From Wikipedia
History
In Gallic times the city of Tours was important as a crossing point of the Loire. Becoming part of the Roman Empire during the 1st century AD, the city was named “Caesarodunum” (“hill of Caesar”). The name evolved in the 4th century when the original Gallic name, Turones, became first “Civitas Turonum” then “Tours”. It was at this time that the amphitheatre of Tours, one of the five largest amphitheatres of the Empire, was built. Tours became the metropolis of the Roman province of Lugdunum towards 380–388, dominating the Loire Valley, Maine and Brittany. One of the outstanding figures of the history of the city was Saint Martin, second bishop who shared his coat with a naked beggar in Amiens. This incident and the importance of Martin in the medieval Christian West made Tours, and its position on the route of pilgrimage to Santiago de Compostela, a major centre during the Middle Ages.
Middle Ages
In the 6th century Gregory of Tours, author of the Ten Books of History, made his mark on the town by restoring the cathedral destroyed by a fire in 561. Saint Martin’s monastery benefited from its inception, at the very start of the 6th century from patronage and support from the Frankish king, Clovis, which increased considerably the influence of the saint, the abbey and the city in Gaul. In the 9th century, Tours was at the heart of the Carolingian Rebirth, in particular because of Alcuin abbot of Marmoutier.
In 732 AD, Abdul Rahman Al Ghafiqi and a large army of Muslim horsemen from Al-Andalus advanced 500 kilometres (311 miles) deep into France, and were stopped at Tours by Charles Martel and his infantry igniting the Battle of Tours. The outcome was defeat for the Muslims, preventing France from Islamic conquest. In 845, Tours repulsed the first attack of the Viking chief Hasting (Haesten). In 850, the Vikings settled at the mouths of the Seine and the Loire. Still led by Hasting, they went up the Loire again in 852 and sacked Angers, Tours and the abbey of Marmoutier.
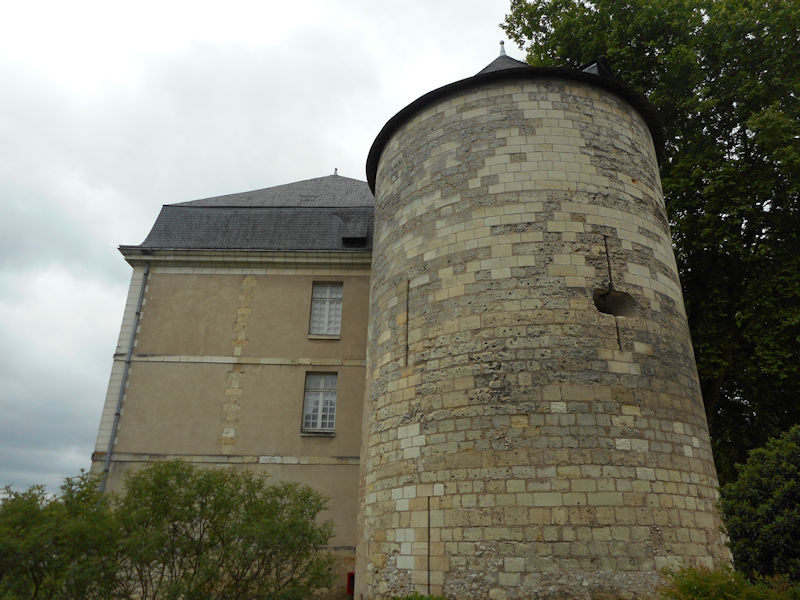
During the Middle Ages, Tours consisted of two juxtaposed and competing centres. The “City” in the east, successor of the late Roman ‘castrum’, was composed of the archiepiscopal establishment (the cathedral and palace of the archbishops) and of the castle of Tours, seat of the authority of the Counts of Tours (later Counts of Anjou) and of the King of France. In the west, the “new city” structured around the Abbey of Saint Martin was freed from the control of the City during the 10th century (an enclosure was built towards 918) and became “Châteauneuf”. This space, organized between Saint Martin and the Loire, became the economic centre of Tours. Between these two centres remained Varennes, vineyards and fields, little occupied except for the Abbaye Saint-Julien established on the banks of the Loire. The two centres were linked during the 14th century.
