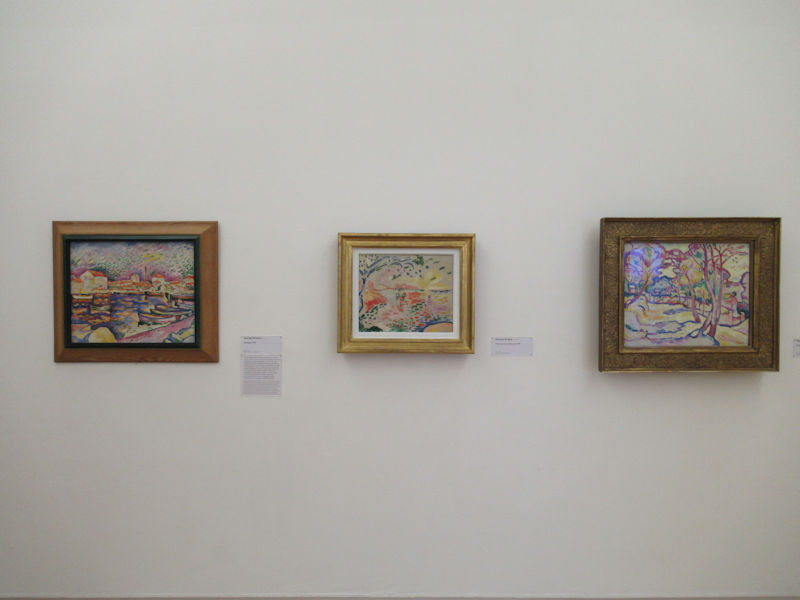
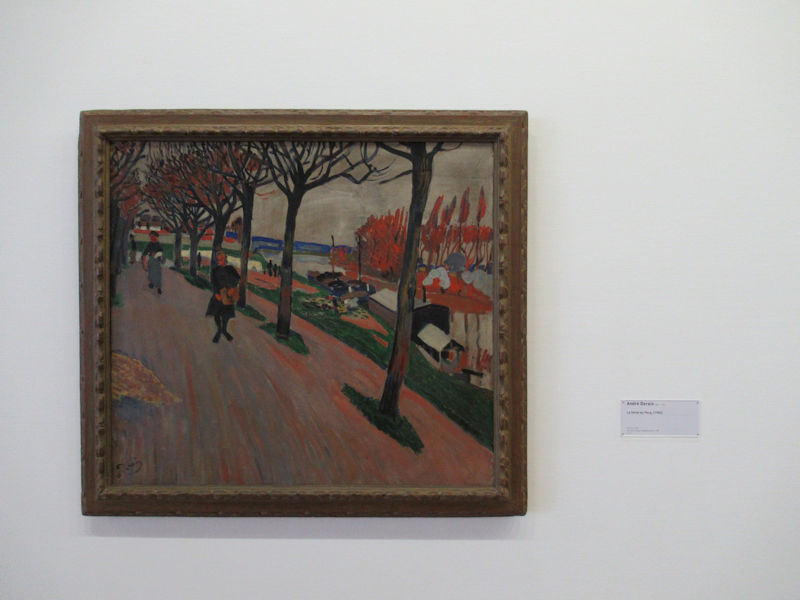
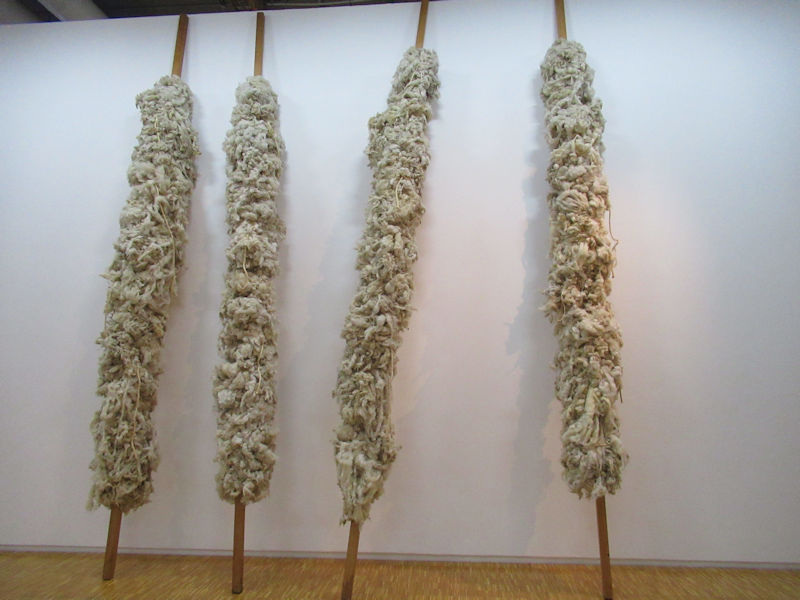
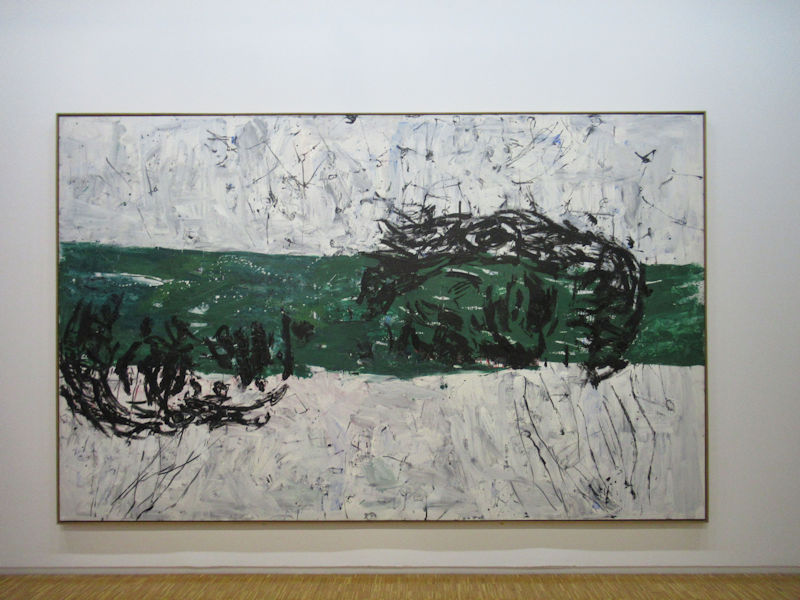
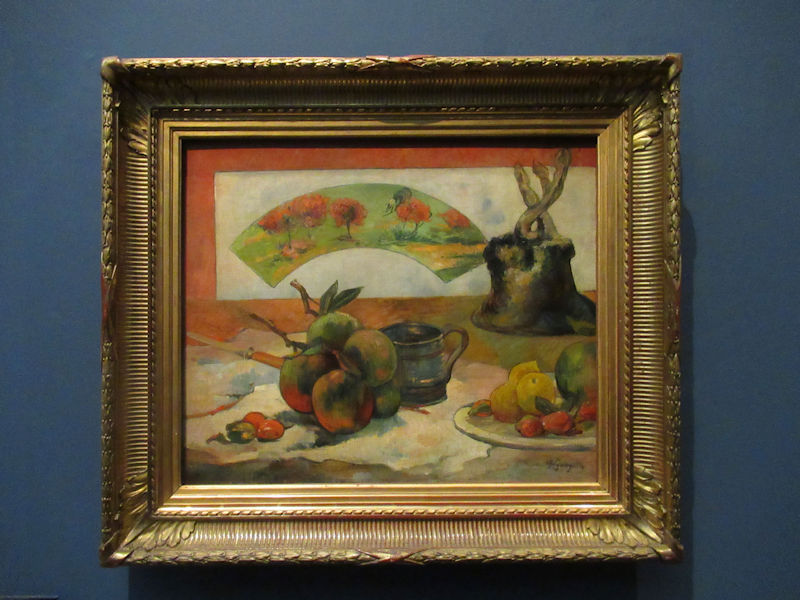
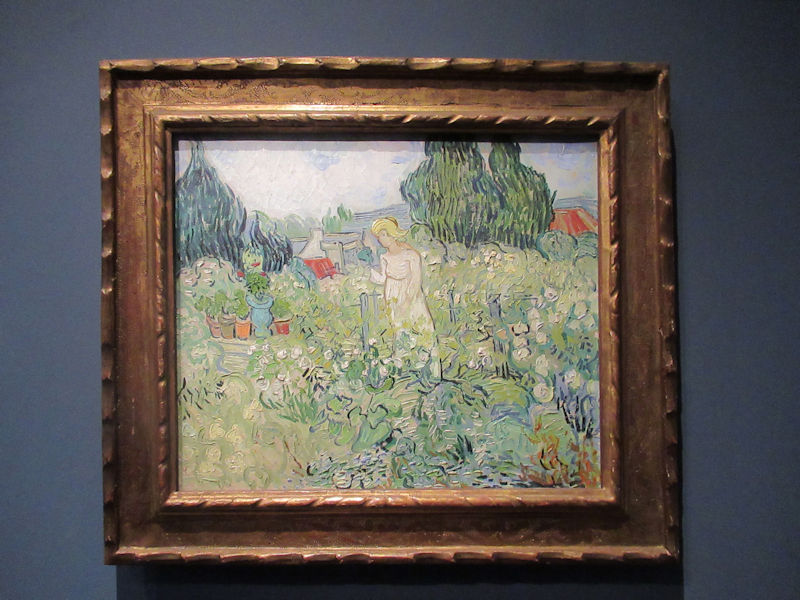
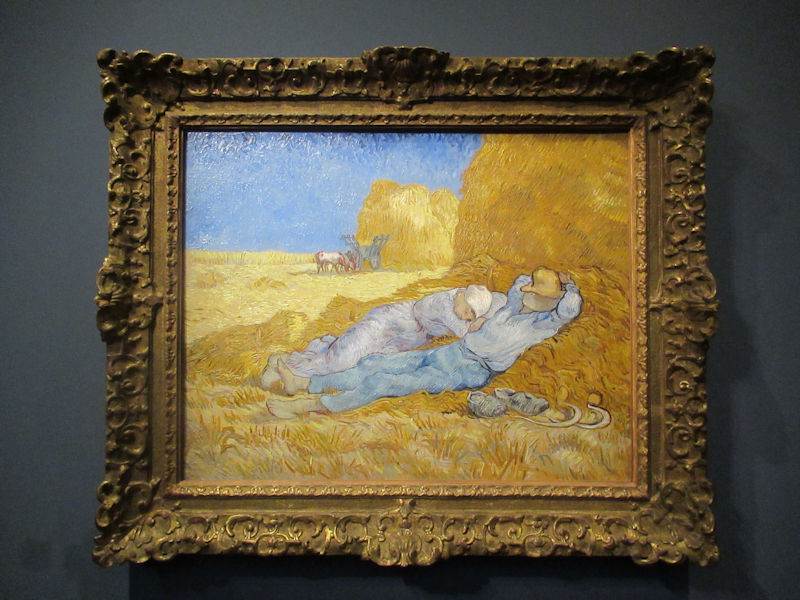
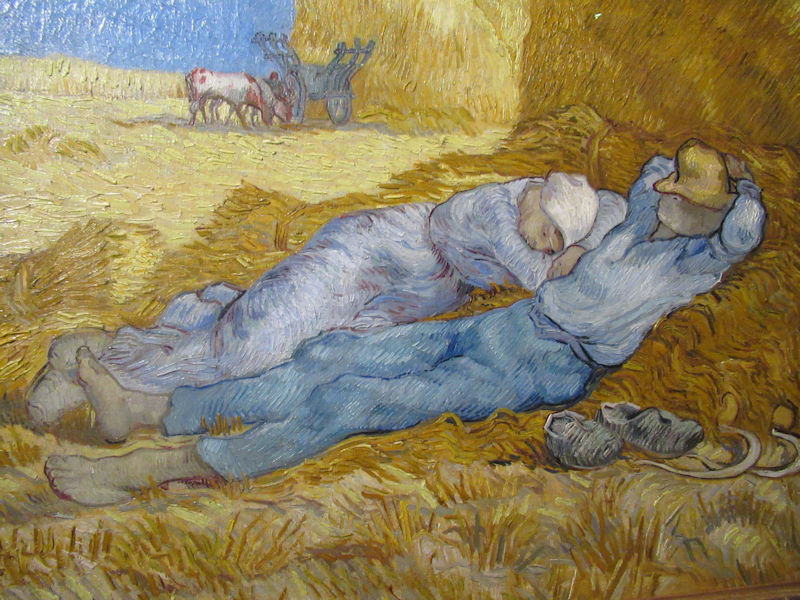
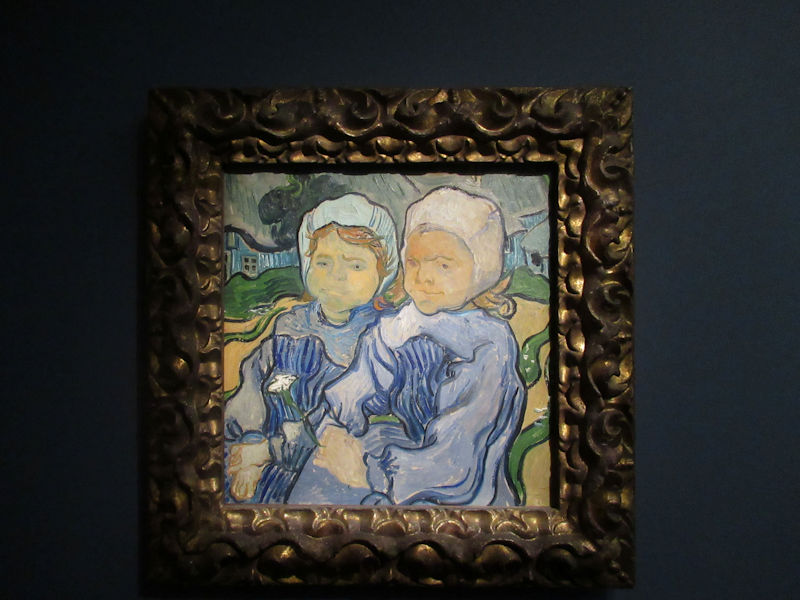
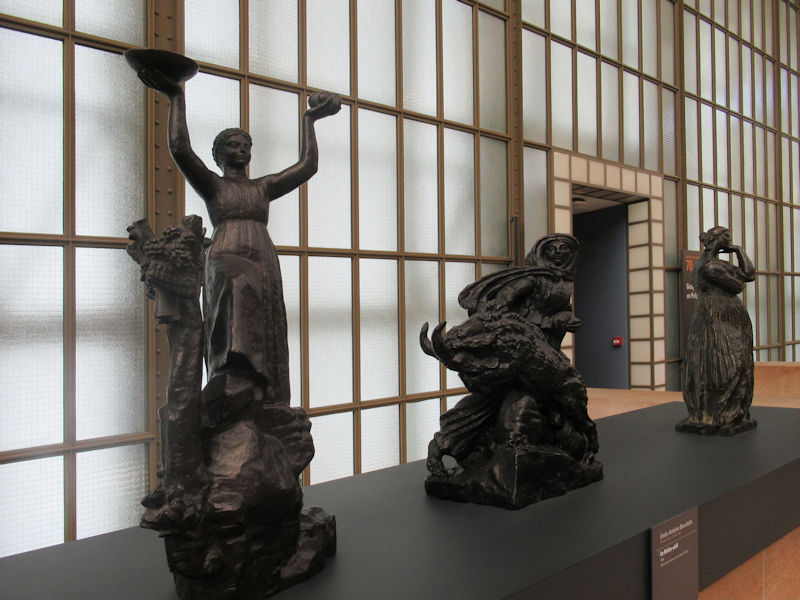
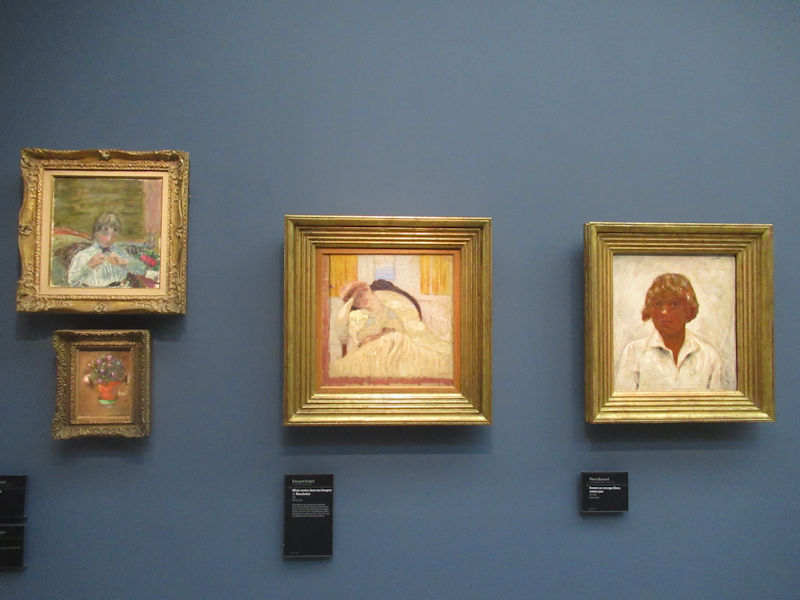
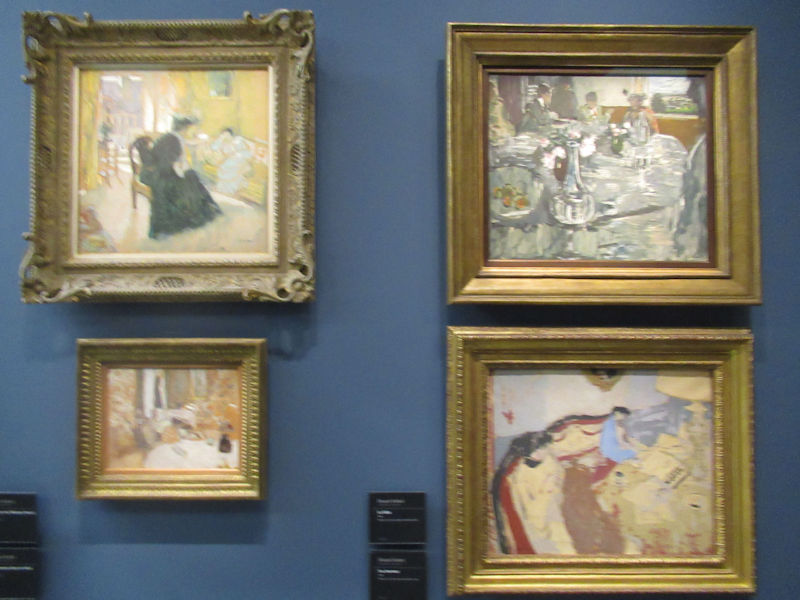
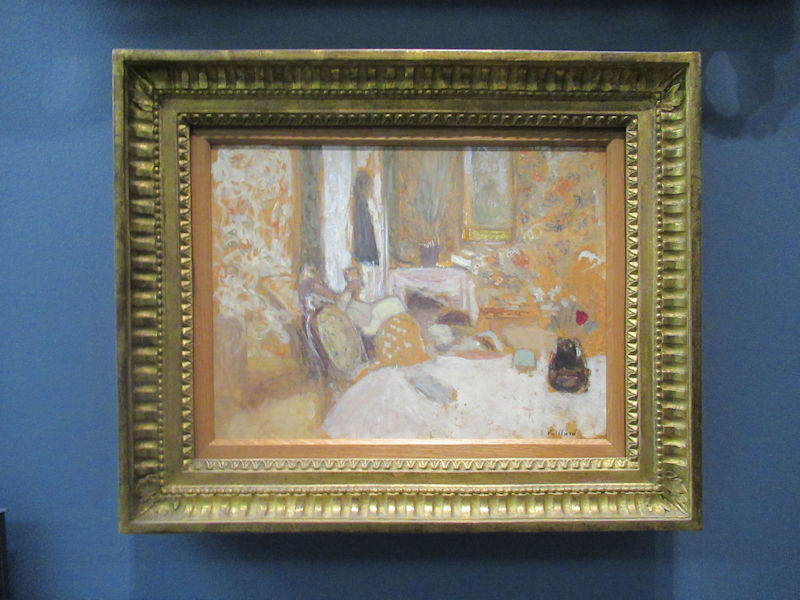
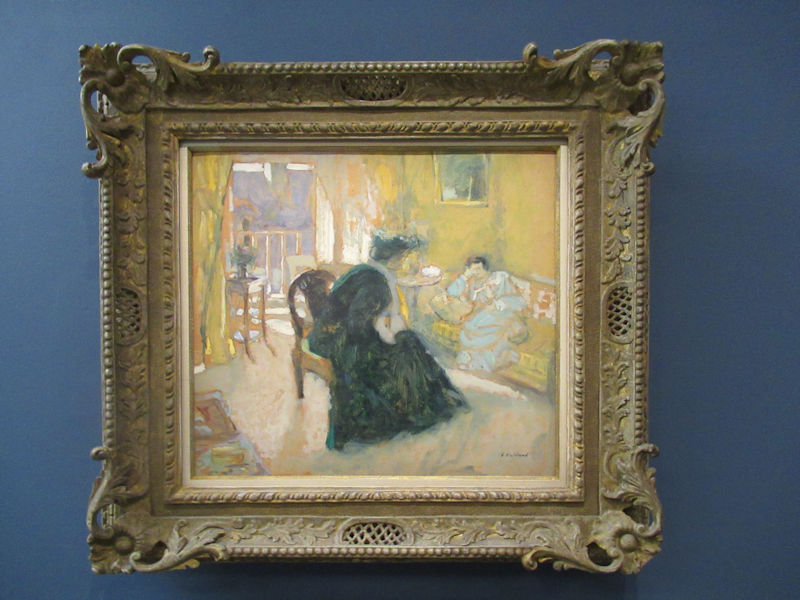
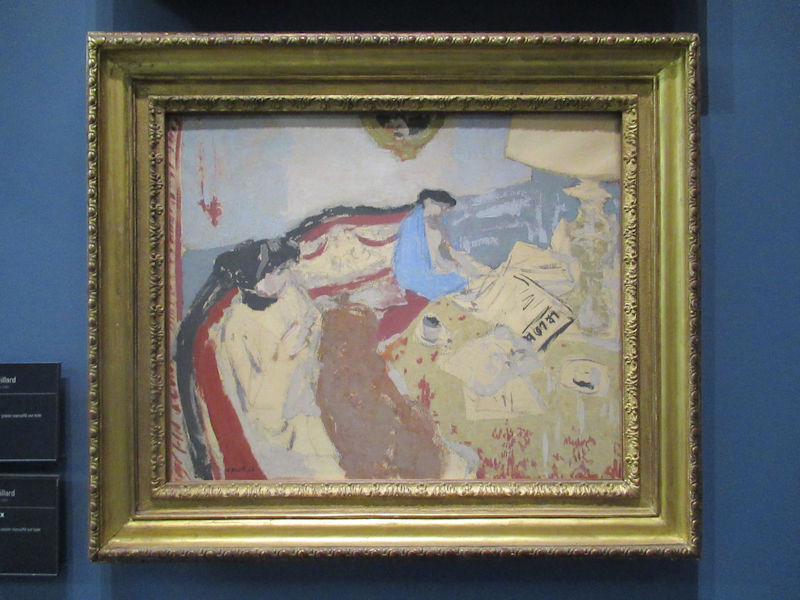
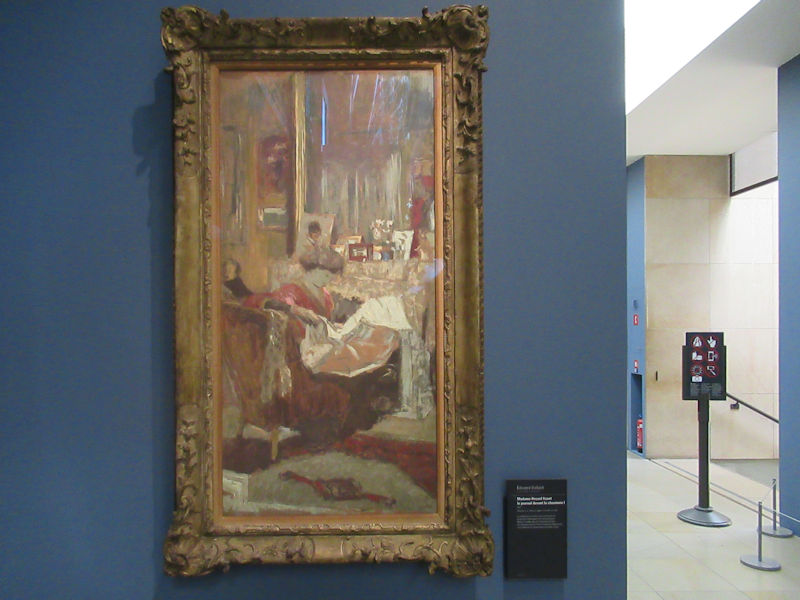
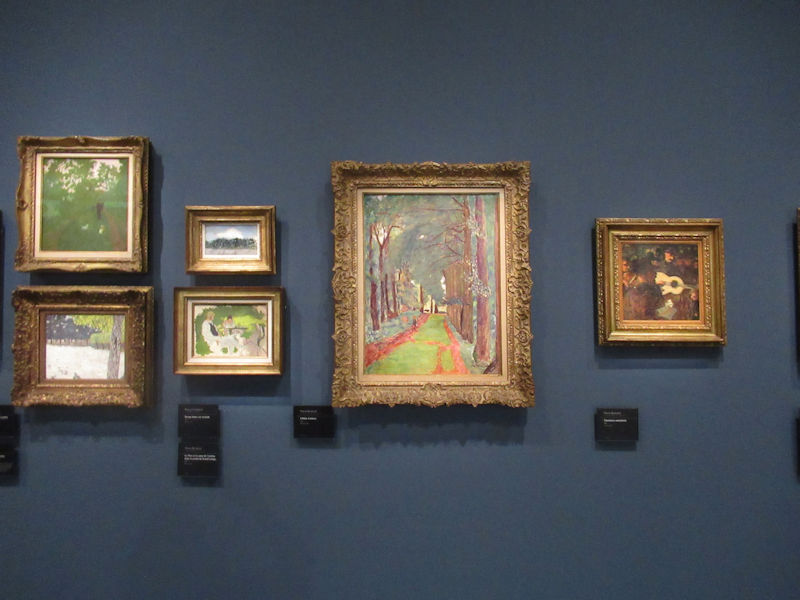
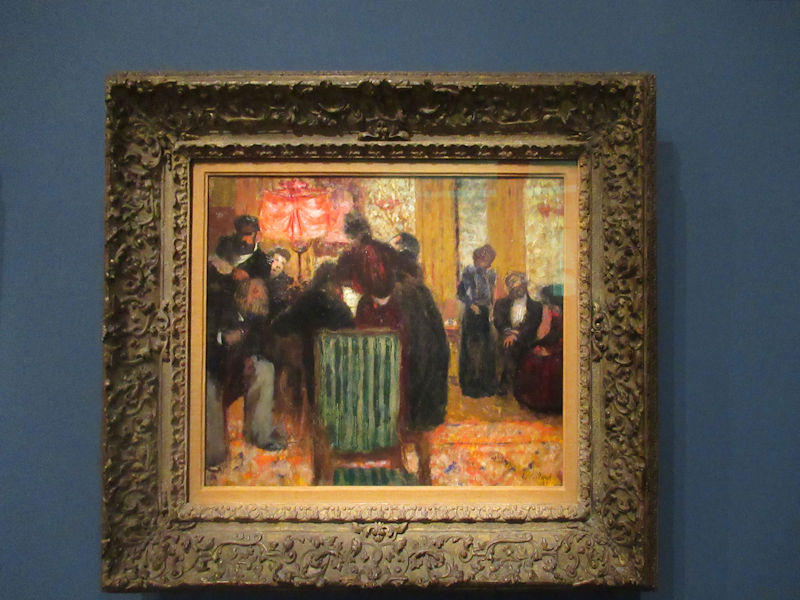