france_louis_xi-1

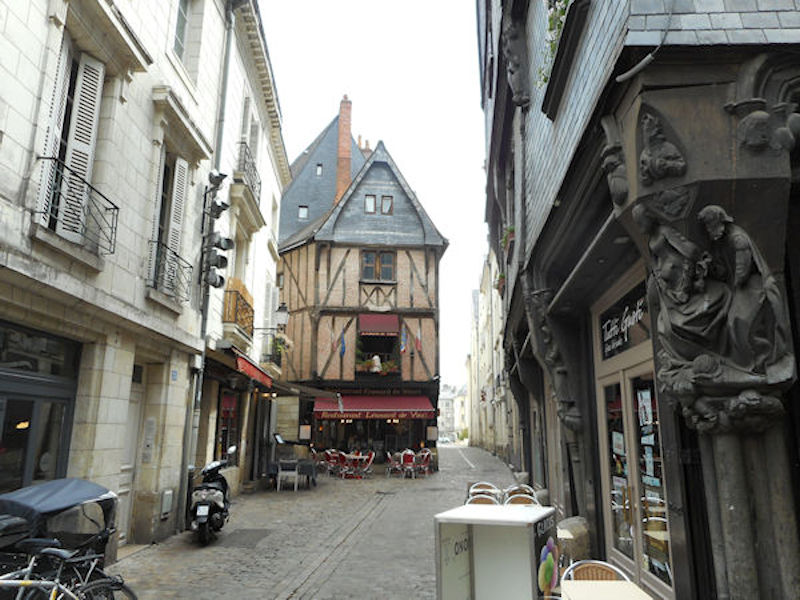
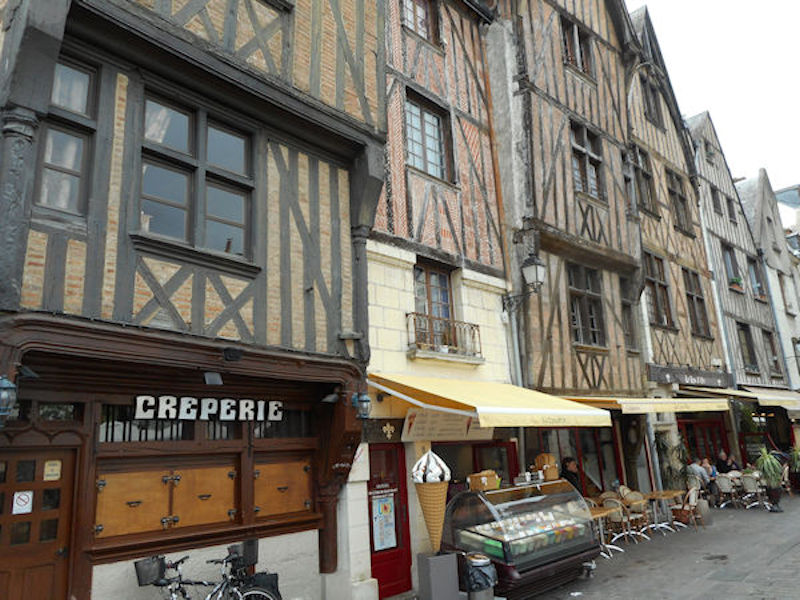
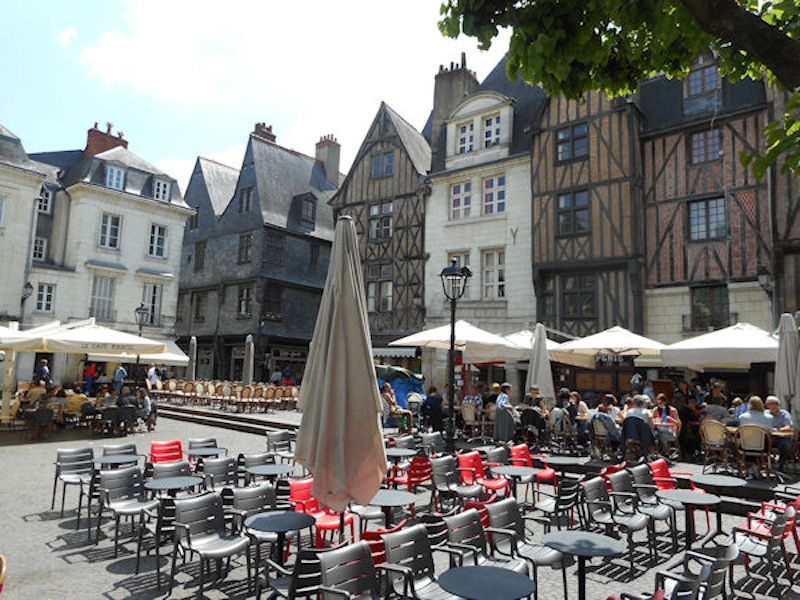
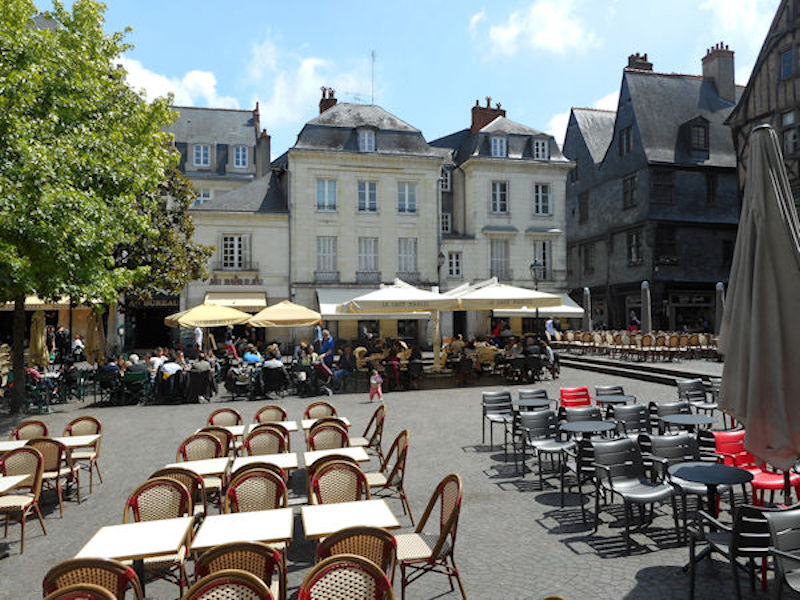
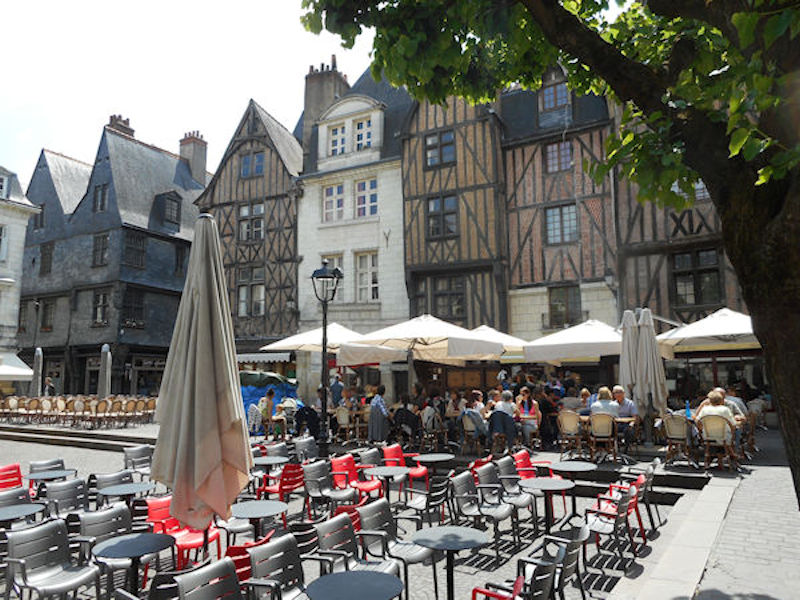
Place Plumereau, Medieval buildings
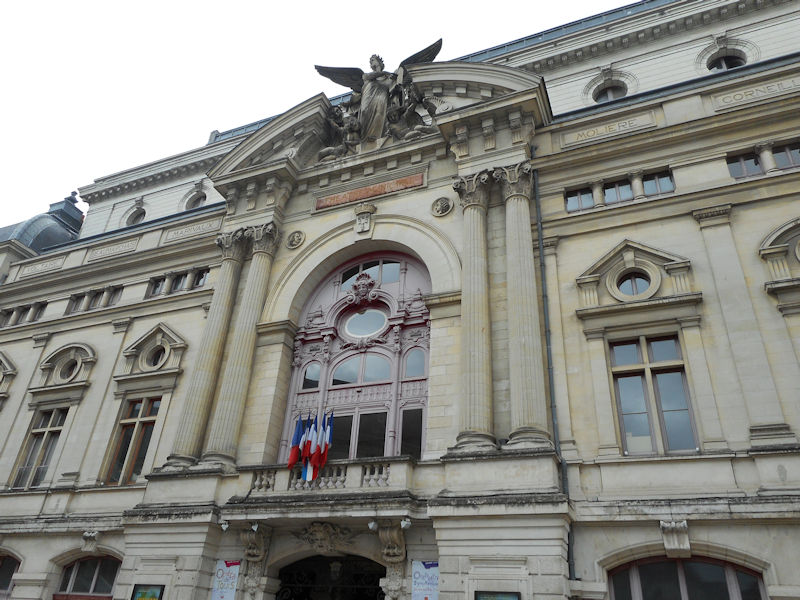
Tours became the capital of the county of Tours or Touraine, territory bitterly disputed between the counts of Blois and Anjou – the latter were victorious in the 11th century. It was the capital of France at the time of Louis XI, who had settled in the castle of Montils (today the castle of Plessis in La Riche, western suburbs of Tours). Tours and Touraine remained until the 16th century a permanent