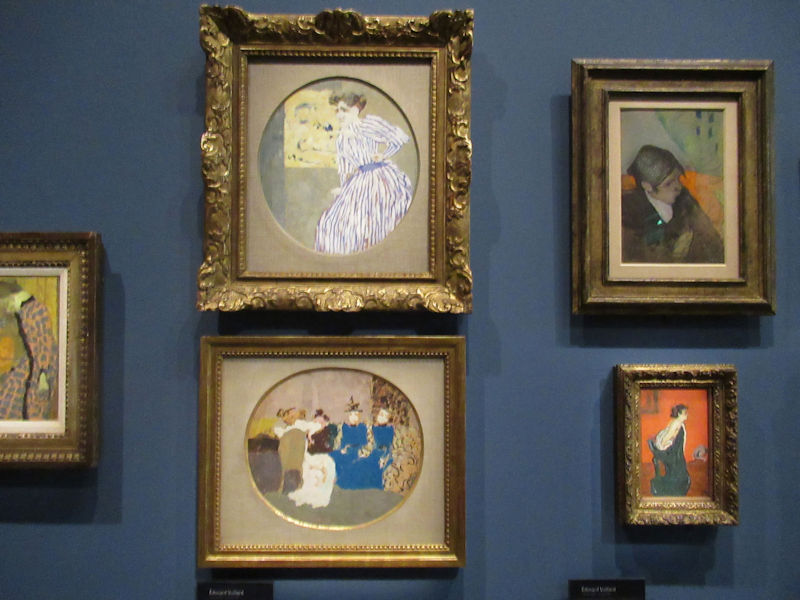
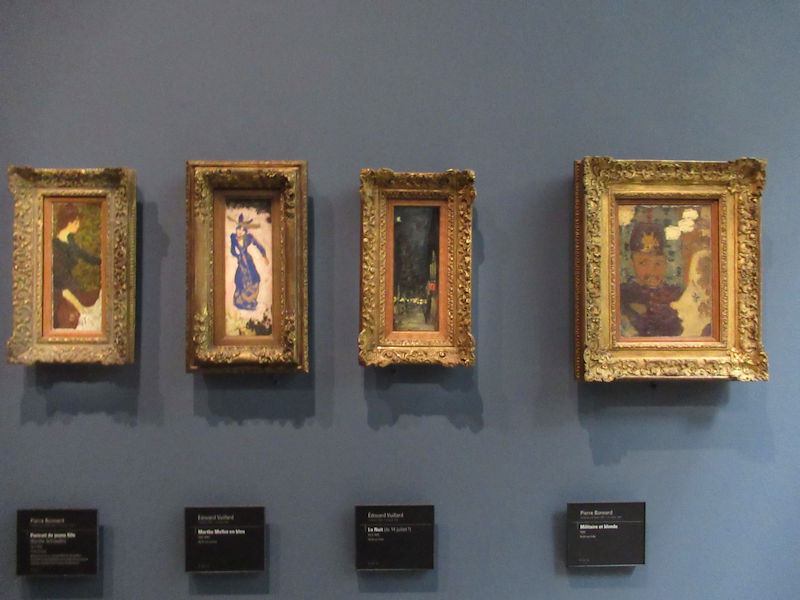
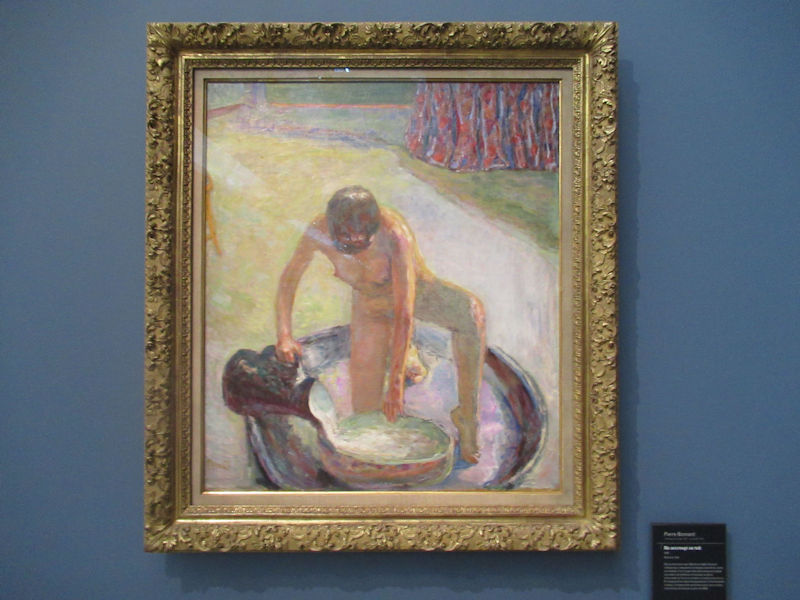
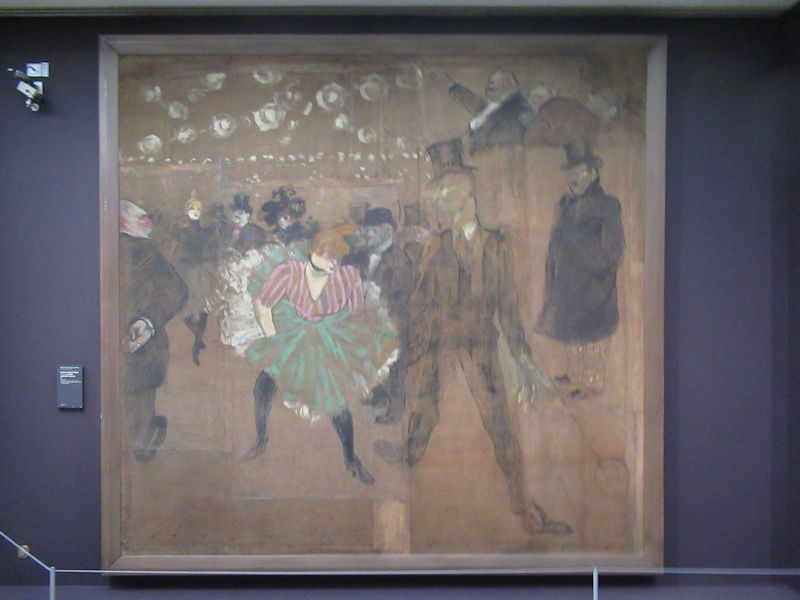
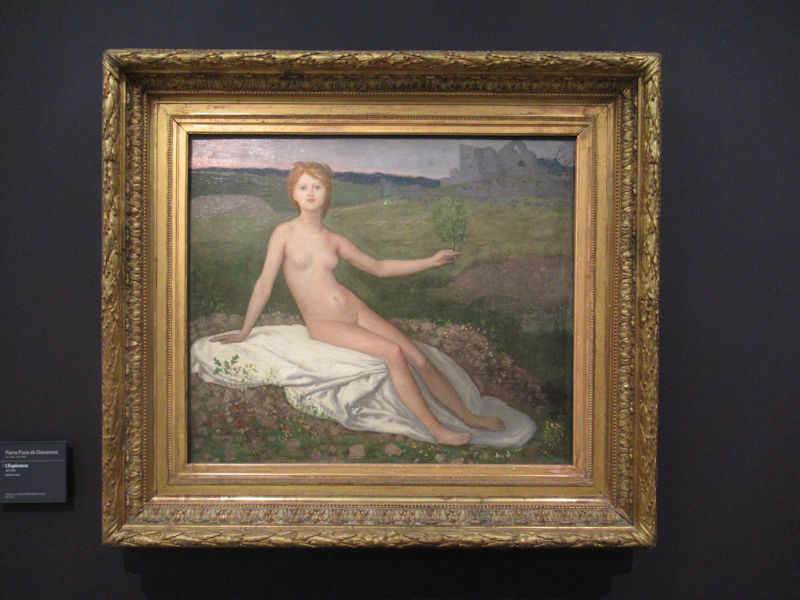
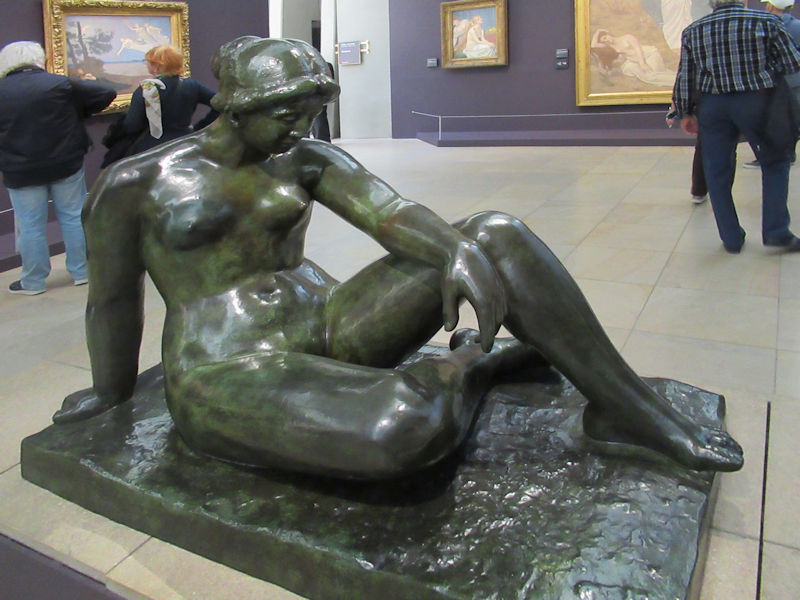
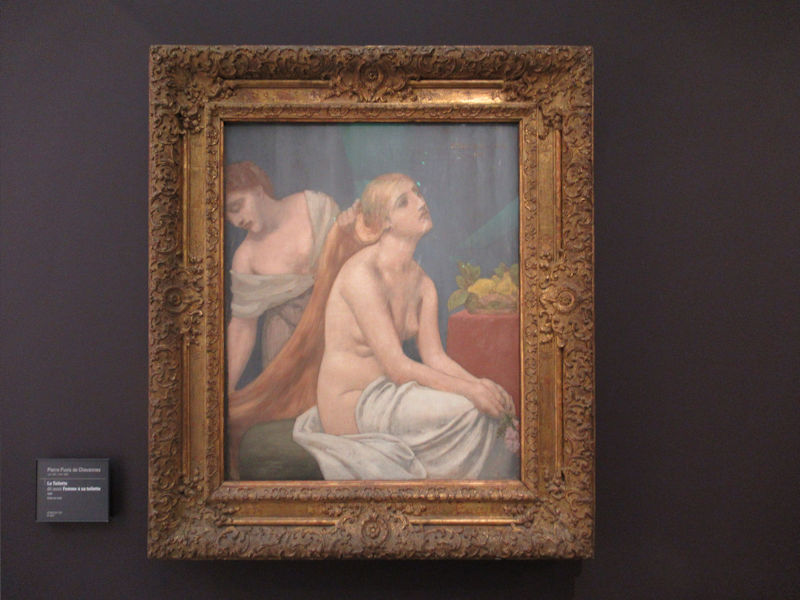
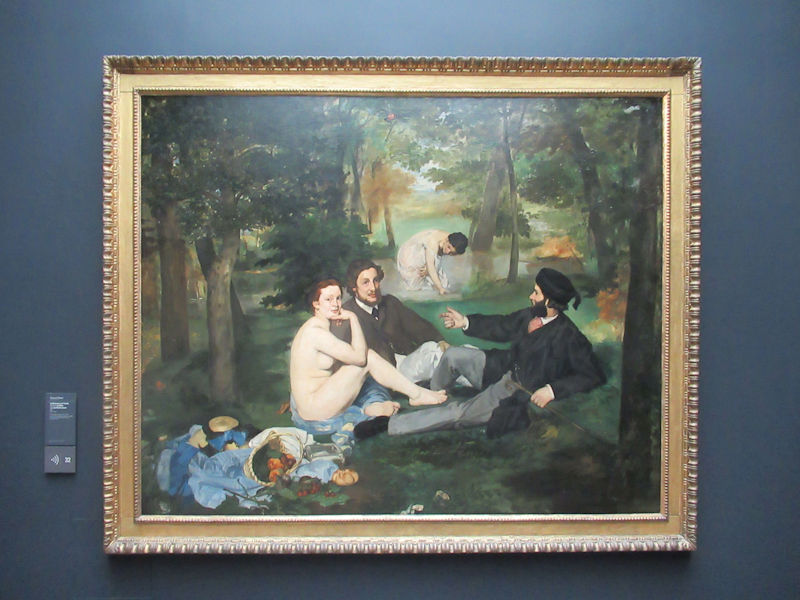
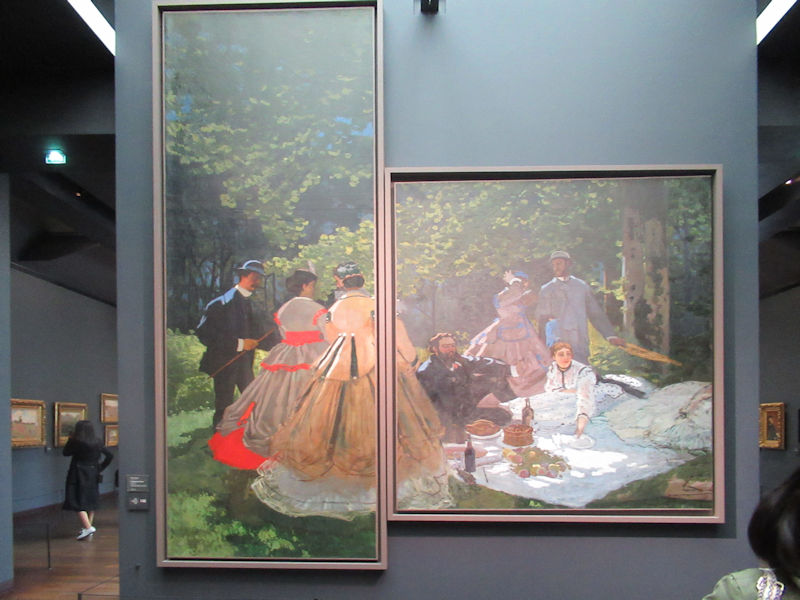
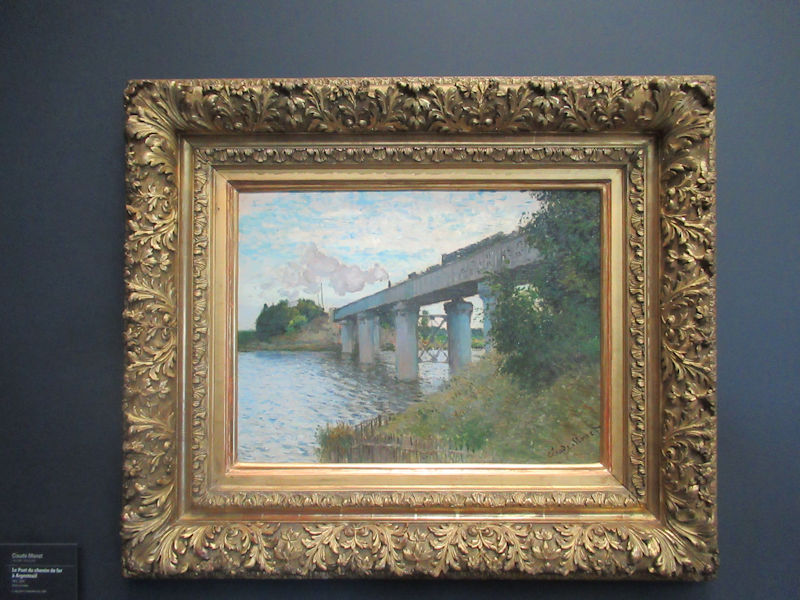
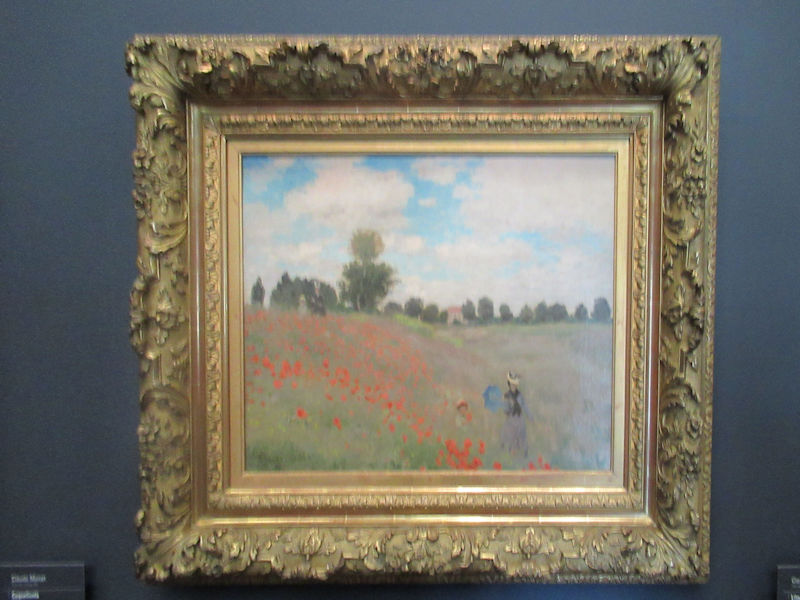
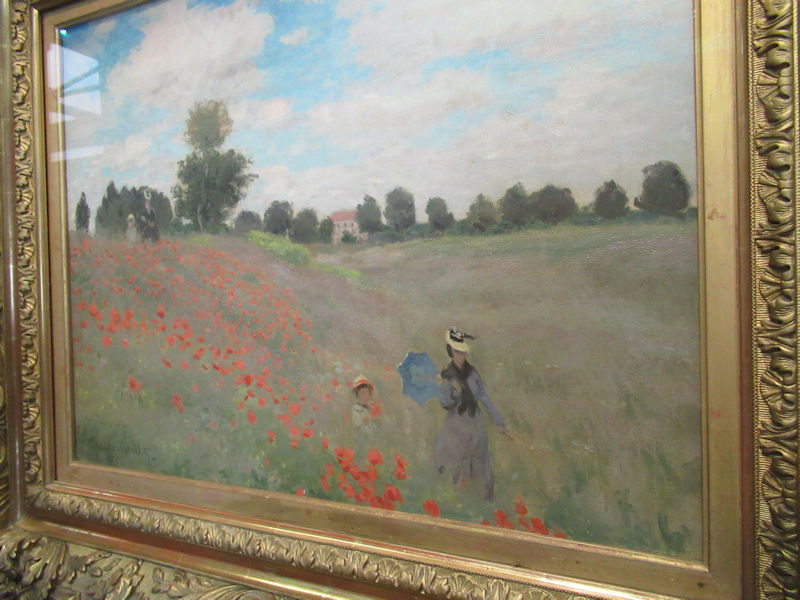
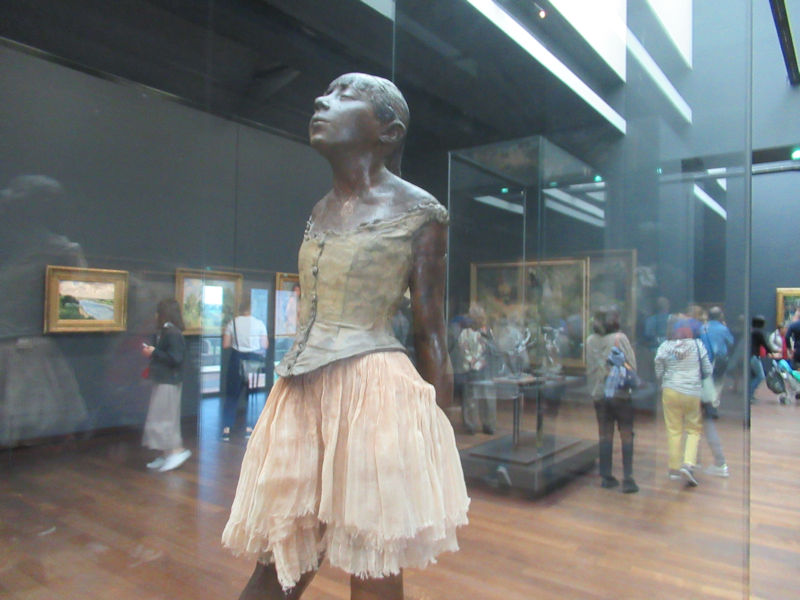
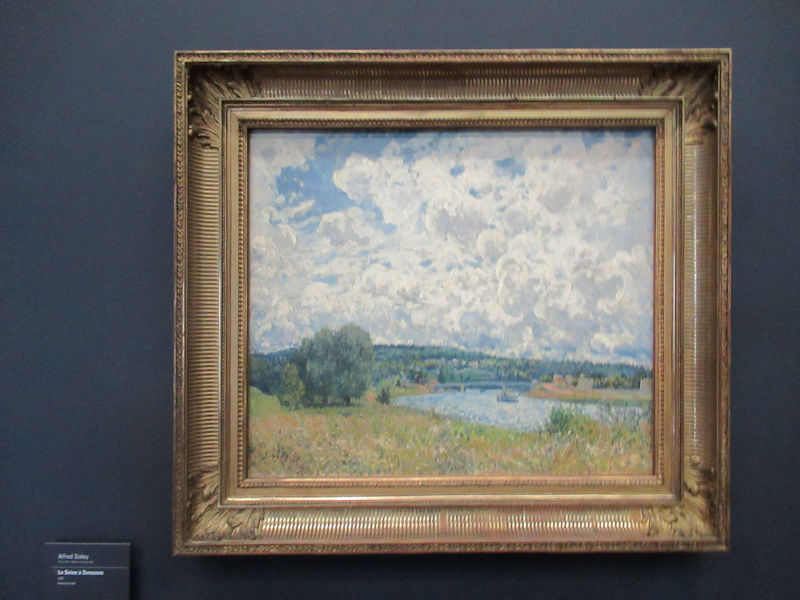
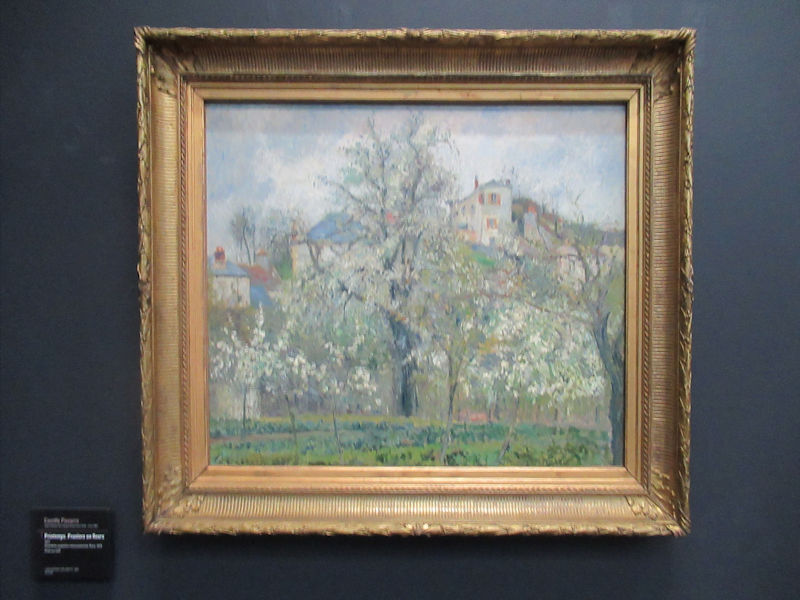
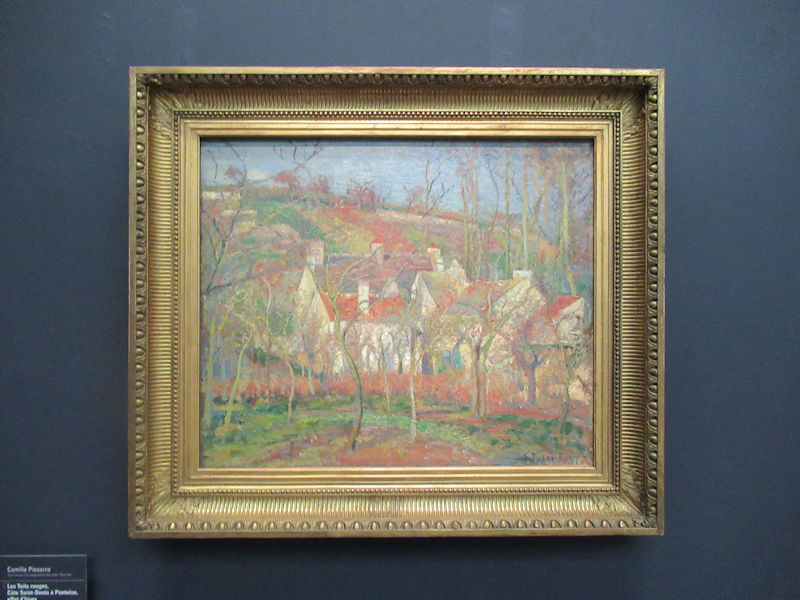
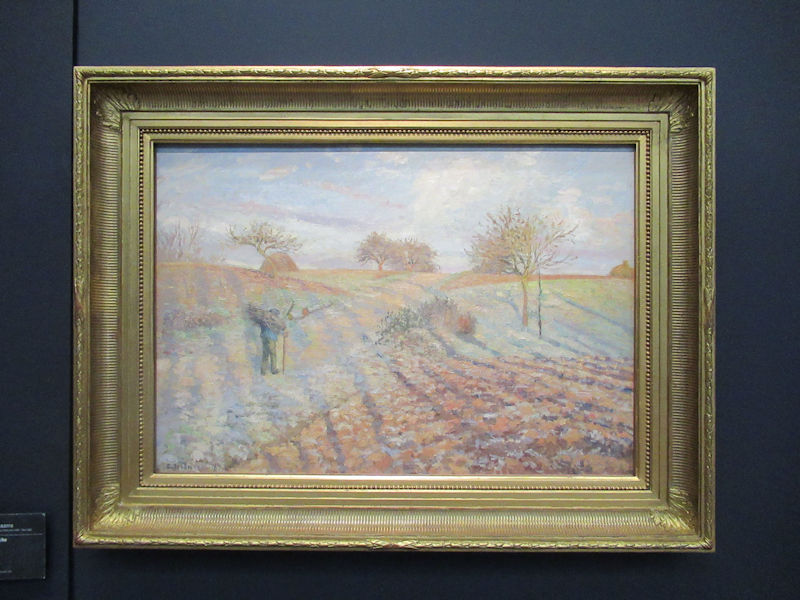
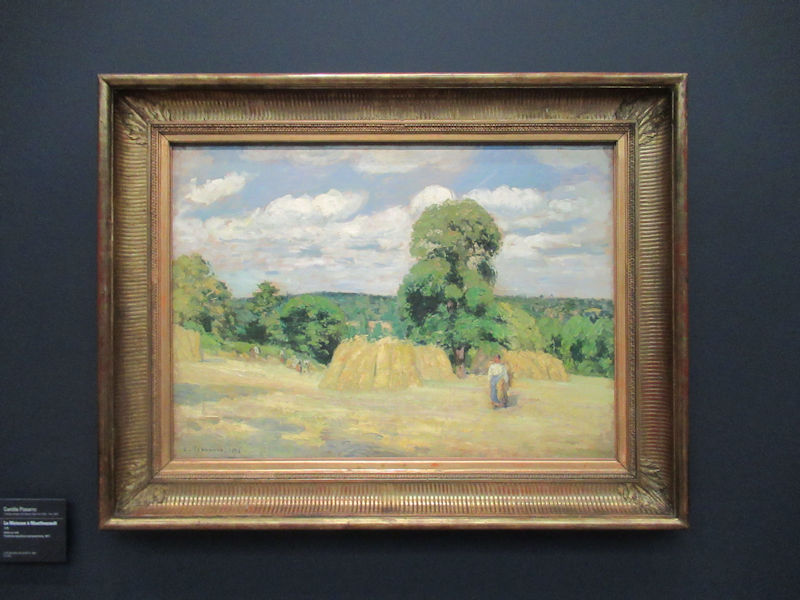
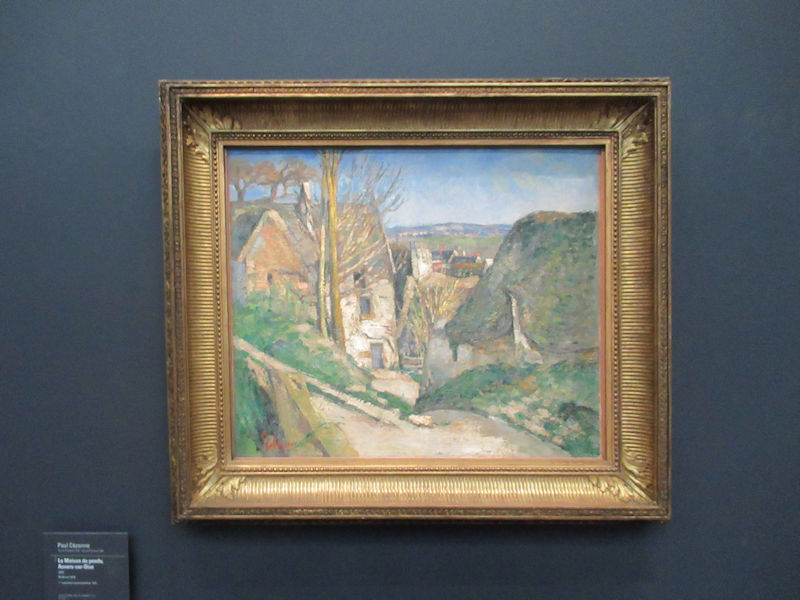
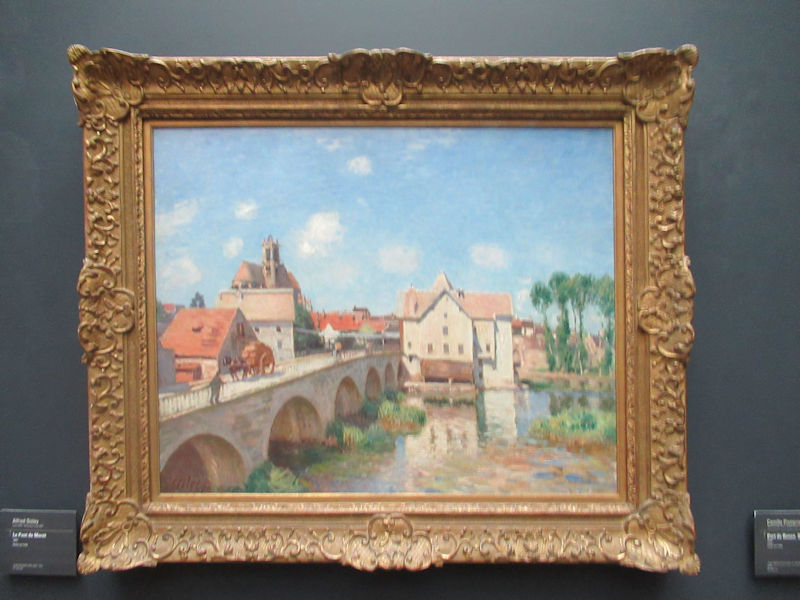
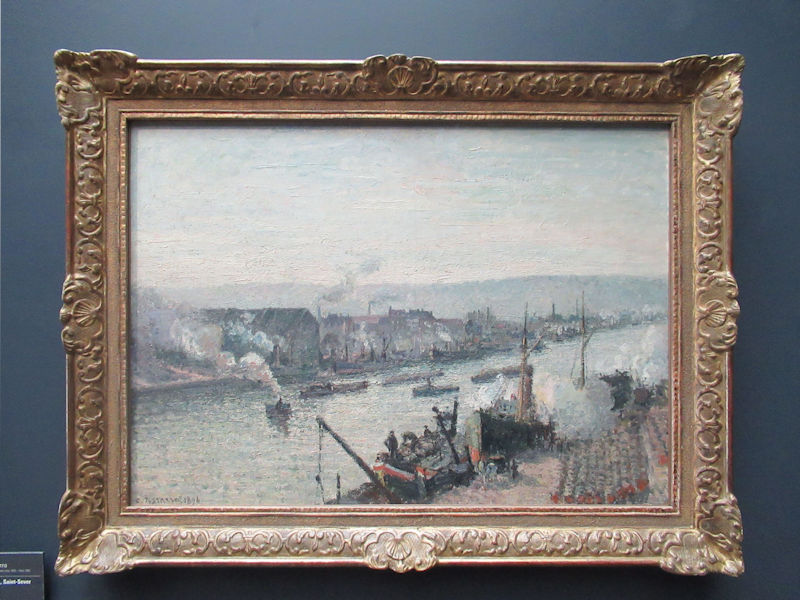
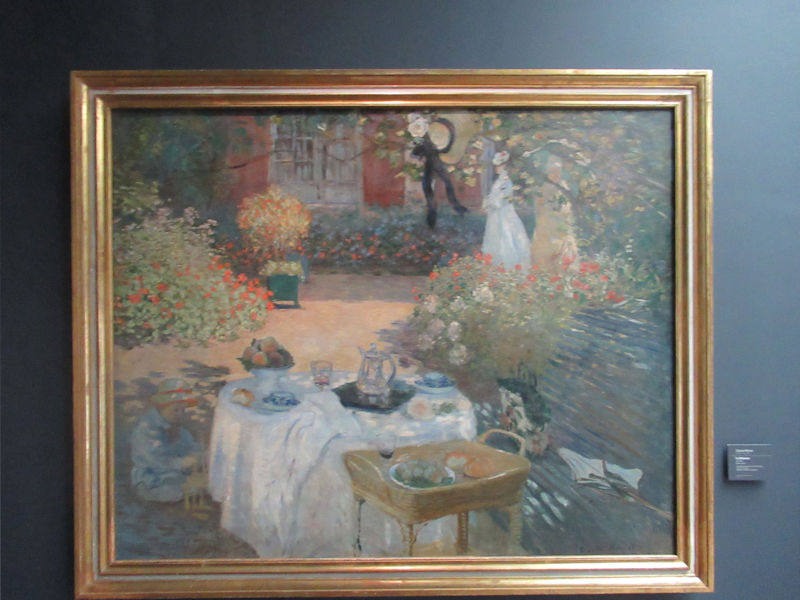
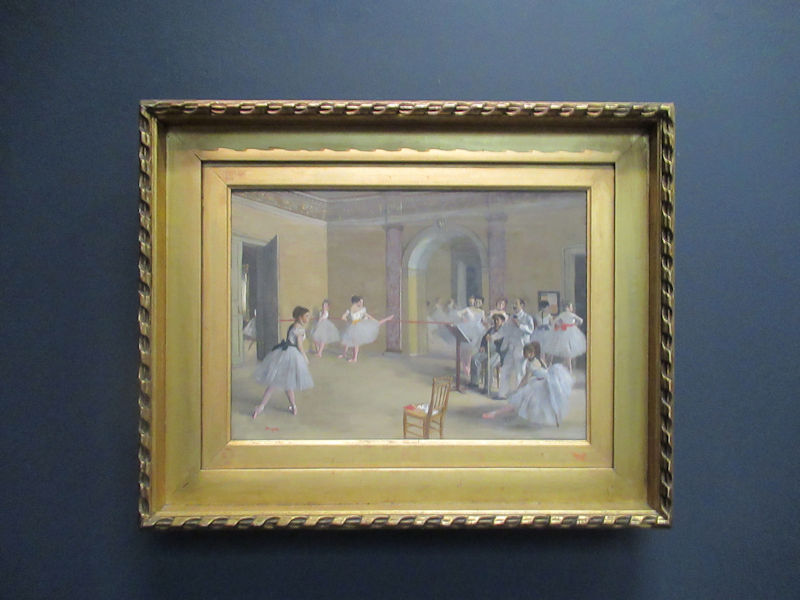
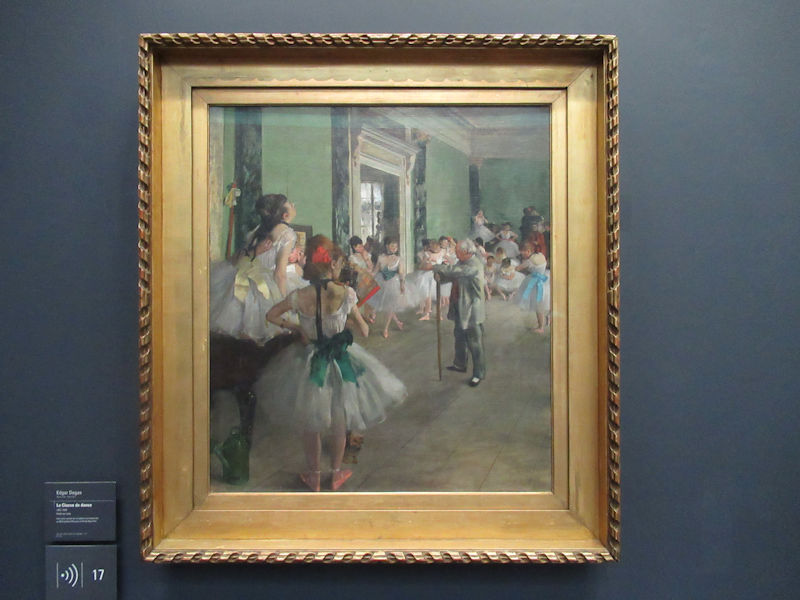
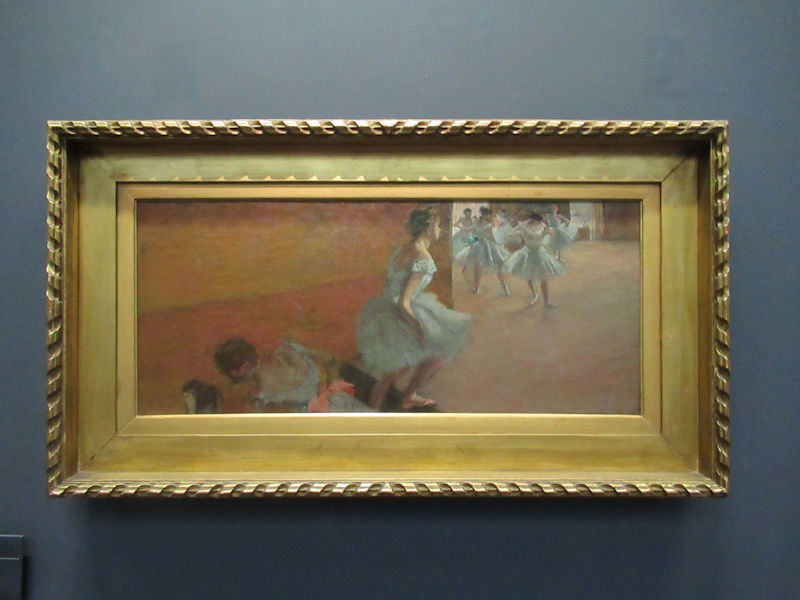
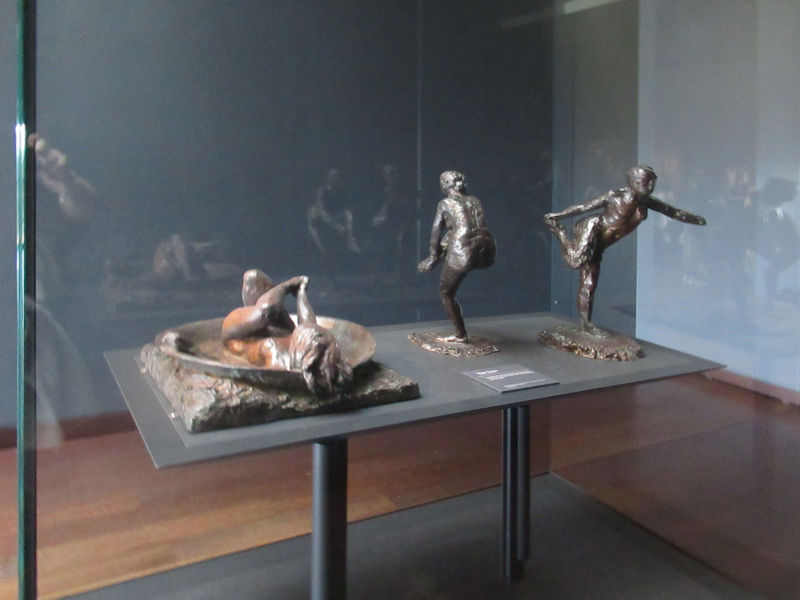
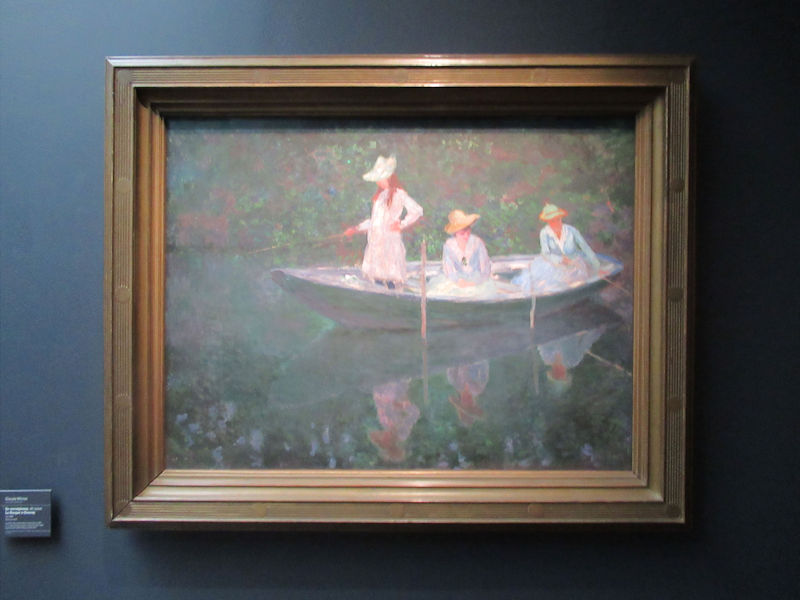
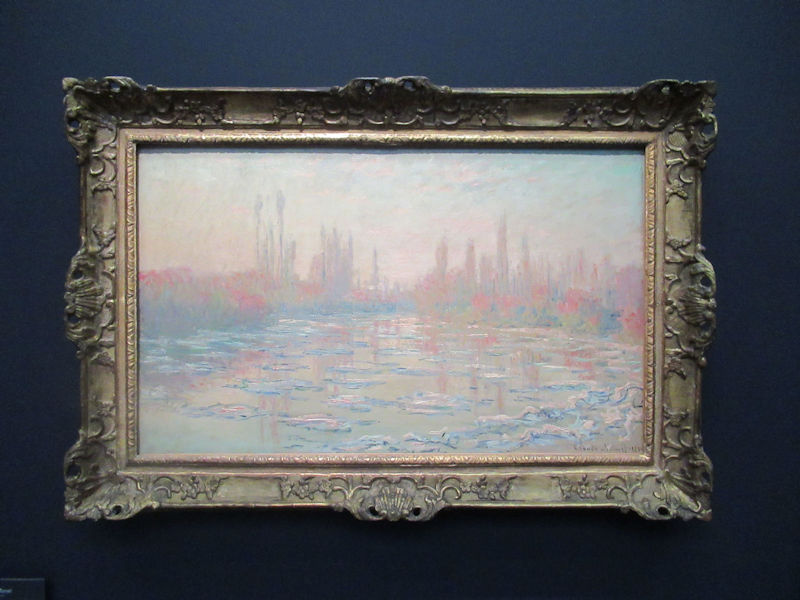
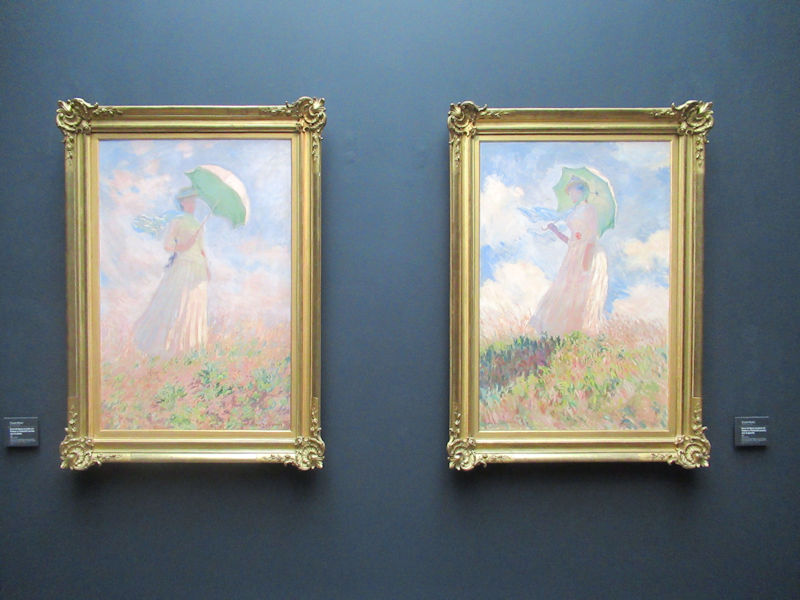
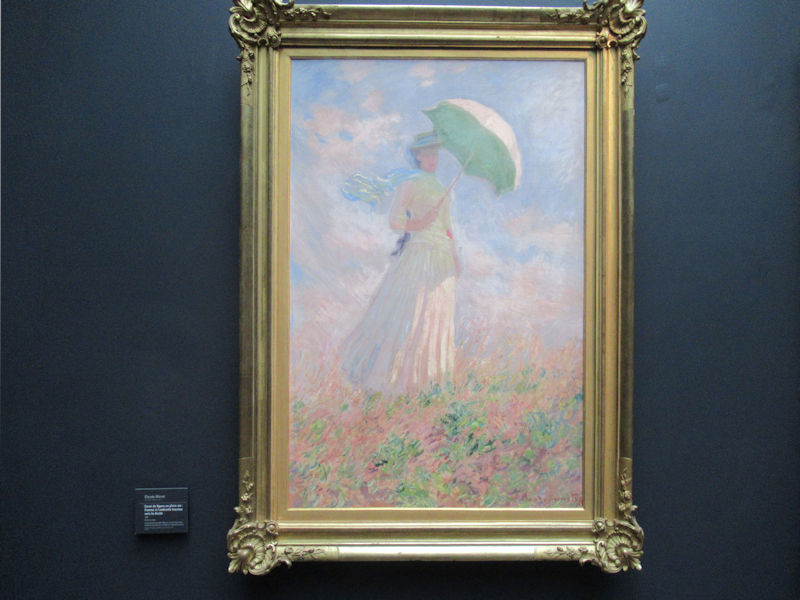
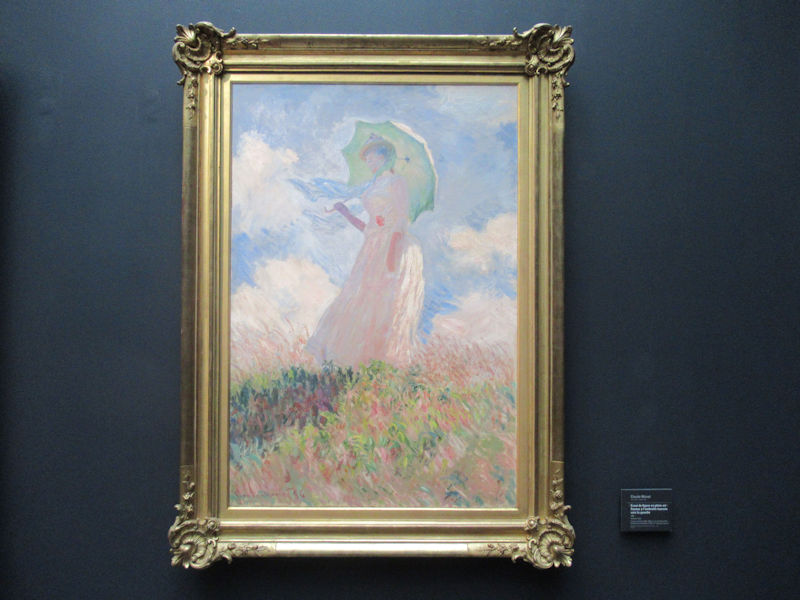
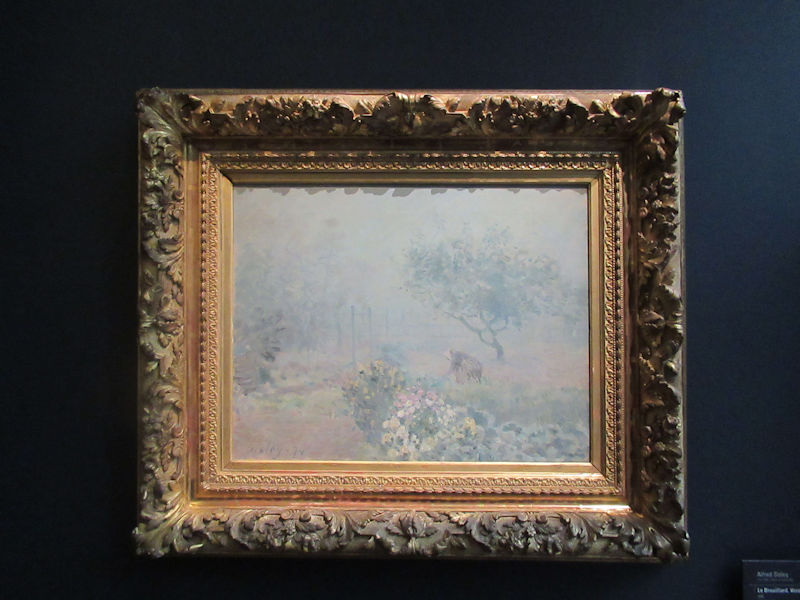
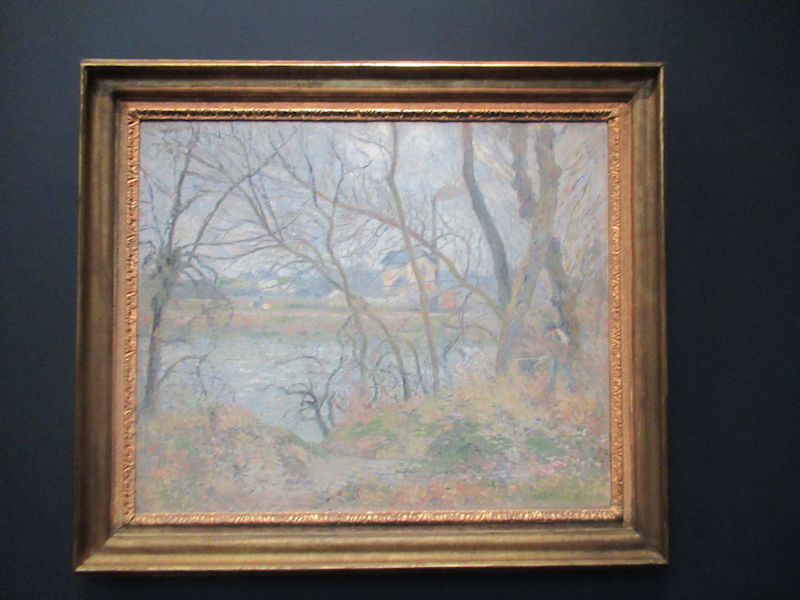
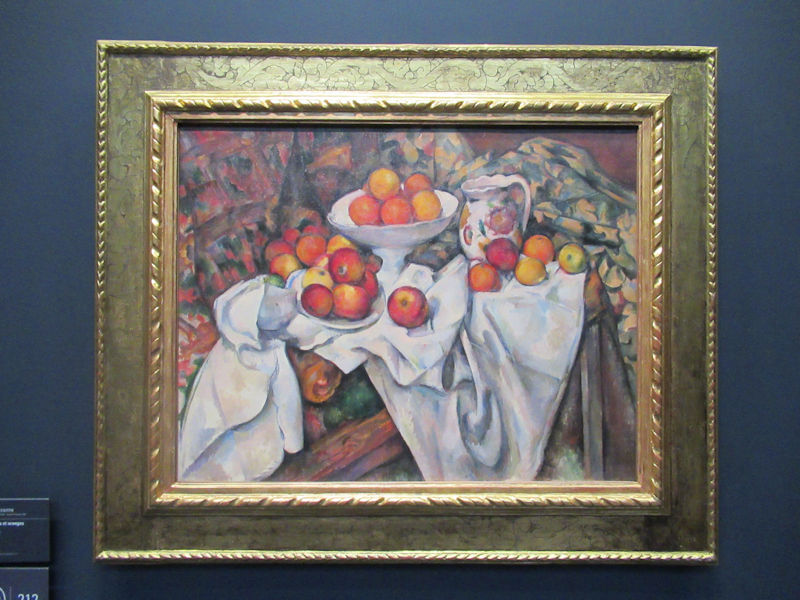
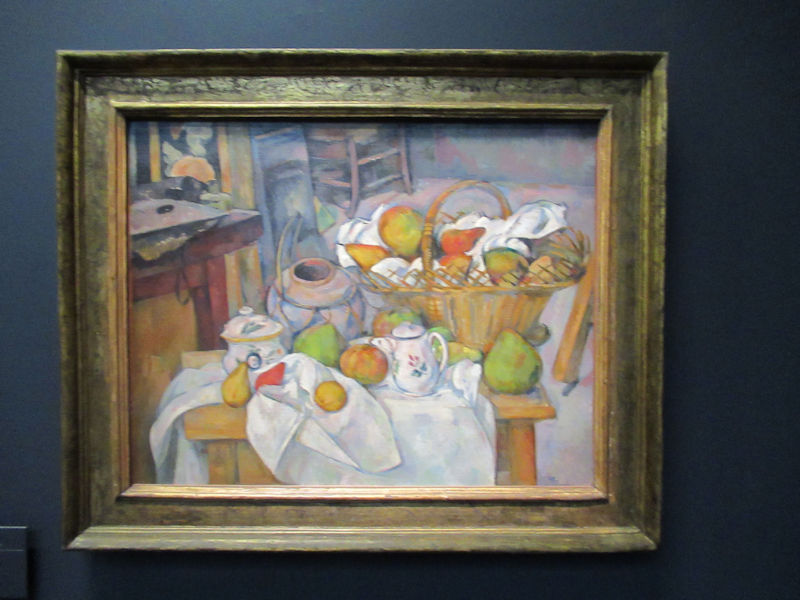
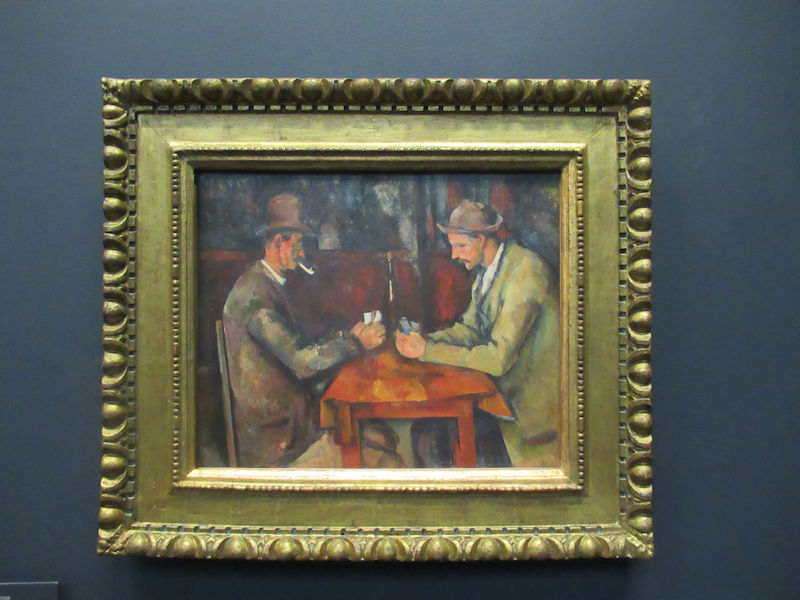
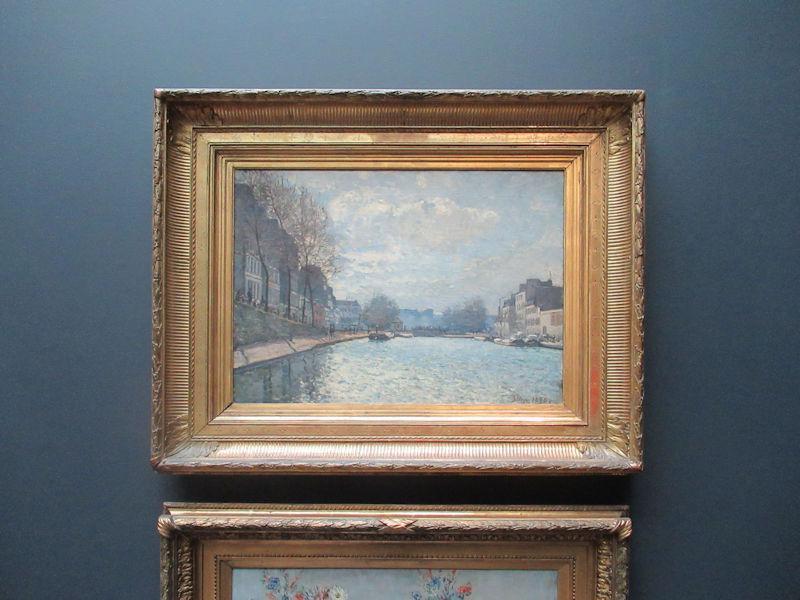