residence of the kings and court. The rebirth gave Tours and Touraine many private mansions and castles, joined together to some extent under the generic name of the Châteaux of the Loire. It is also at the time of Louis XI that the silk industry was introduced and despite difficulties, the industry still survives to this day.

Louis XI, called “Louis the Prudent”, was a monarch of
the House of Valois who ruled as King of France from 1461 to 1483
16th–18th centuries

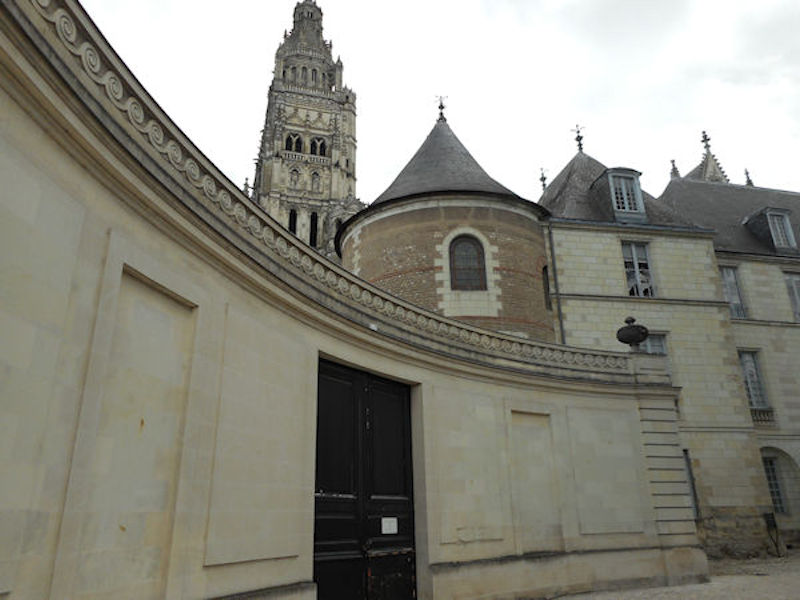
Tours Cathedral, 15th-century Flamboyant Gothic west front with Renaissance pinnacles, completed 1547.
Charles IX passed through the city at the time of his royal tour of France between 1564 and 1566, accompanied by the Court and various noblemen: his brother the Duke of Anjou, Henri de Navarre, the cardinals of Bourbon and Lorraine. At this time, the Catholics returned to power in Angers: the intendant assumed the right to nominate the aldermen. The Massacre of Saint-Barthelemy was not repeated at Tours. The Protestants were imprisoned by the aldermen – a measure which prevented their extermination. The permanent return of the Court to Paris and then Versailles marked the beginning of a slow but permanent decline. Guillaume the Metayer (1763–1798), known as Rochambeau, the well known counter-revolutionary chief of Mayenne, was shot here on 8th Thermidor Year VI (26th July 1798).