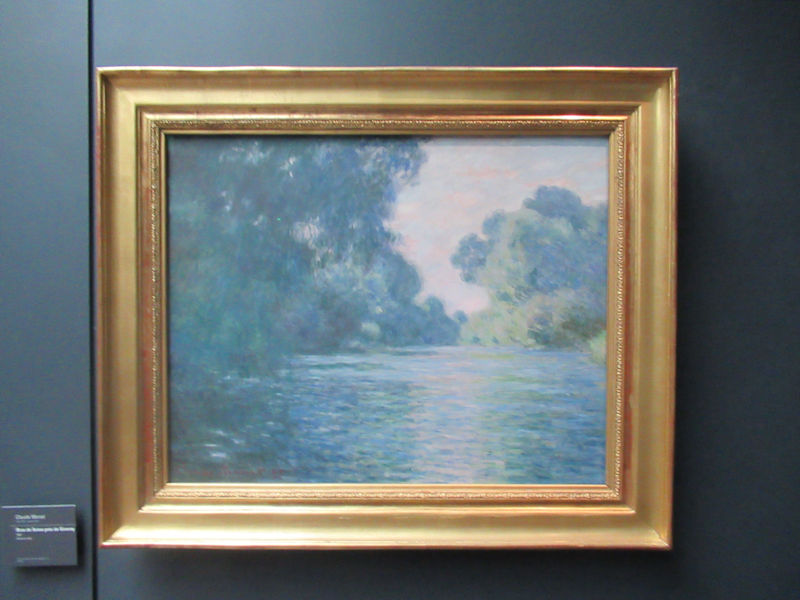
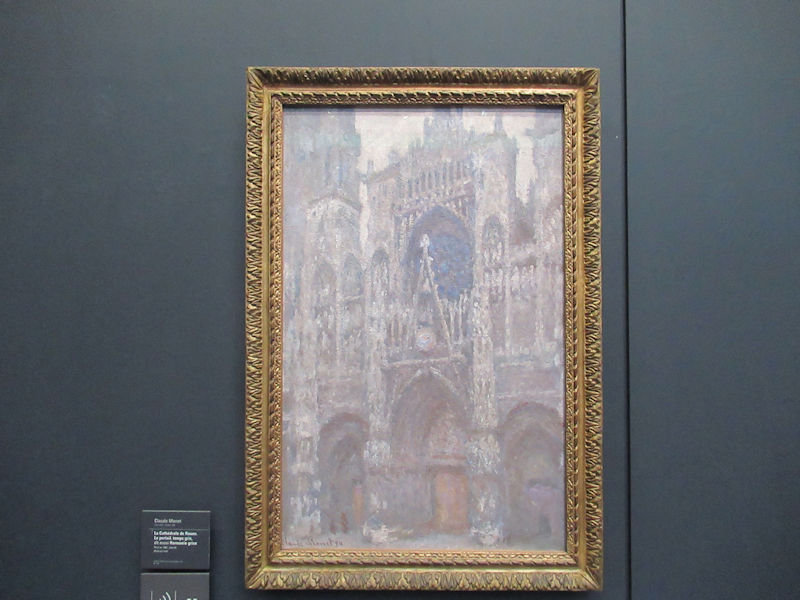
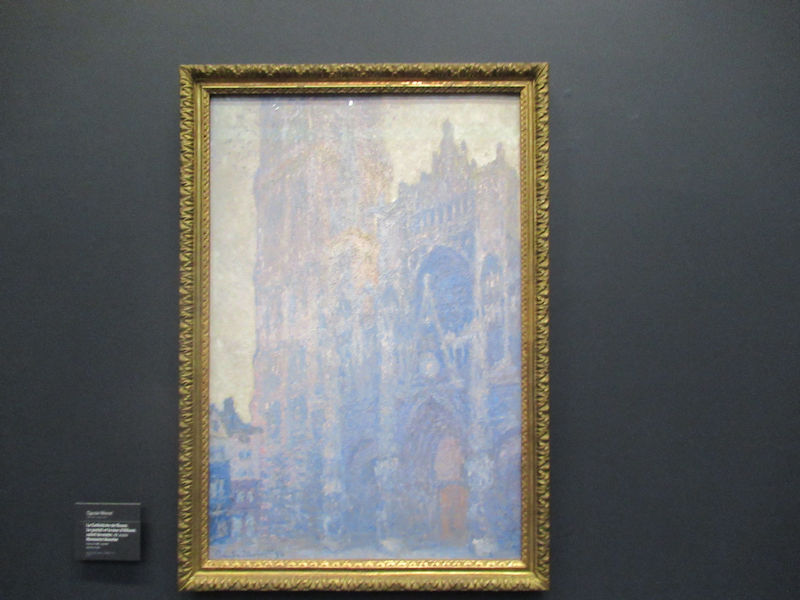
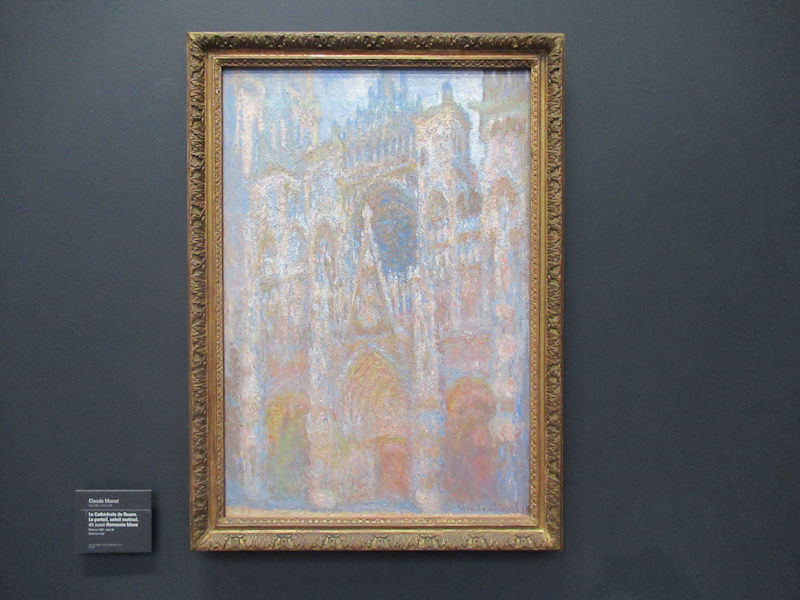
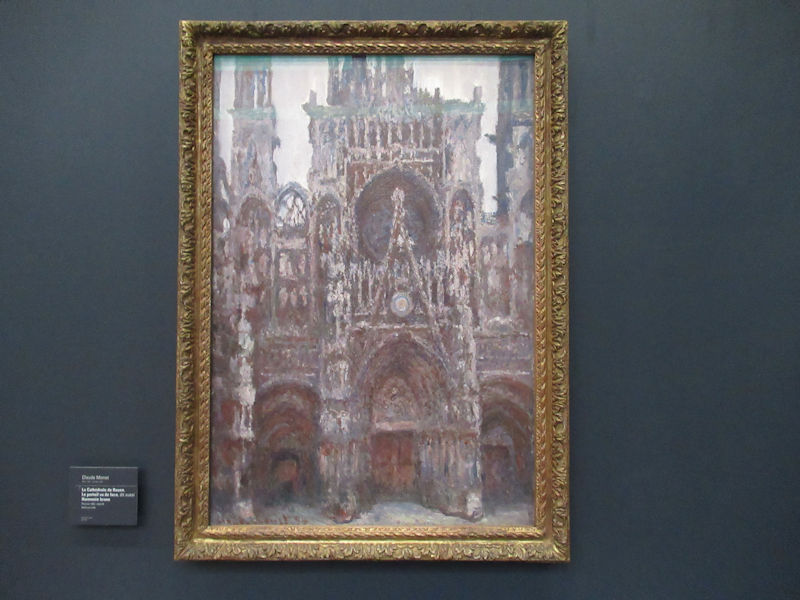
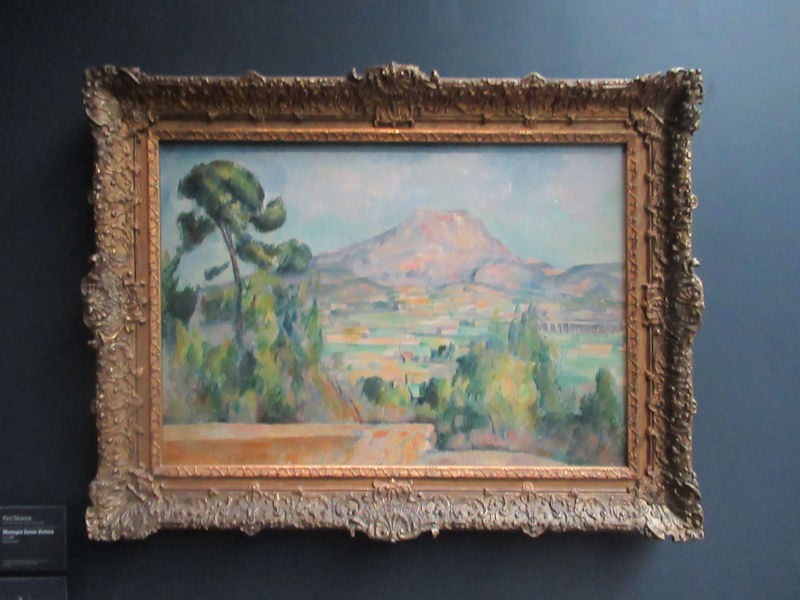
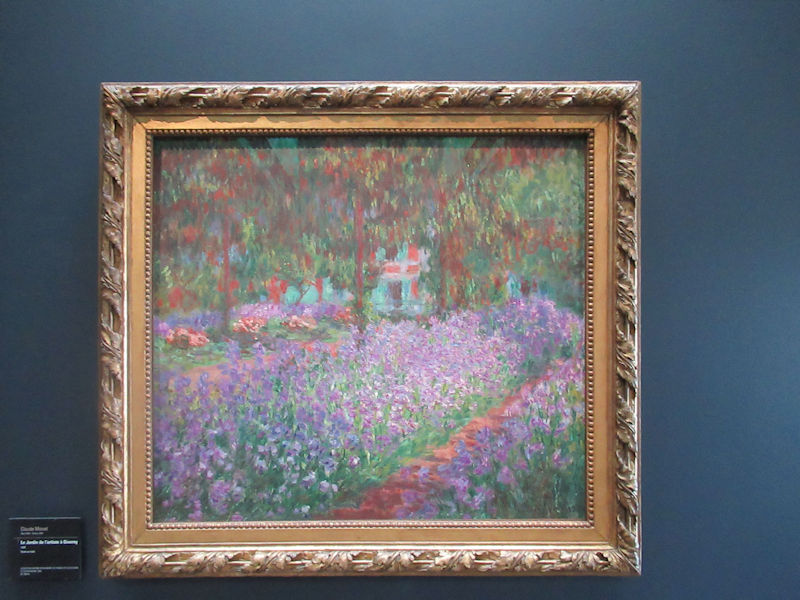
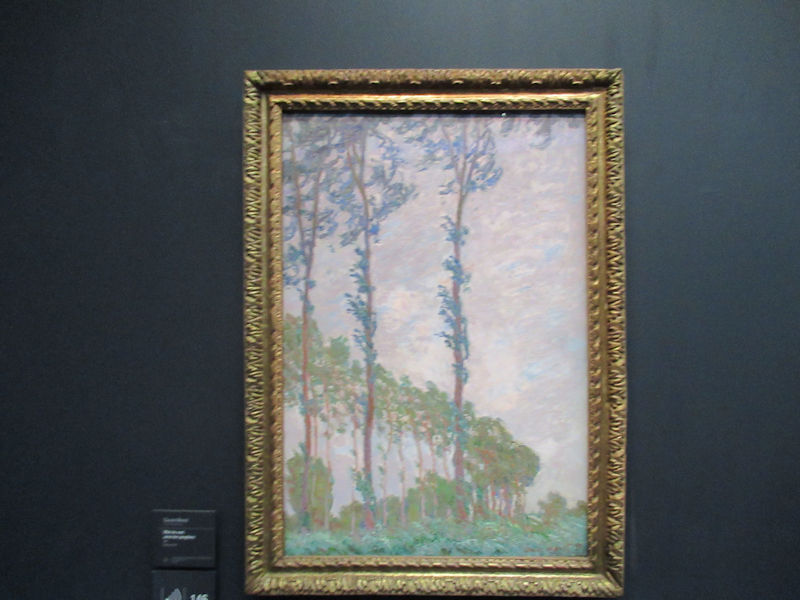
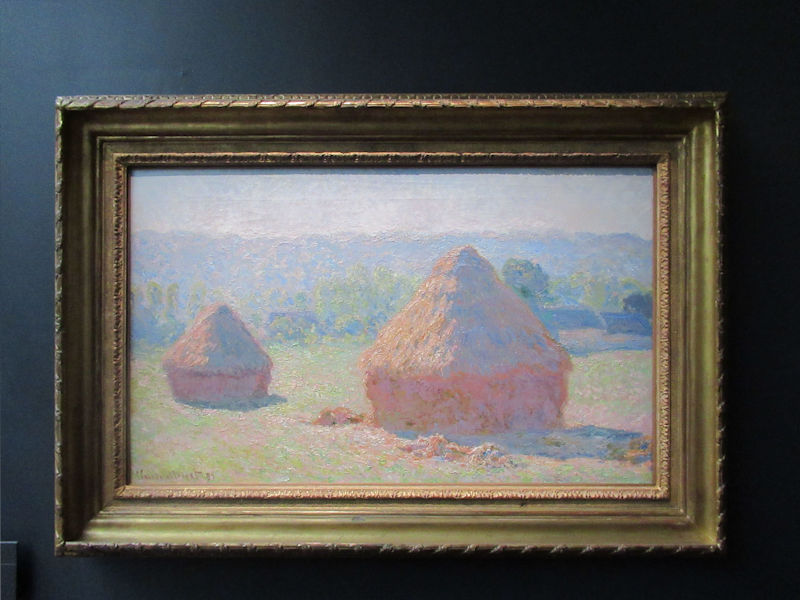
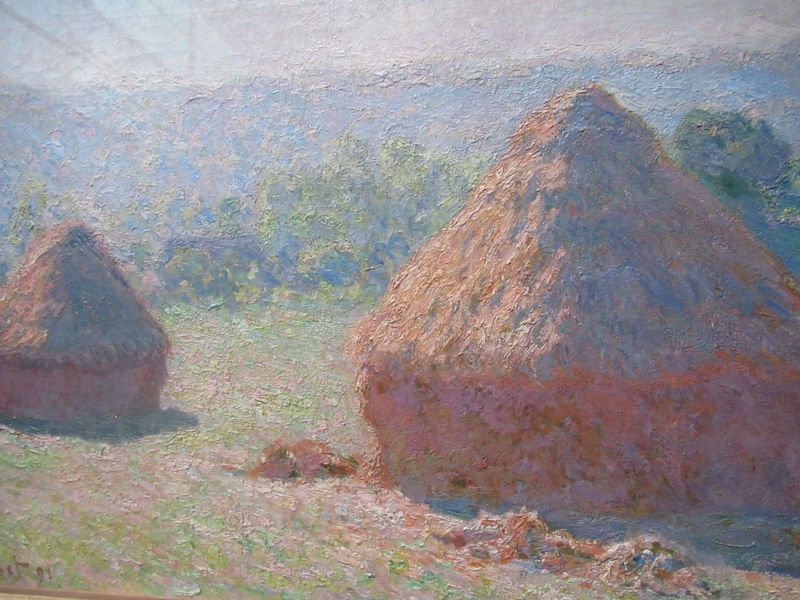
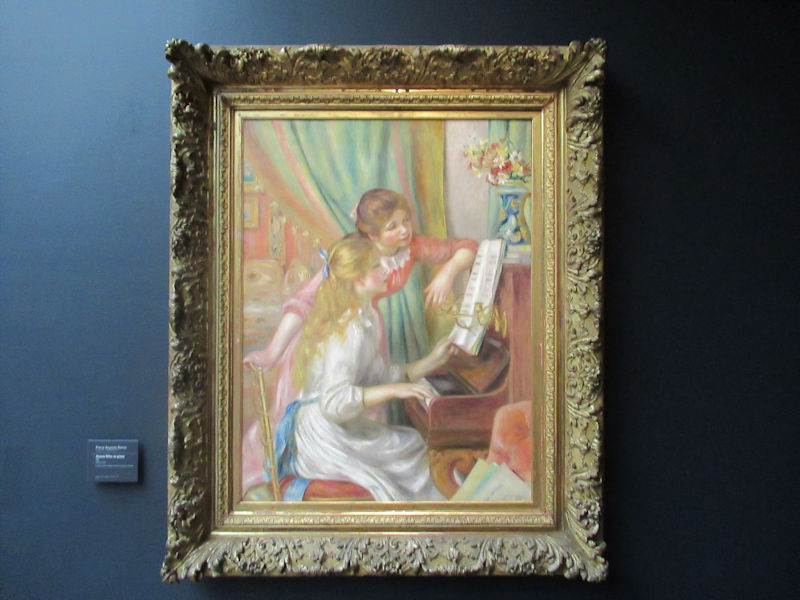
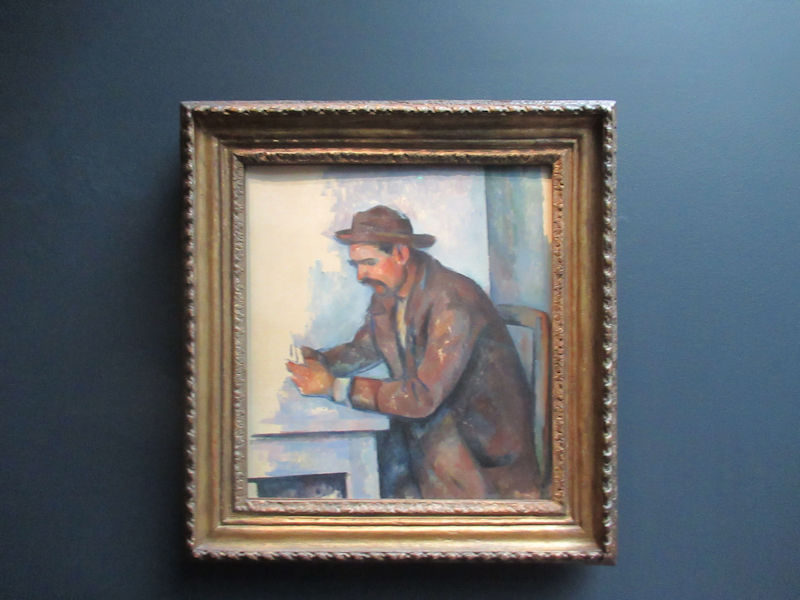
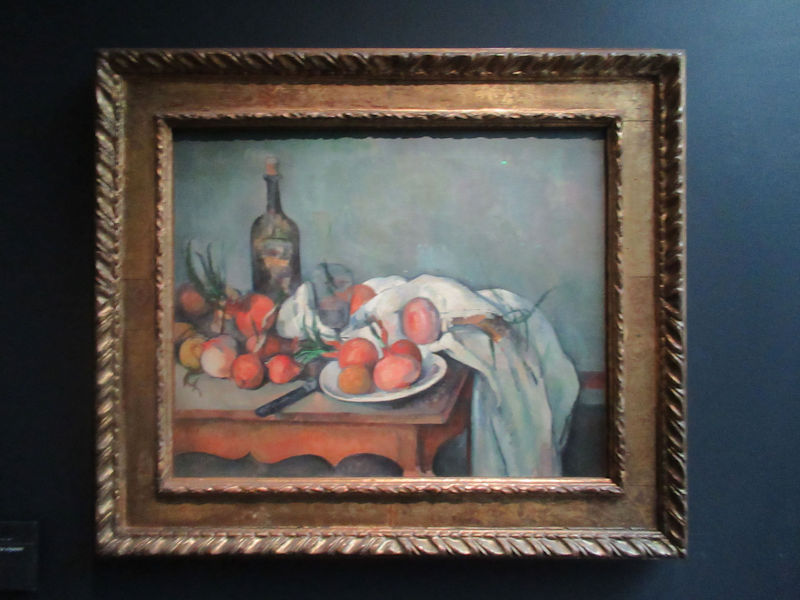
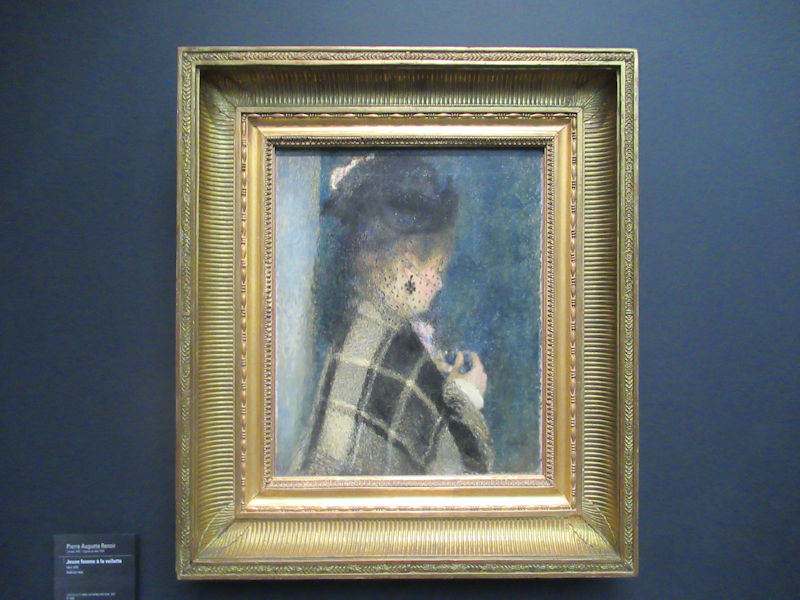
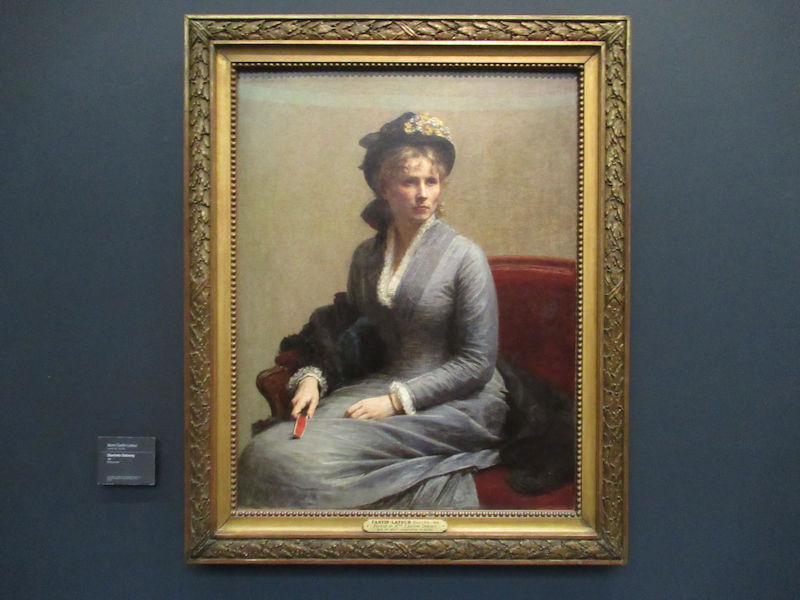
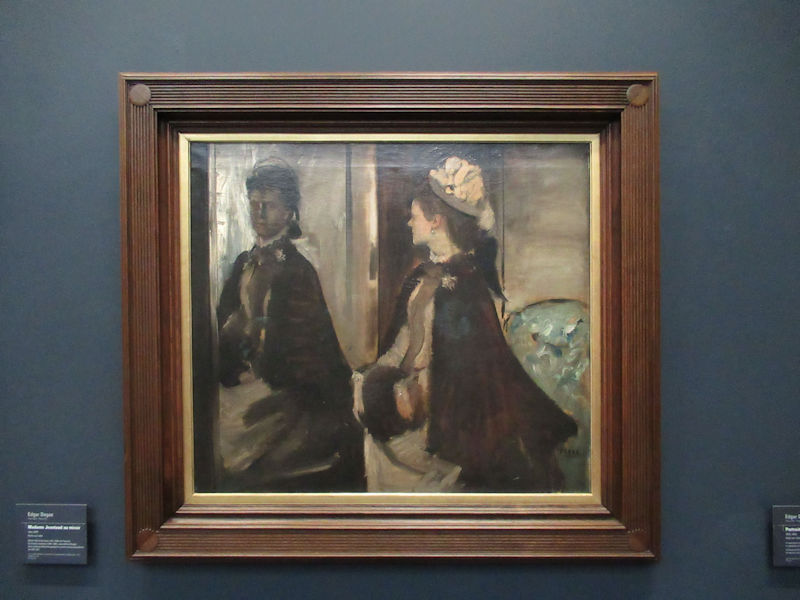
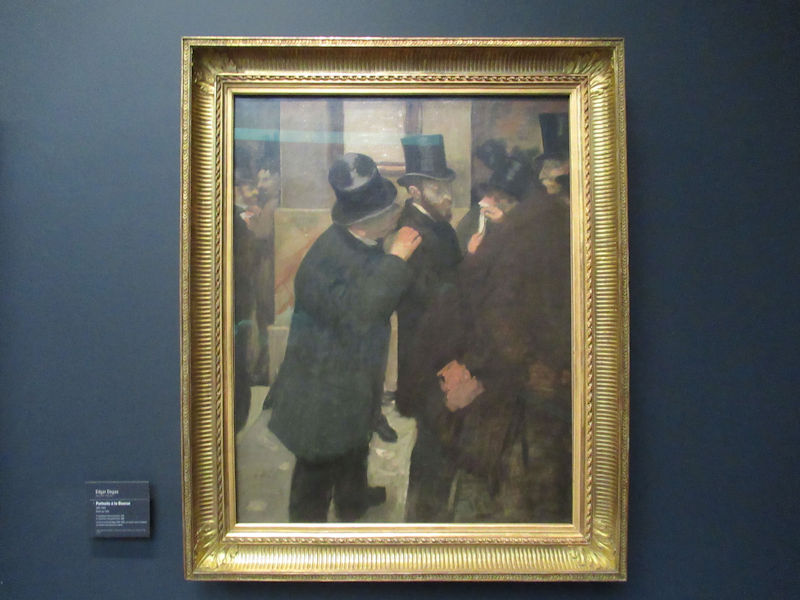
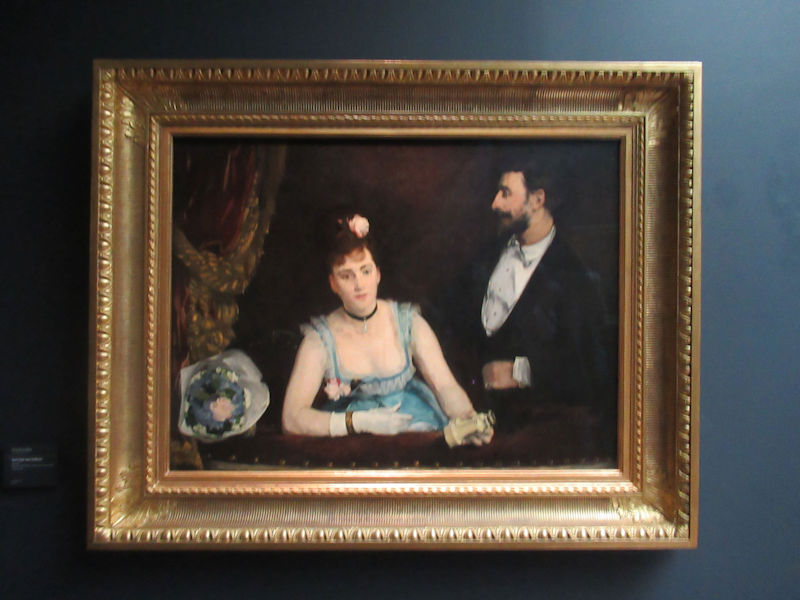
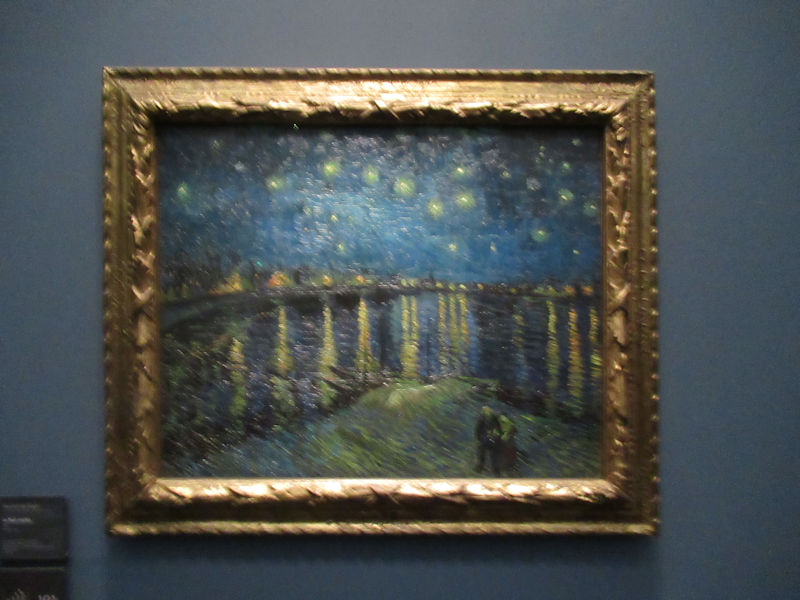
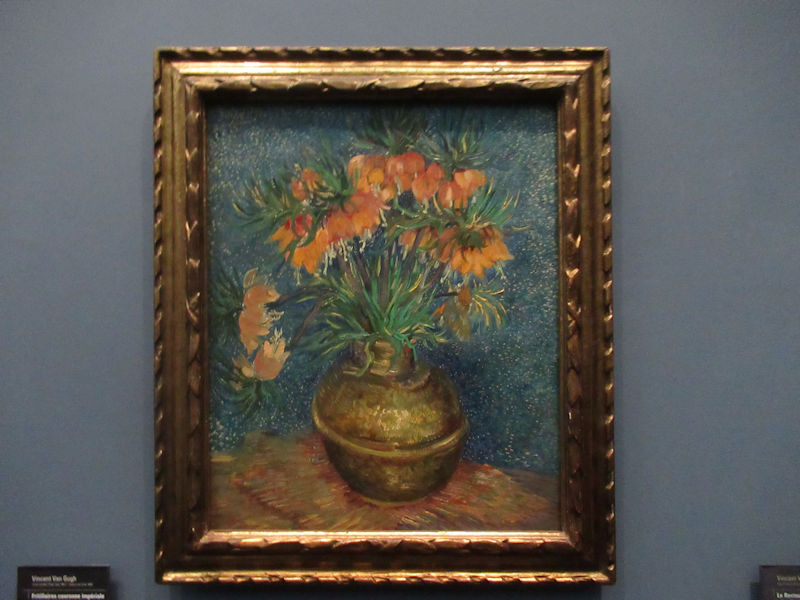
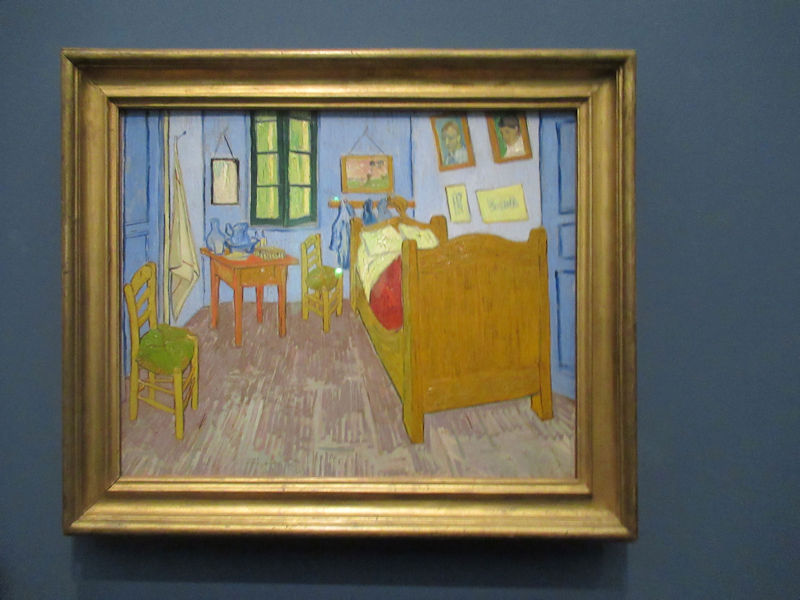
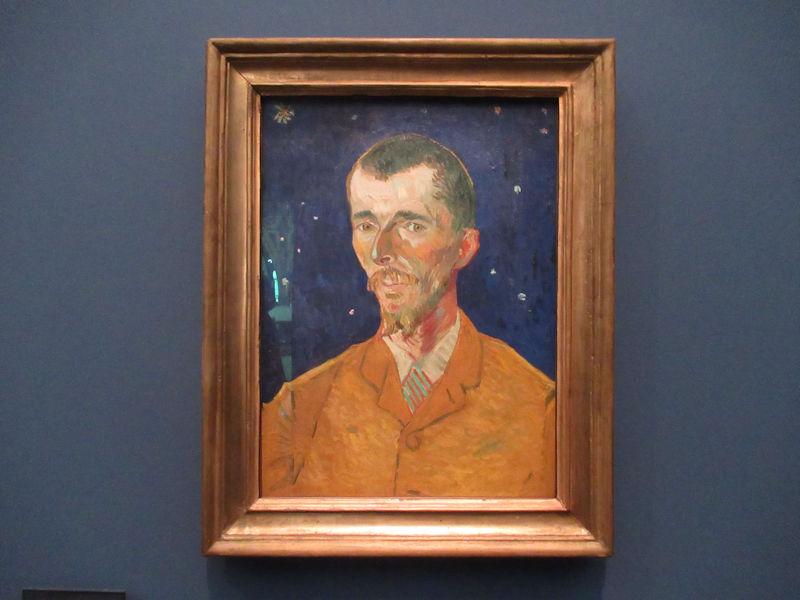
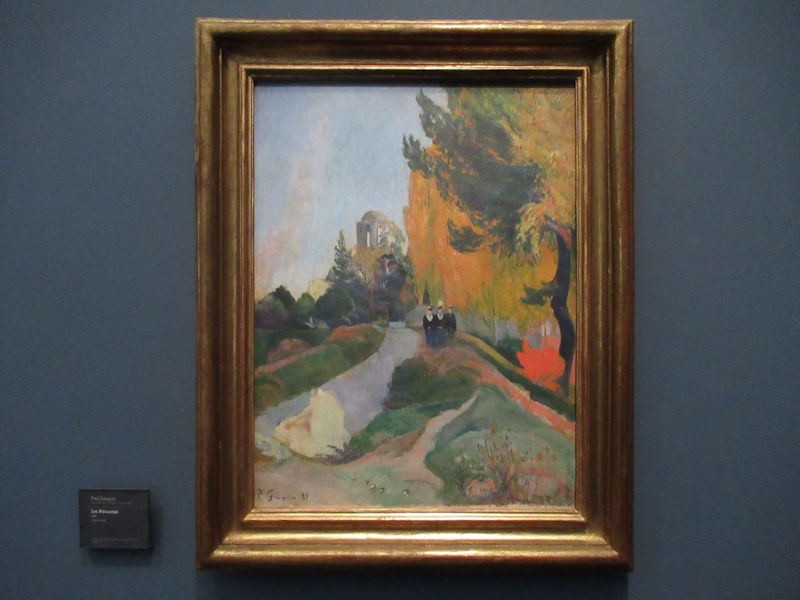
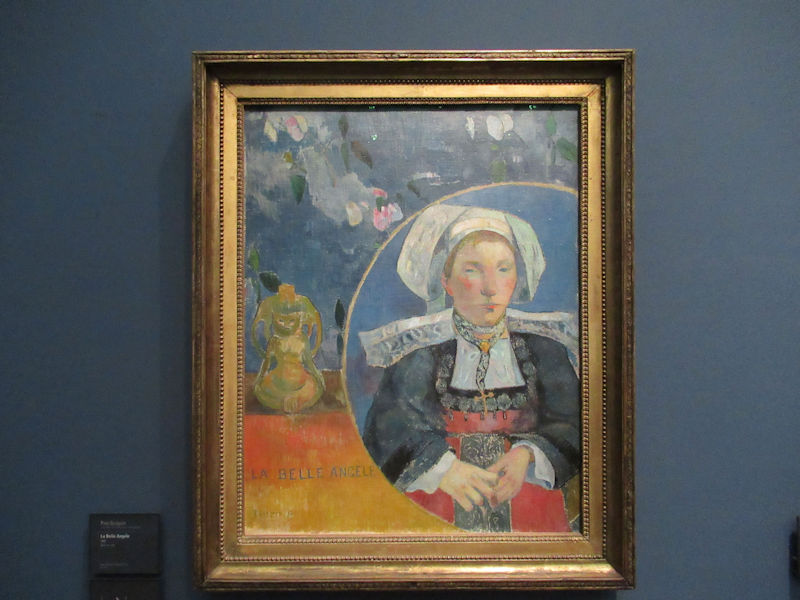
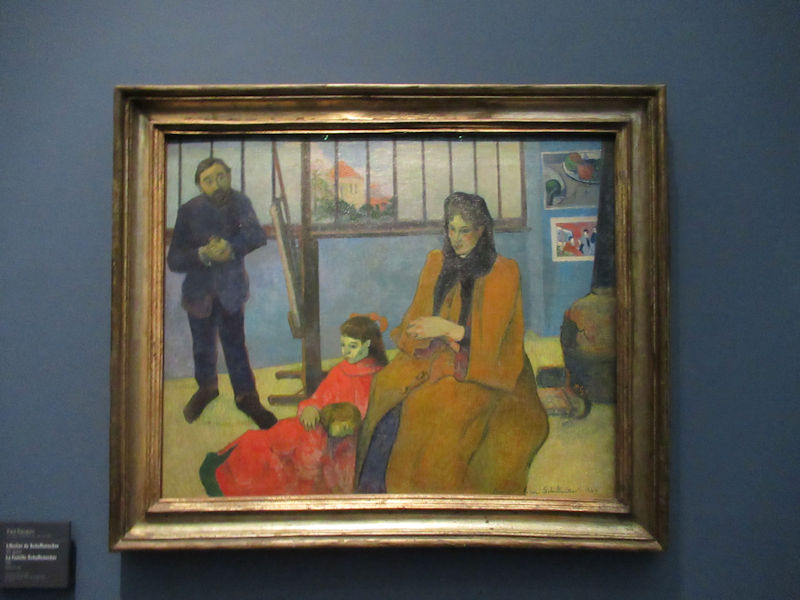
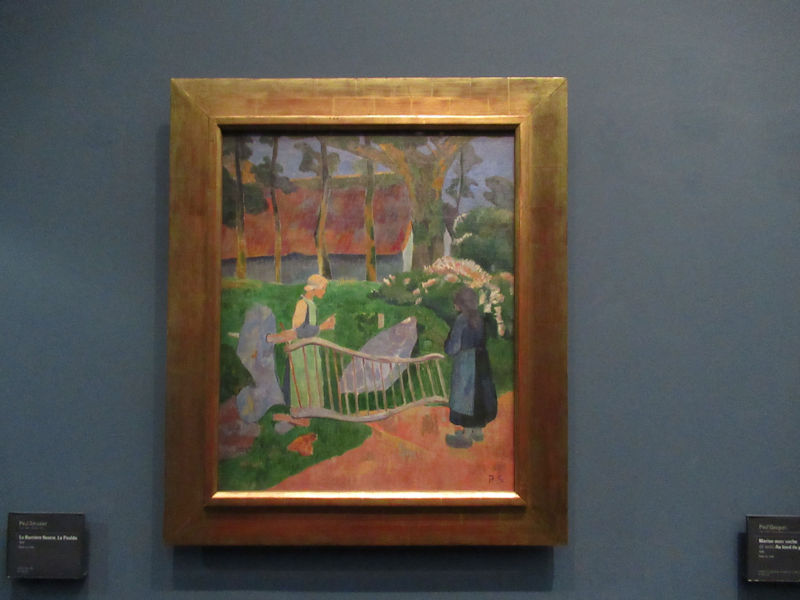
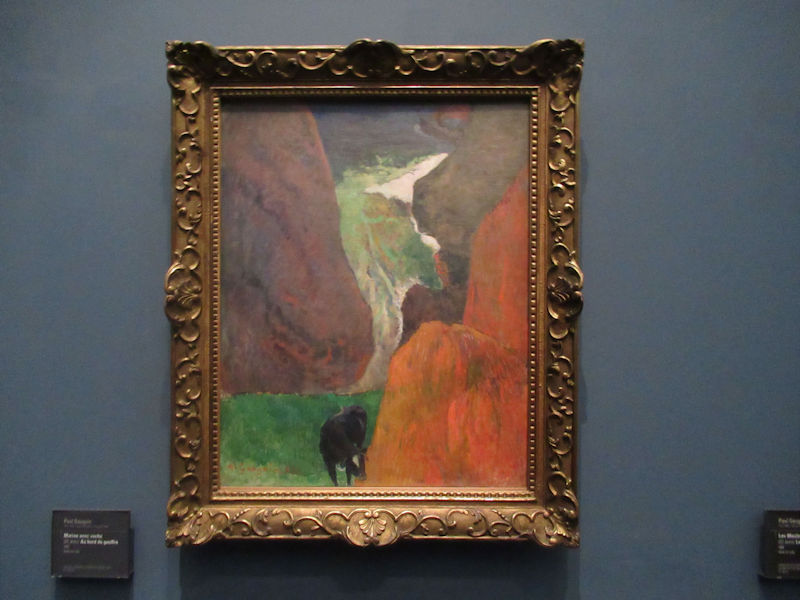
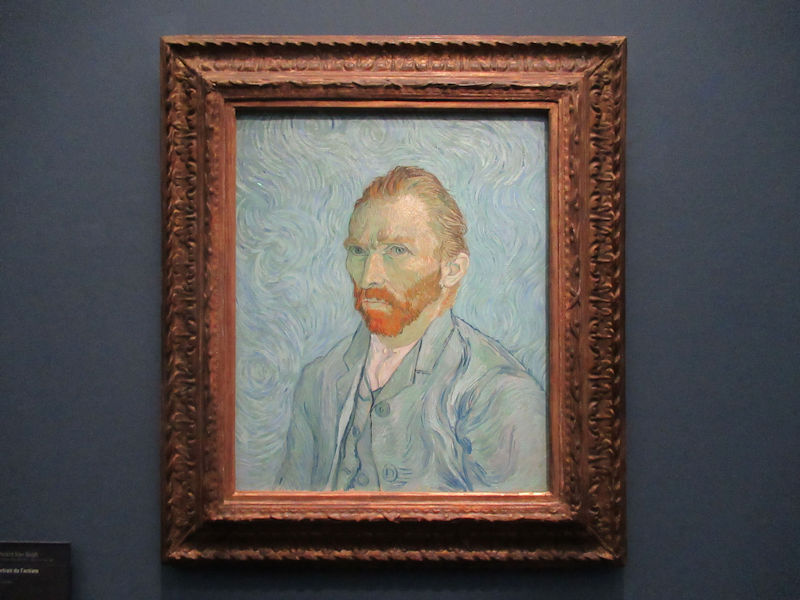
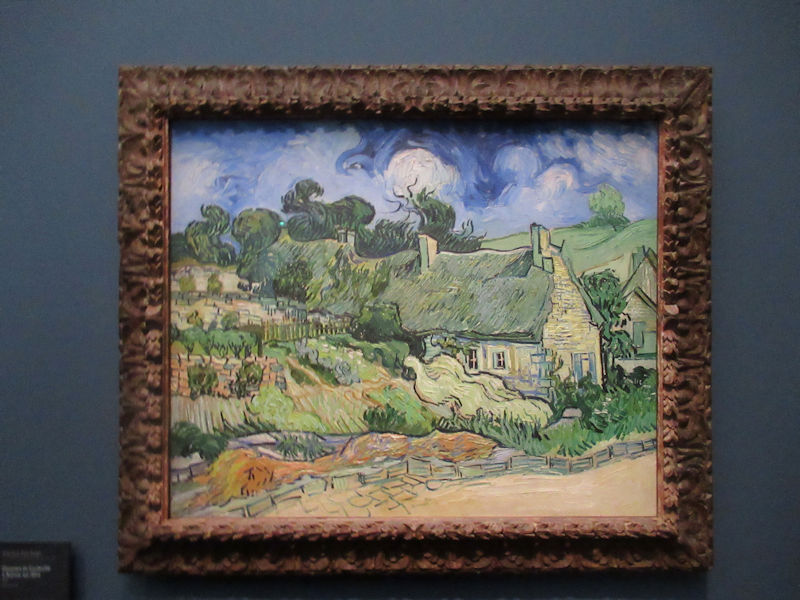
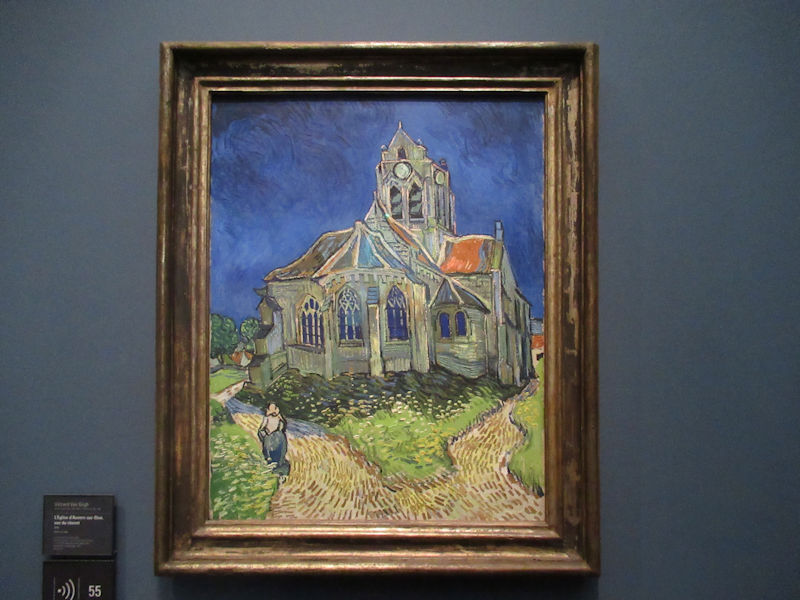
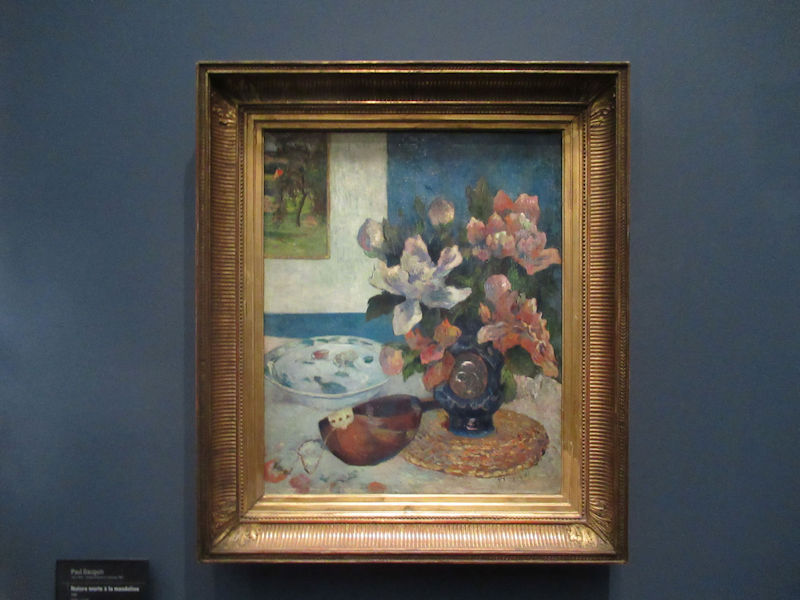
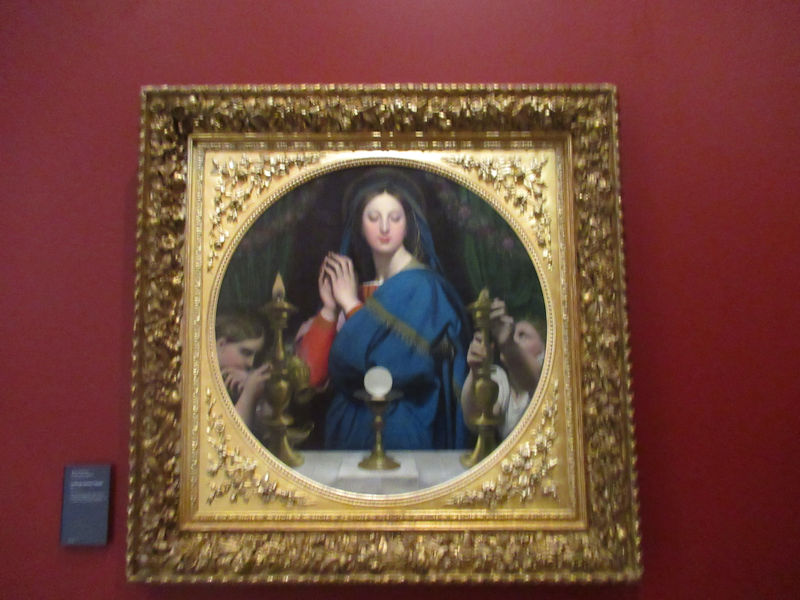
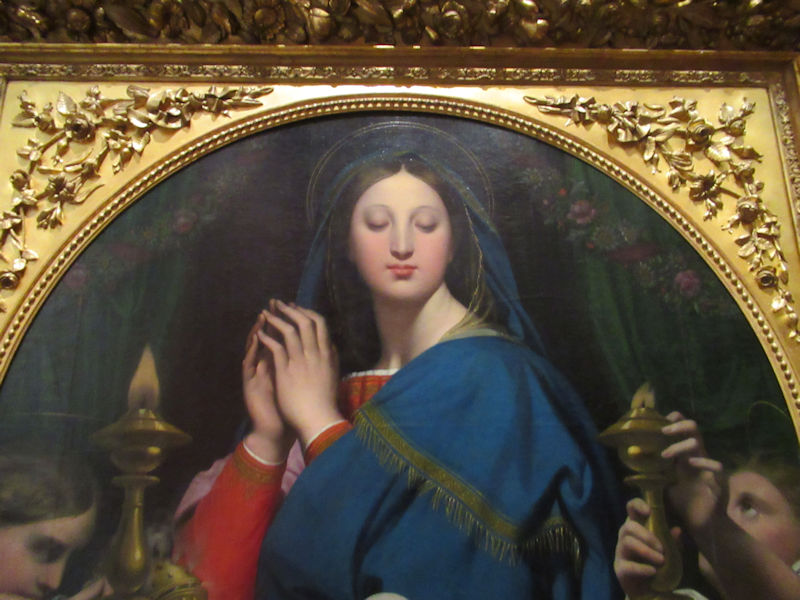
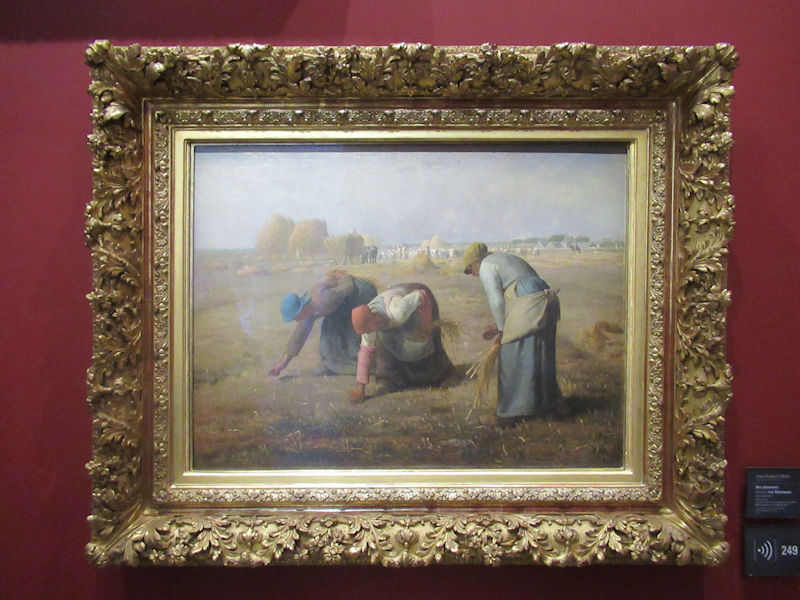
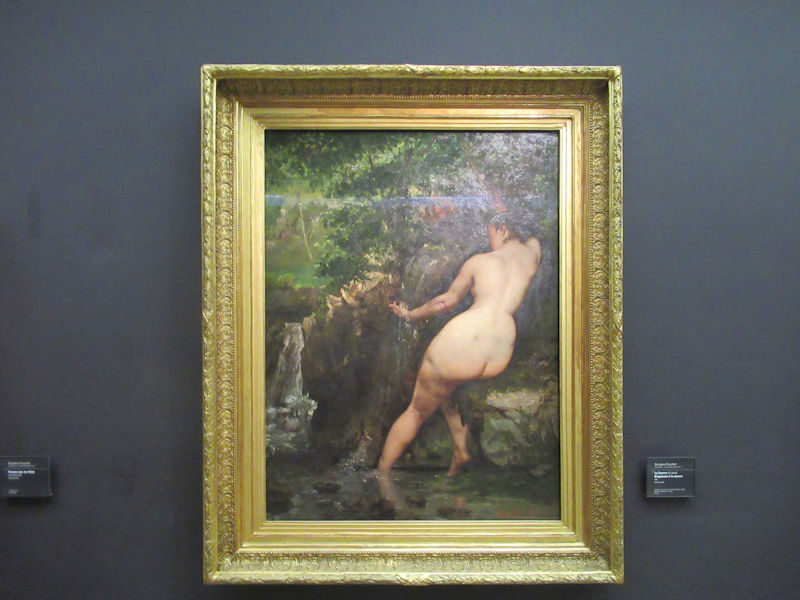
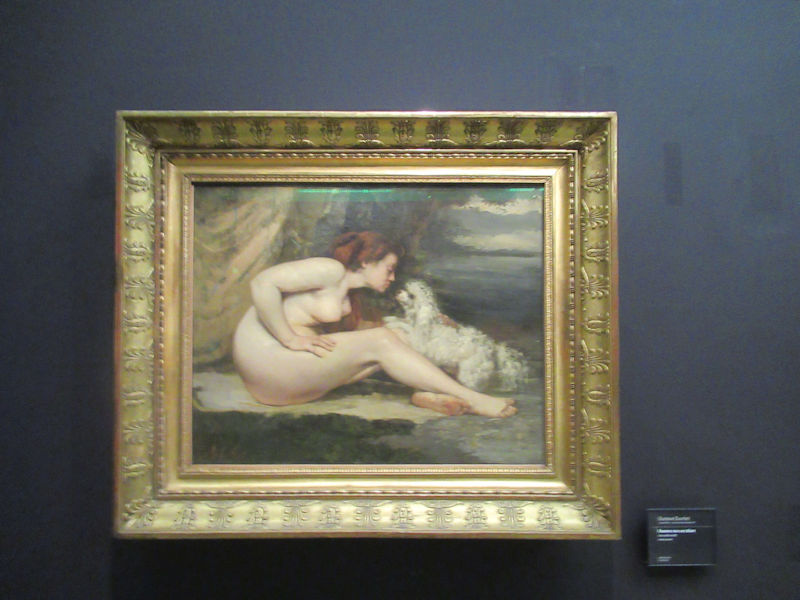
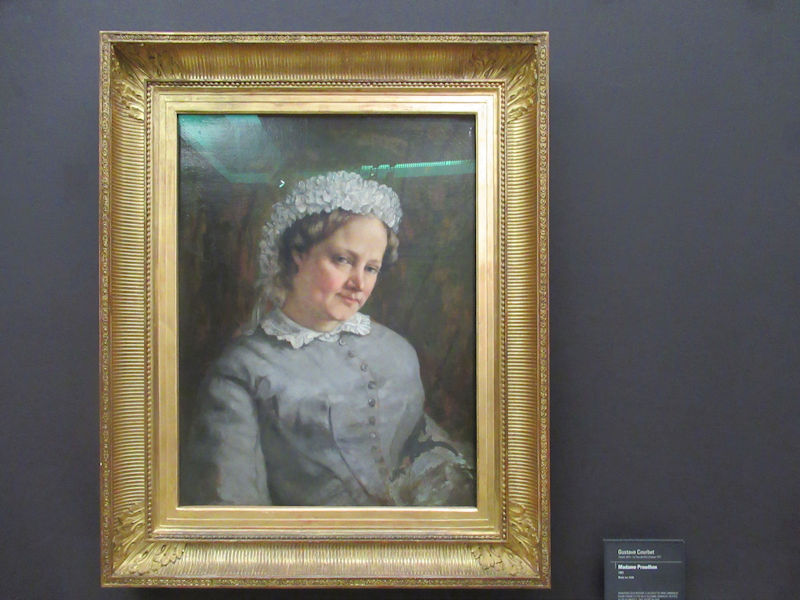