19th–20th centuries

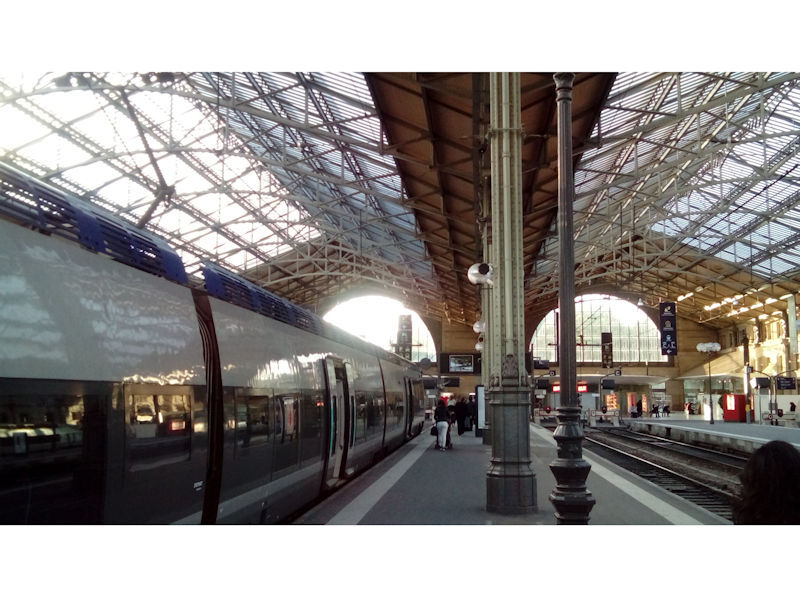
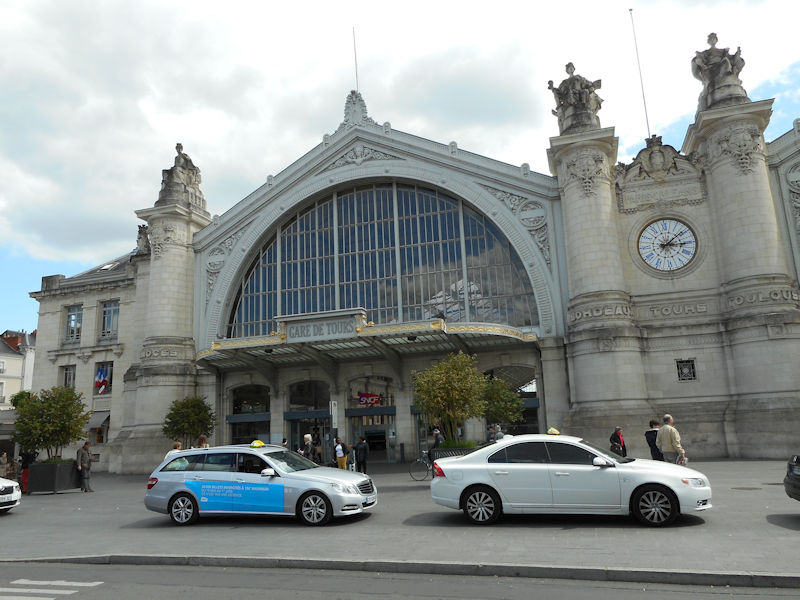
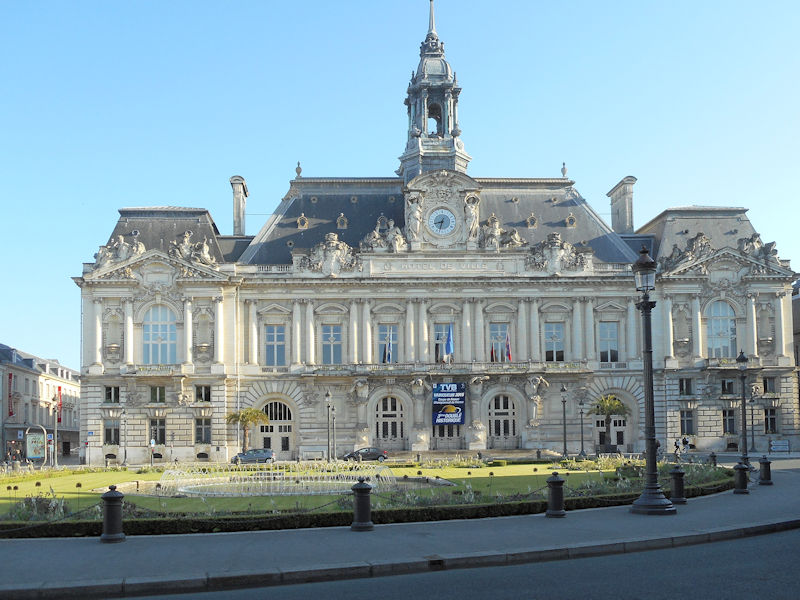
Gare de Tours, Place du Général-Leclerc, Tours
It was the arrival of the railway in the 19th century which saved the city by making it an important nodal point. The main railway station is known as Tours-Saint-Pierre-des-Corps. At that time, Tours was expanding towards the south into a district known as the Prébendes. The importance of the city as a centre of communications contributed to its revival and, as the 20th century progressed, Tours became a dynamic conurbation, economically oriented towards the service sector.