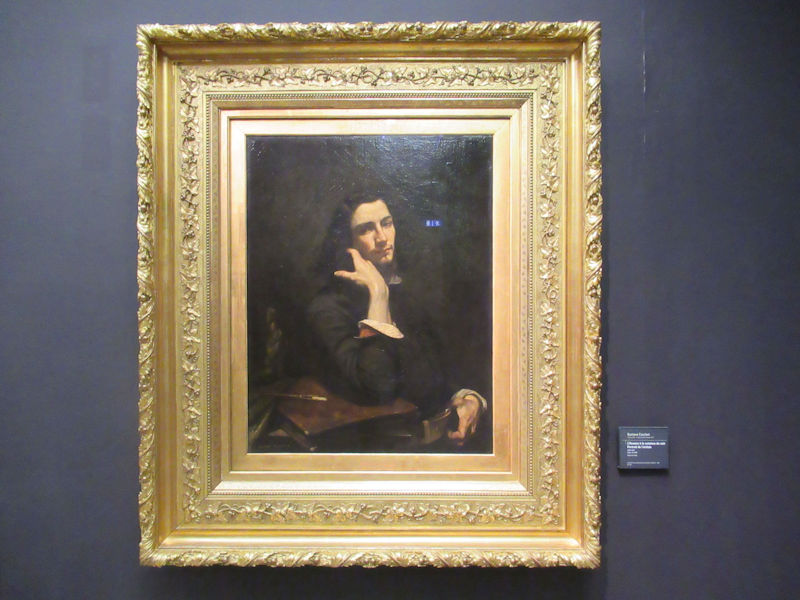
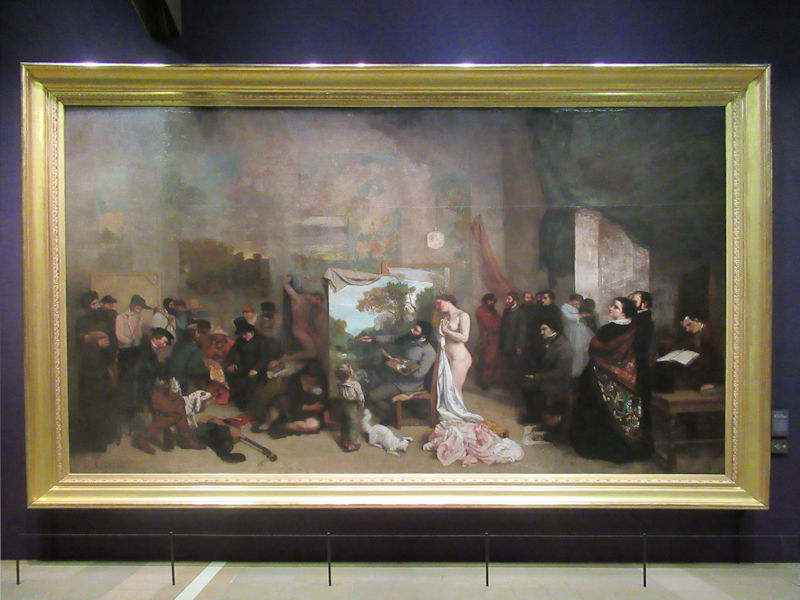
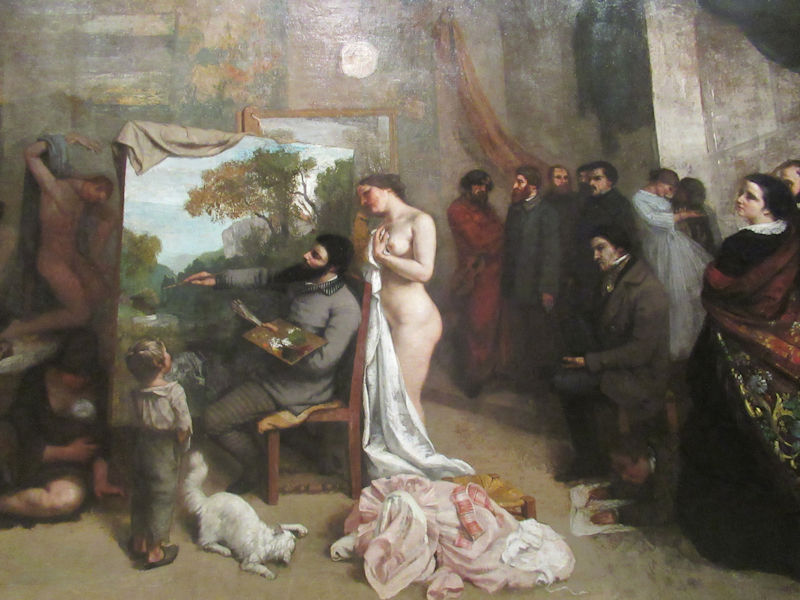
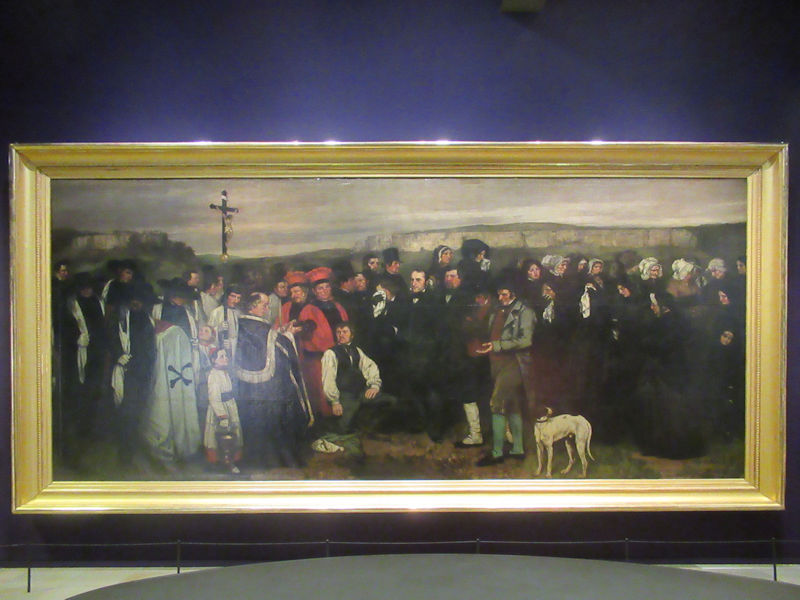
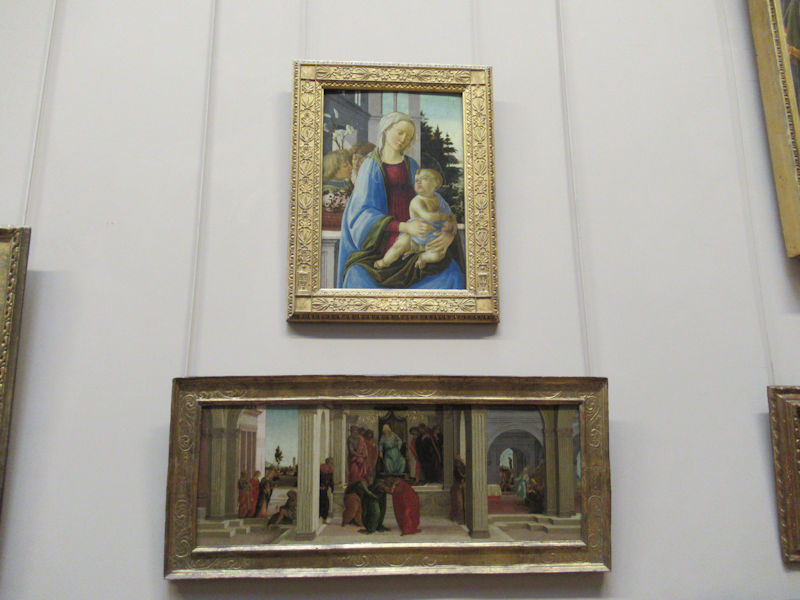
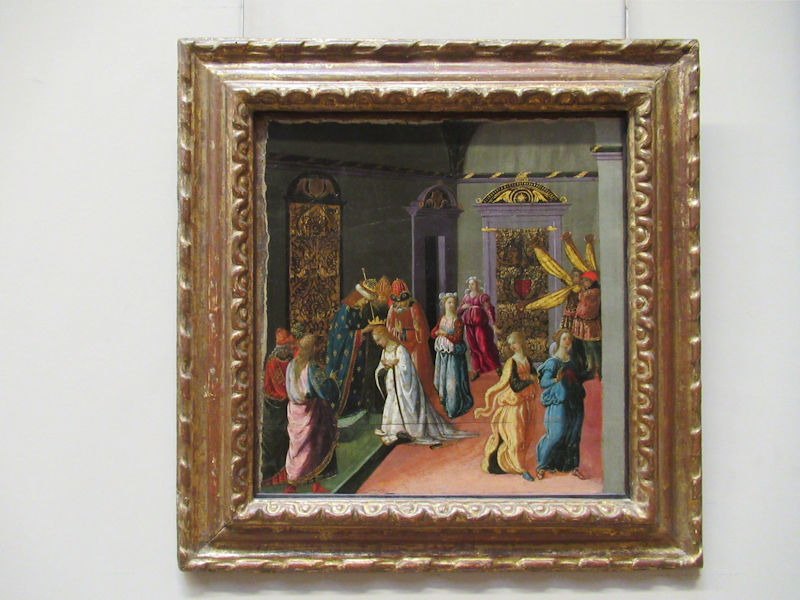
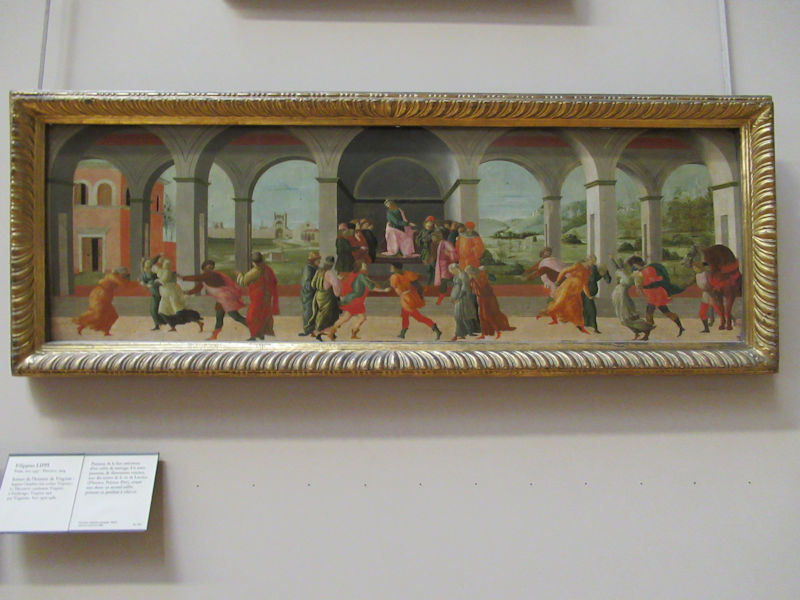
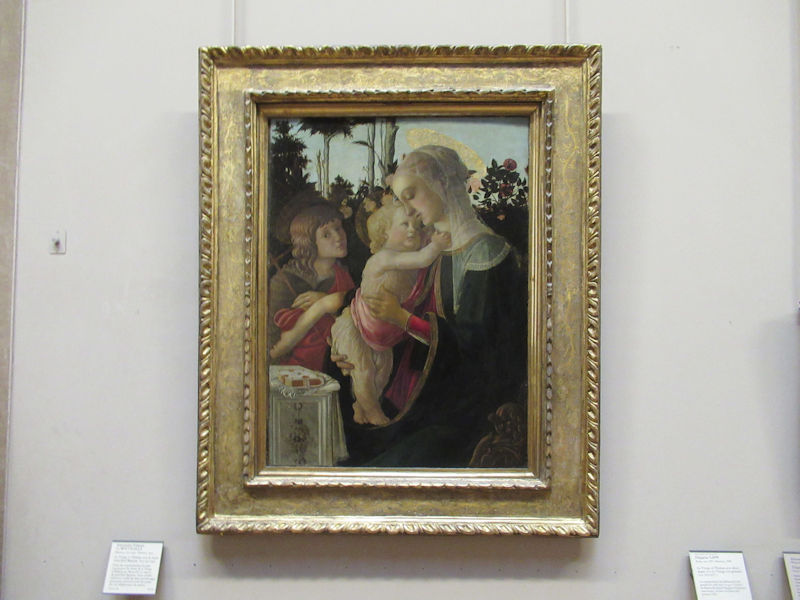
Many styles of modern art, including Fauvism, Expressionism, Cubism, Dada, Abstract art, Surrealism are represented with works by Matisse, André Derain, Maurice de Vlaminck, Raoul Dufy, Albert Marquet, Le Douanier Rousseau, Paul Signac, Georges Braque, Pablo Picasso, Jean Metzinger, Albert Gleizes, Fernand Léger, Juan Gris, Frida Kahlo, Ernst Ludwig Kirchner, August Macke, Alexej von Jawlensky, Emil Nolde, Oskar Kokoschka, Otto Dix, George Grosz, Kurt Schwitters, Marcel Duchamp, Francis Picabia, Carlo Carrà, Umberto Boccioni, Giacomo Balla, Gino Severini, Marc Chagall, Natalia Goncharova, Mikhail Larionov, Alexander Rodchenko, František Kupka, Piet Mondrian, Theo van Doesburg, Paul Klee, Wassily Kandinsky, Kasimir Malevich, Jacques Villon, Robert Delaunay, Sonia Delaunay, Georges Rouault, Balthus, Max Beckmann, Constantin Brâncuși, Alexander Calder, Chaïm Soutine, Amedeo Modigliani, Kees van Dongen, Jean Arp, Giorgio de Chirico, André Breton, Magritte, Max Ernst, Joan Miró, Man Ray, Alberto Giacometti, René Iché, Nicolas de Staël, André Masson, Yves Tanguy, Jean Tinguely, Simon Hantaï, Yves Klein, Jackson Pollock, Mark Rothko, Barnett Newman, Willem de Kooning, and Francis Bacon.
Contemporary art (art from 1960 on)
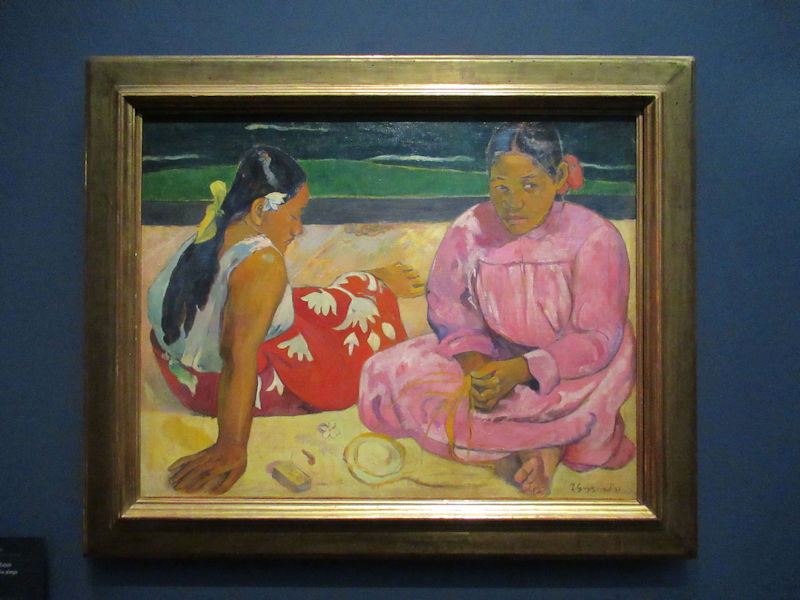
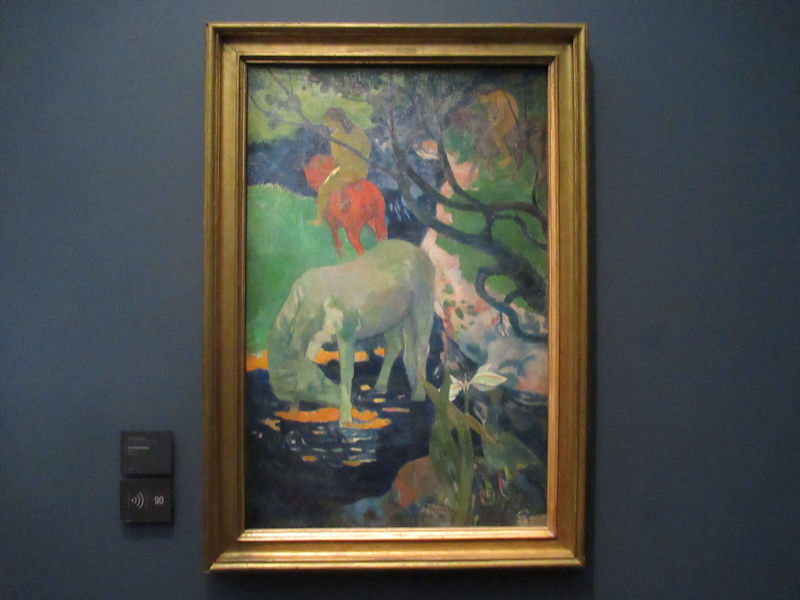
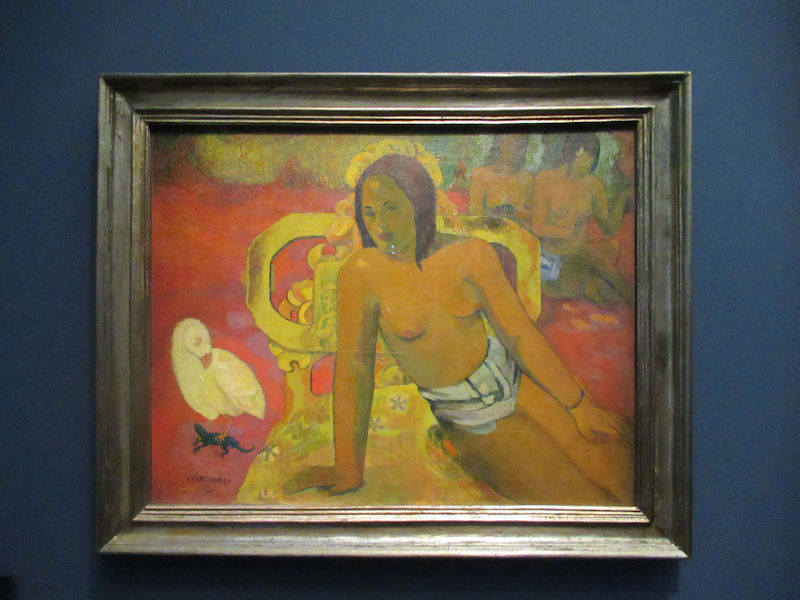
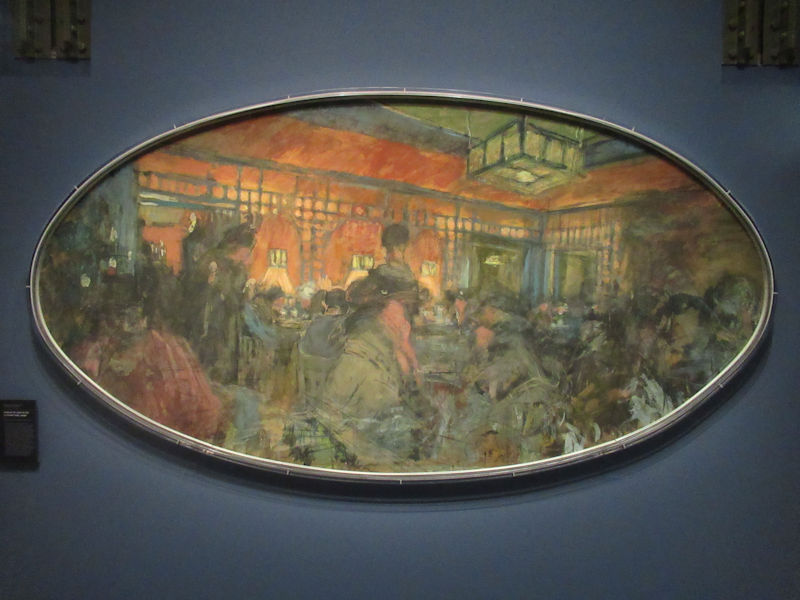
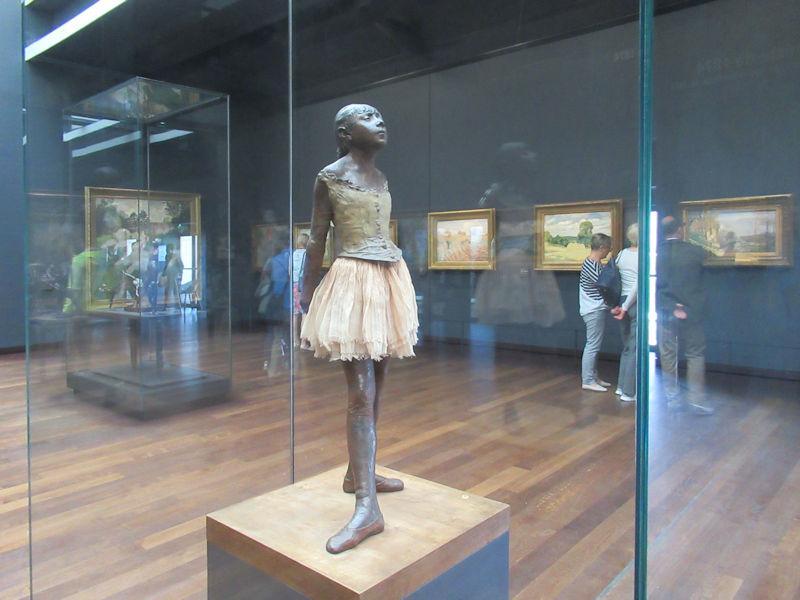
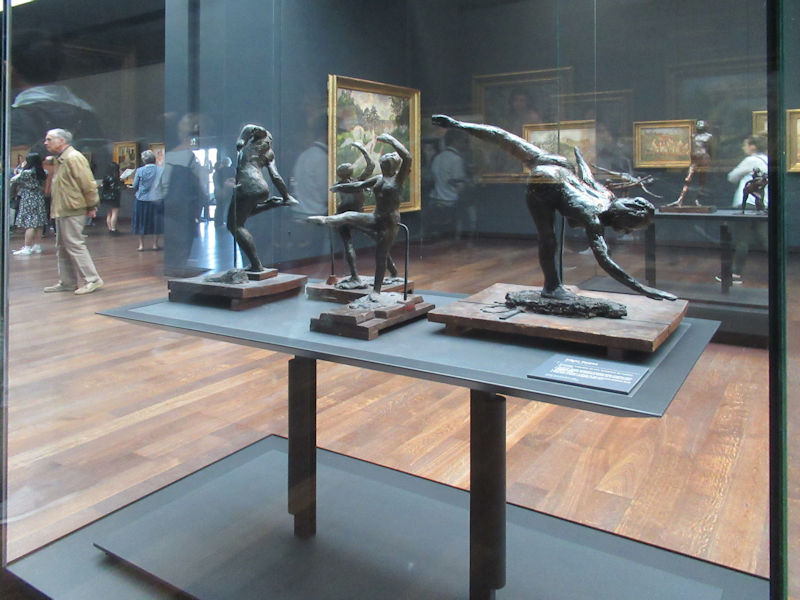
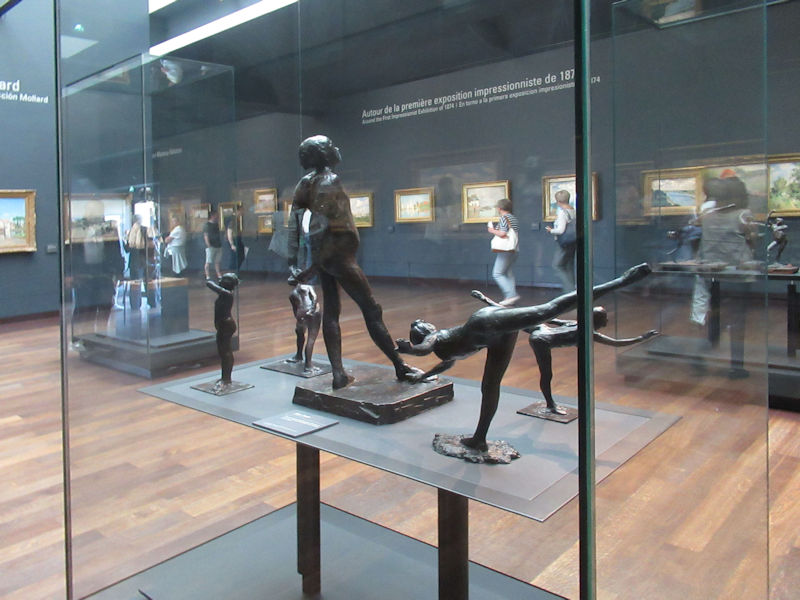
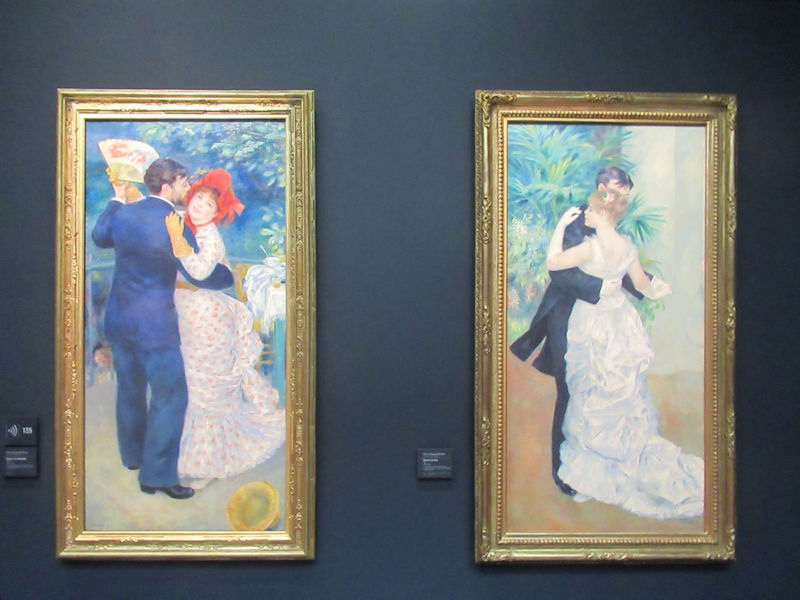
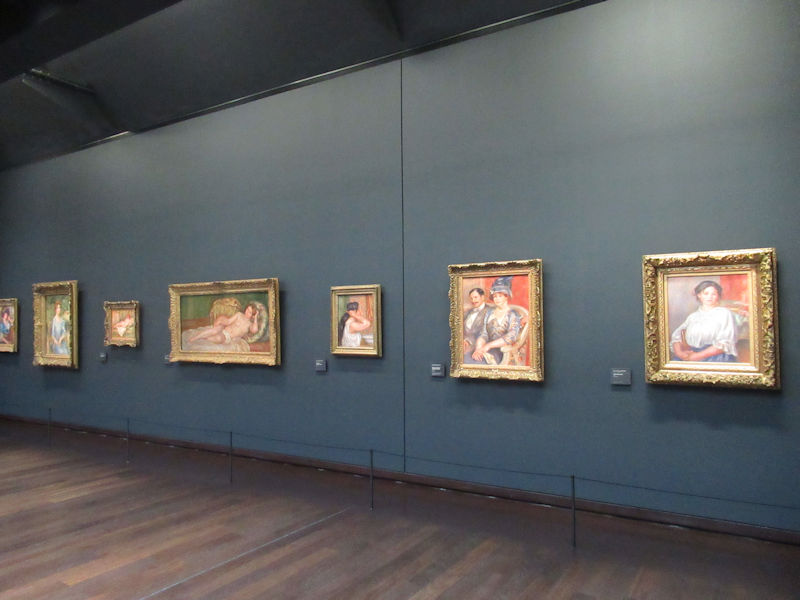
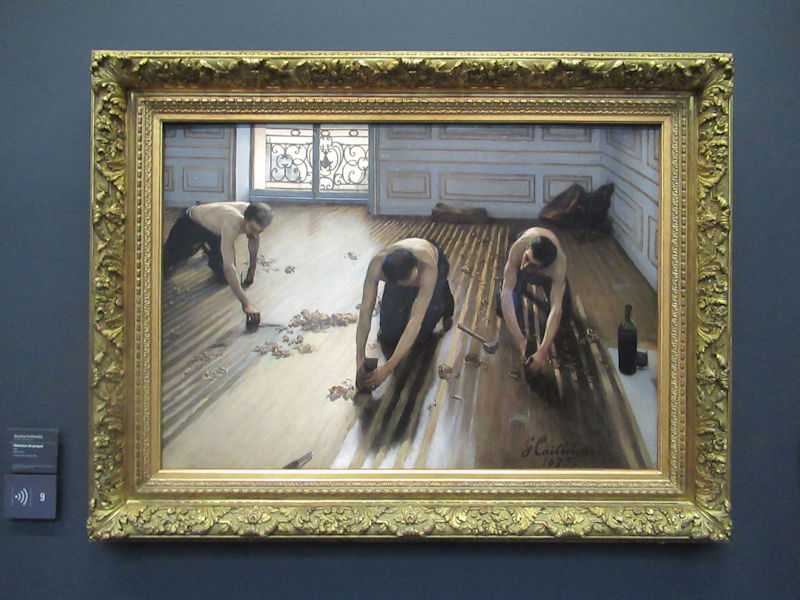
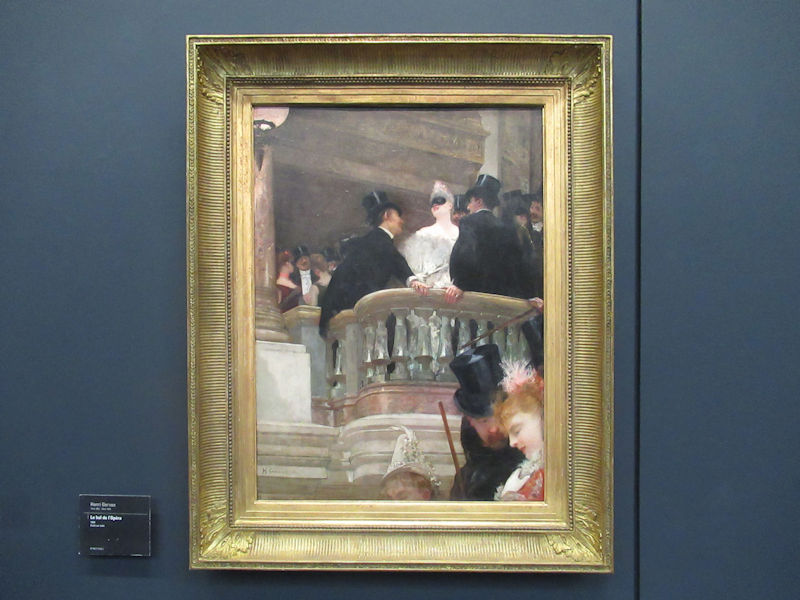
Pop Art, Nouveau Réalisme, Conceptual art and other tendencies or groups are represented with works by Andy Warhol, Richard Hamilton, Rauschenberg, Dan Flavin, Eduardo Arroyo, Dan Graham, Daniel Buren, George Brecht, Arman, César, Bill Viola, Anish Kapoor, Wim Delvoye, Yves Klein, Niki de Saint-Phalle, Yaacov Agam, Vasarely, John Cage, Cindy Sherman, Dieter Roth, Beuys, Roy Lichtenstein, Burhan Dogancay, Dubuffet, Nam June Paik, Wolf Vostell, Gilbert & George, David Hockney and Louise Bourgeois.
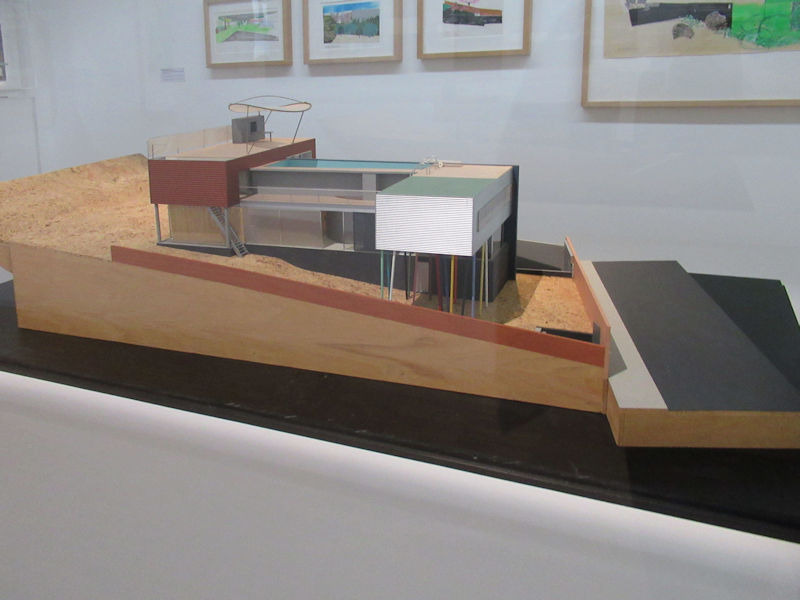
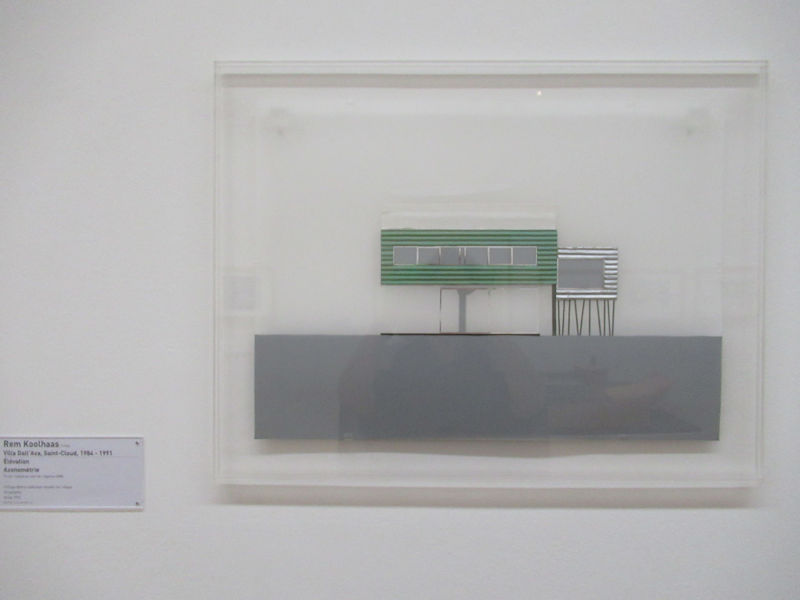
Works of architecture and design include Philippe Starck, Jean Nouvel, and Dominique Perrault.
![]()
An icon of 20th-century architecture
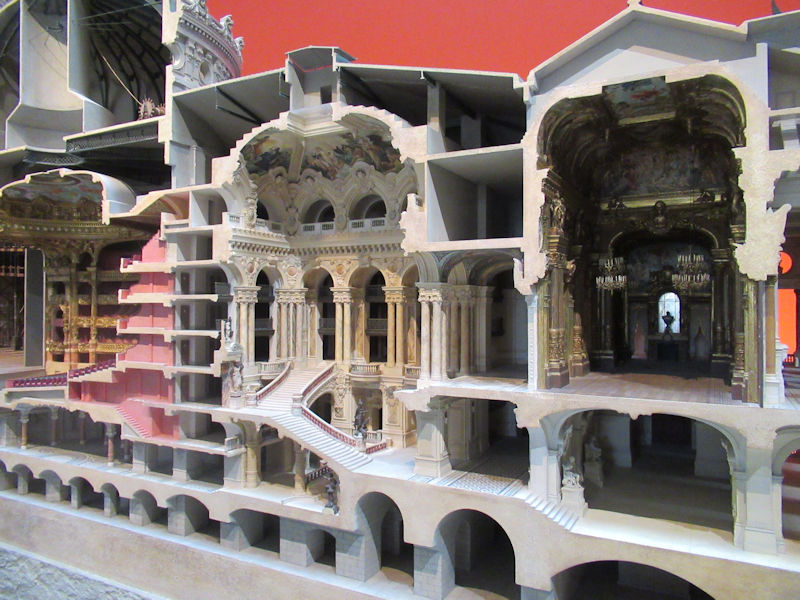
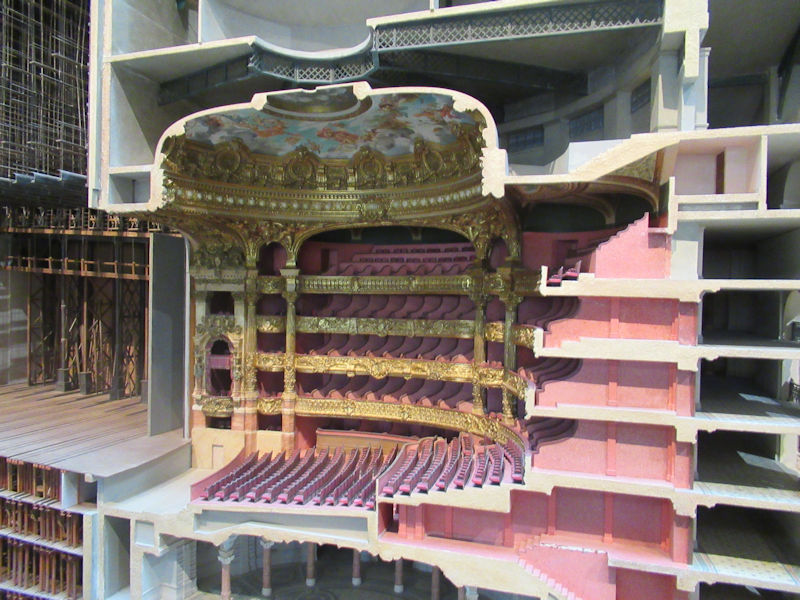
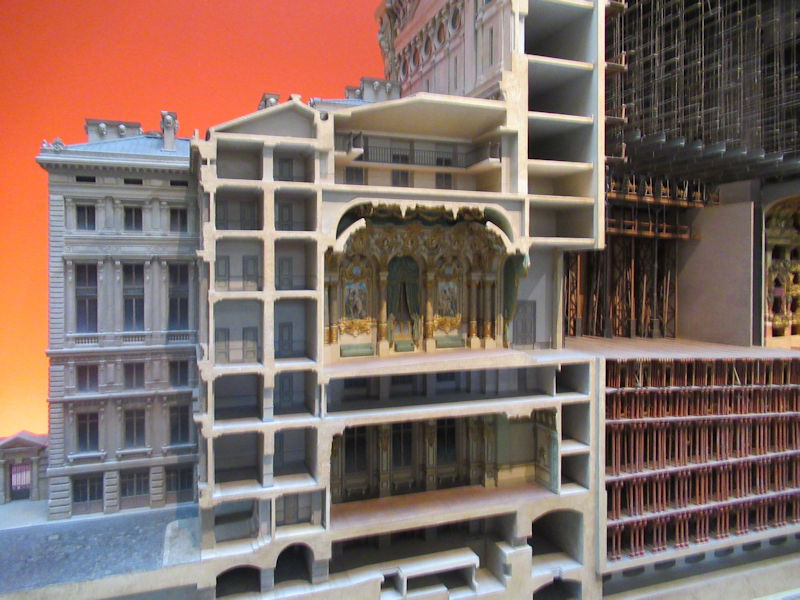
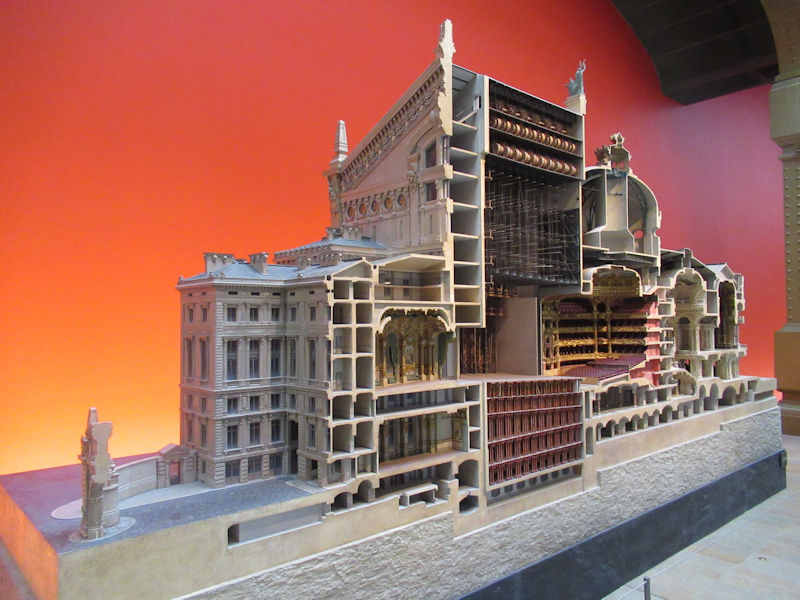
Designed as an “evolving spatial diagram” by architects Renzo Piano and Richard Rogers, the architecture of the Centre Pompidou boasts a series of technical characteristics that make it unique in the world – the inspiration, even the prototype, of a new generation of museums and cultural centres. It is distinctive firstly in the way it frees up the space inside, with each floor extending through the building entirely uninterrupted by load-bearing structures. The whole of each 7 500 m2 floor is thus available for the display of works or other activities, and can be divided up and reorganised at will, ensuring maximum flexibility. With its use of steel (15 000 tons) and glass (11 000 m²) and the externalisation of its load-bearing structure together with circulation and services, it was a truly pioneering building for its time, an heir to the great iron buildings of the Industrial Age. In many ways futuristic, the Centre Pompidou is heir to the architectural utopias of the 1960s, exemplified in the work of Archigram and Superstudio. Its innovative, even revolutionary character has made the Centre Pompidou one of the most emblematic buildings of the 20th century.
Click Refresh to view slider