First World War
The city was greatly affected by the First World War. A force of 25,000 American soldiers arrived in 1917, setting up textile factories for the manufacture of uniforms, repair shops for military equipment, munitions dumps, an army post office and an American military hospital at Augustins. Thus Tours became a garrison town with a resident general staff. The American presence is remembered today by the Woodrow Wilson bridge over the Loire, which was officially opened in July 1918 and bears the name of the man who was President of the USA from 1913 to 1921. Three American air force squadrons, including the 492nd, were based at the Parçay-Meslay airfield, their personnel playing an active part in the life of the city.
Inter-war years
In 1920, the city was host to the Congress of Tours, which saw the creation of the French Communist Party.
Second World War
Tours was also marked by the Second World War. In 1940 the city suffered massive destruction, and for four years it was a city of military camps and fortifications. From 10 to 13 June 1940, Tours was the temporary seat of the French government before its move to Bordeaux. German incendiary bombs caused a huge fire which blazed out of control from 20 to 22 June and destroyed part of the city centre. Some architectural masterpieces of the 16th and 17th centuries were lost, as was the monumental entry to the city. The Wilson Bridge (known locally as the ‘stone bridge’) carried a water main which supplied the city; the bridge was dynamited to slow the progress of the German advance. With the water main severed and unable to extinguish the inferno, the inhabitants had no option but to flee to safety. More heavy air raids by Allied forces devastated the area around the railway station in 1944, causing several hundred deaths.
Post-war developments
A plan for the rebuilding of the downtown area drawn up by the local architect Camille Lefèvre was adopted even before the end of the war. The plan was for 20 small quadrangular blocks of housing to be arranged around the main road (la rue Nationale), which was widened. This regular layout attempted to echo, yet simplify, the 18th-century architecture. Pierre Patout succeeded Lefèvre as the architect in charge of rebuilding in 1945. At one time there was talk of demolishing the southern side of the rue Nationale in order to make it in keeping with the new development.
The recent history of Tours is marked by the personality of Jean Royer, who was Mayor for 36 years and helped to save the old town from demolition by establishing one of the first Conservation Areas. This example of conservation policy would later inspire the Malraux Law for the safeguarding of historic city centres. In the 1970s, Jean Royer also extended the city to the south by diverting the course of the River Cher to create the districts of Rives du Cher and des Fontaines; at the time, this was one of the largest urban developments in Europe. In 1970, the François Rabelais University was founded; this is centred on the bank of the Loire in the downtown area, and not – as it was then the current practice – in a campus in the suburbs. The latter solution was also chosen by the twin university of Orleans. Royer’s long term as Mayor was, however, not without controversy, as exemplified by the construction of the practical – but aesthetically unattractive – motorway which runs along the bed of a former canal just 1,500 metres (4,900 feet) from the cathedral. Another bone of contention was the original Vinci Congress Centre by Jean Nouvel. This project incurred debts although it did, at least, make Tours one of France’s principal conference centres.
Jean Germain, a member of the Socialist Party, became Mayor in 1995 and made debt reduction his priority. Ten years later, his economic management is regarded as much wiser than that of his predecessor, the financial standing of the city having returned to a stability. However, the achievements of Jean Germain are criticised by the municipal opposition for a lack of ambition: no large building projects comparable with those of Jean Royer have been instituted under his double mandate. This position is disputed by those in power, who affirm their policy of concentrating on the quality of life, as evidenced by urban restoration, the development of public transport and cultural activities.
CLICK Refresh FOR SLIDES





























